H3C Technologies H3C S5830V2 Series Switches User Manual
Page 101
90
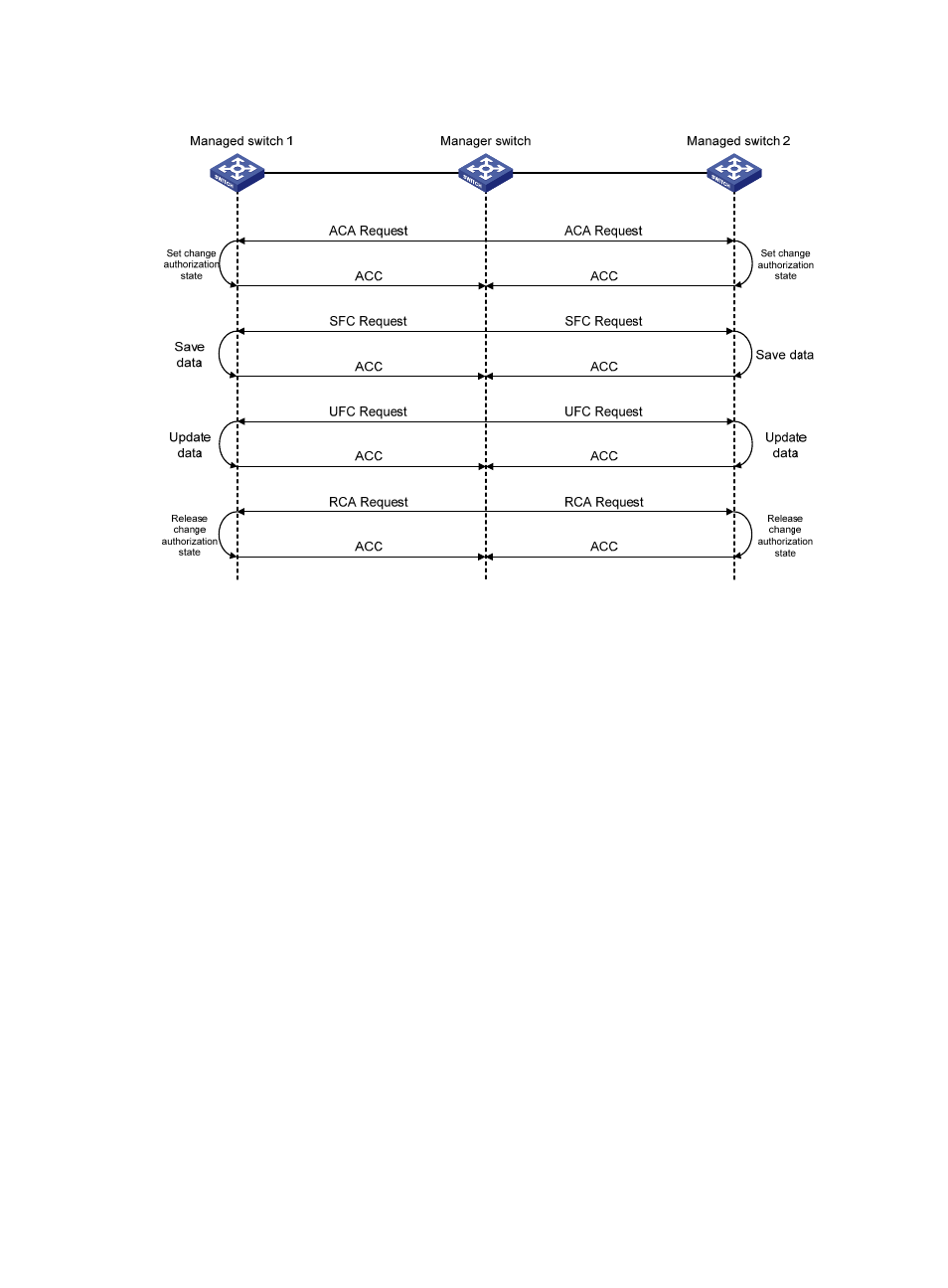
Figure 30 Distribution process
The distribution process is as follows:
1.
The manager switch obtains the status of each managed switch through an ACA request, which
carries the fabric-wide list of domain IDs (addresses of all switches in the fabric) known to the
manager switch. After sending the ACA request, the manager switch enters the locked state. After
receiving the ACA request, a managed switch compares its list of domain IDs with that in the
packet.
{
If they are consistent, the fabric is in stable state. In this case, the managed switch is prepared
for synchronization, replies with an ACC (acknowledgement) packet, and enters the change
authorization (locked) state.
A stable fabric actually requires correct and consistent routes and eliminating unreachable
routes. Pay special attention to this in the case of using static routes. Otherwise, data cannot be
correctly distributed.
{
If the managed switch has been in change authorization state or cannot process the ACA
request for some reason, it replies with an RJT (reject) packet.
2.
The manager switch starts data synchronization by sending an SFC request only after receiving
ACC requests from all managed switches. Otherwise, it notifies managed switches to release the
change authorization state by sending an RCA request.
If the managed switch replies with neither an ACC packet nor an RJT packet because of its
abnormal state, the manager switch cannot release its locked state. To prevent this situation, the
manager switch transmits an ACA request up to three times.
{
If no reply is received, the manager switch releases its locked state.
{
If the manager switch becomes abnormal after sending an ACA request, the managed switch
will be in locked state and cannot receive subsequent packets.
Similarly, the managed switch releases its locked state after waiting for a period of time.
