Communication flow – H3C Technologies H3C S5830V2 Series Switches User Manual
Page 15
4
{
If the peer is an N_Port or NP_Port, the G_Port works as an F_Port.
{
If both ends are G_Ports, they both work as E_Ports.
{
If the peer is an F_Port, the negotiation fails.
•
NP_Port—Connects to an F_Port on another FC switch. For more information about NP_Port, see
"
E_Ports connect FC switches to form a fabric, and F_Ports connect the nodes to FC switches in the fabric.
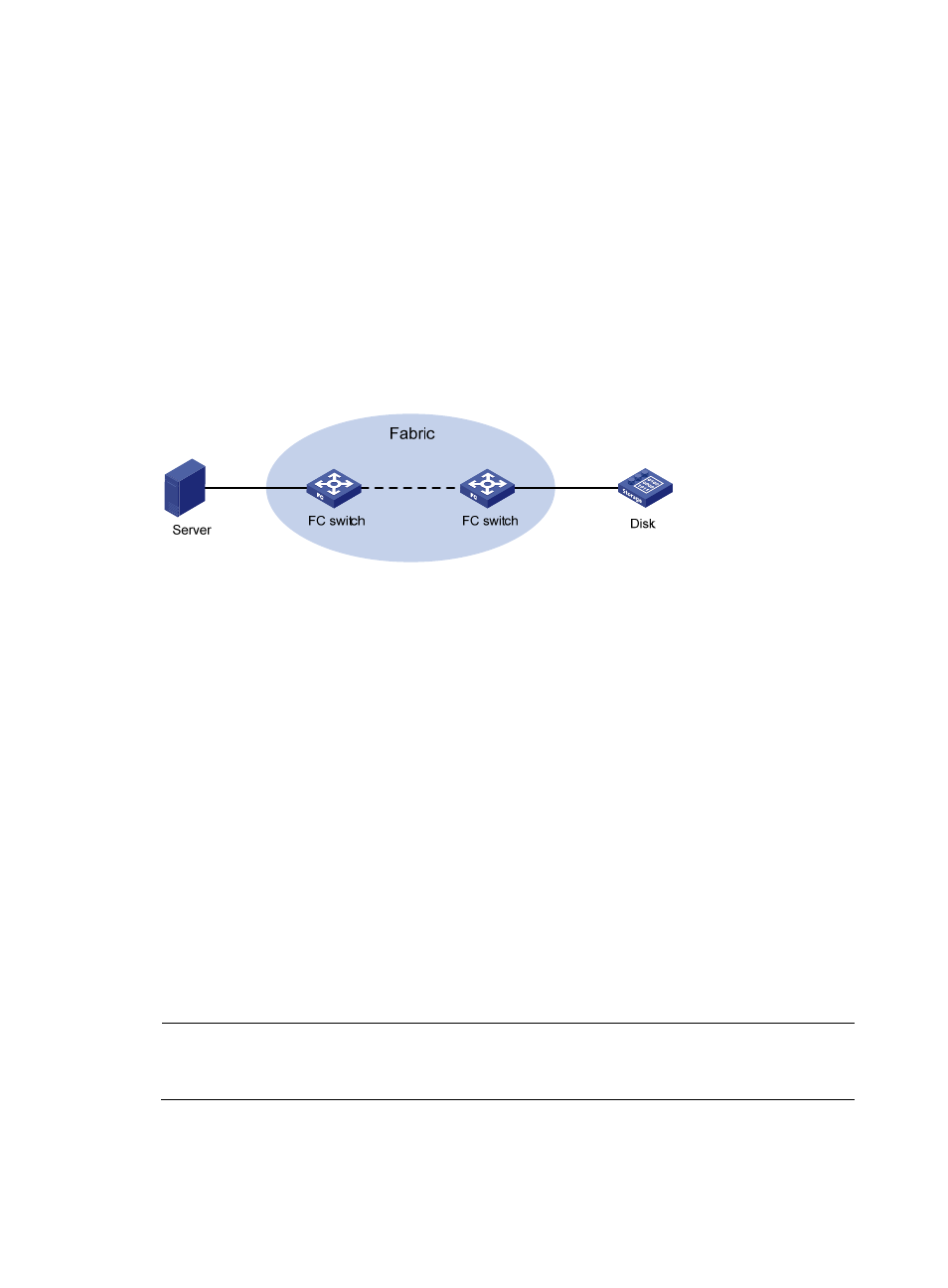
Communication flow
FC switches provide data transmission services. Through FC switches, a server sends instructions and
data to disk devices and reads data from disk devices.
Figure 4 FC SAN communication model
The following takes a server accessing a disk device as an example to see how data communication
occurs in an FC SAN.
1.
The server and the disk device send fabric login (FLOGI) packets to register with the FC switches,
which then assign FC addresses to each directly-connected node.
A FLOGI packet contains information that includes the port WWN, node WWN, and the
expected FC address.
2.
The registered server and disk device send name service registration requests to their respective
access FC switches to register name service information, including FC4 information. Finally, each
FC switch in the fabric stores the name service information for all nodes. For more information
Configuring and obtaining FC4 information of nodes
3.
To access a disk device, the server sends a name service query request to its directly-connected FC
switch to obtain the list of disk devices in the fabric and their WWNs and FC addresses.
4.
After the server obtains the FC address of the disk device, the server can send FC frames (with the
FC address of the disk device as the destination FC address) to the FC switch nearby.
5.
When the FC switch receives the FC frame from the server, it queries its FIB table for a data
forwarding path according to the destination FC address, and forwards the FC frame to the
next-hop FC switch. The next-hop FC switch forwards the FC frame in the same way, until the FC
switch at the last hop forwards the FC frame to the destination disk device.
NOTE:
A FIB table is generated by the FC switch through calculation based on the FC routing protocol or
configured static routes.
