Request_response – H3C Technologies H3C S6300 Series Switches User Manual
Page 68
55
PTP defines two transmission delay measurement mechanisms: Request_Response and Peer Delay. The
basis of the two mechanisms is that the transmission delay from the master clock to the member clock is
the same as that from the member clock to the master clock.
Request_Response
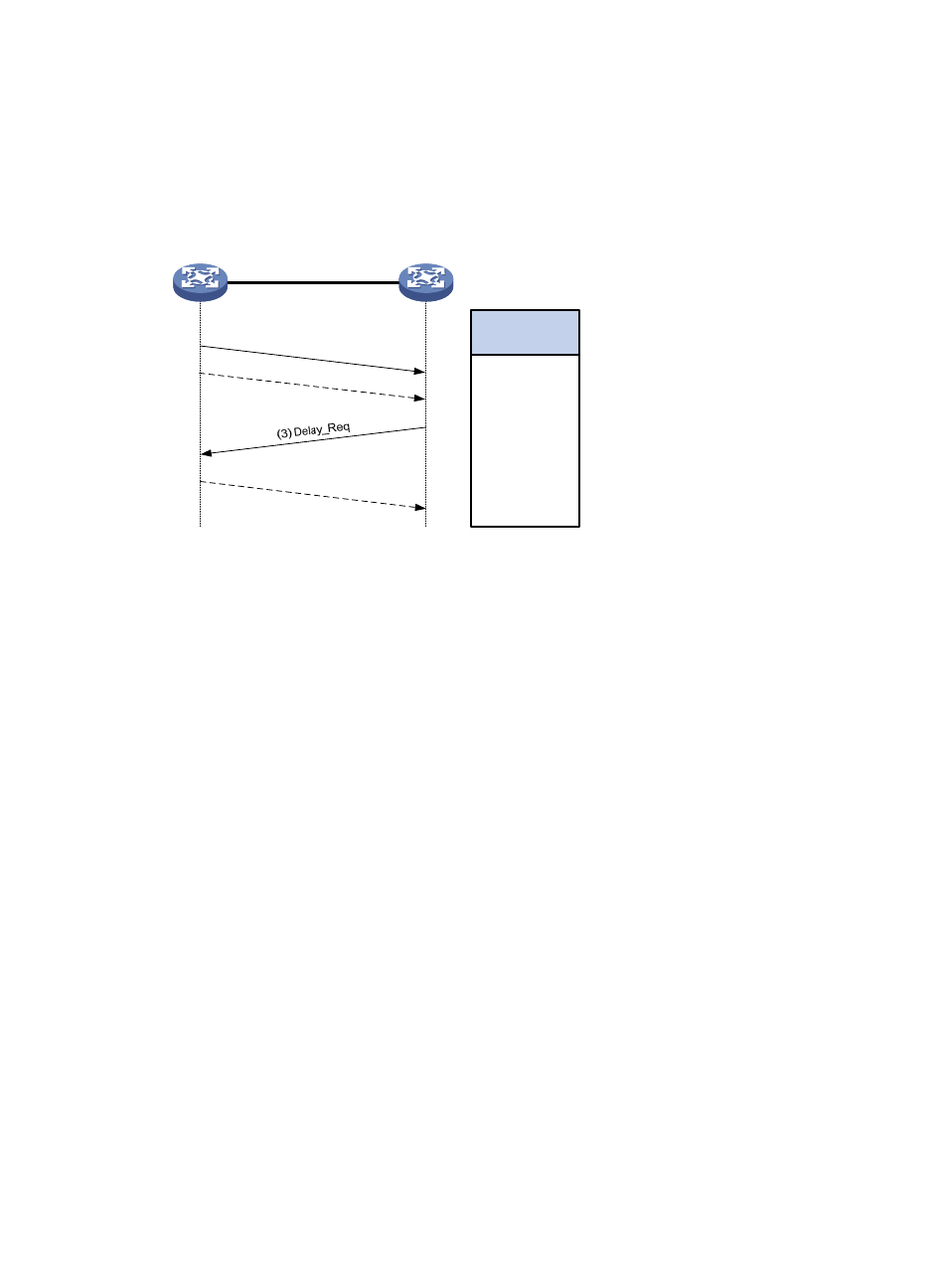
Figure 20 Operation procedure of the Request_Response mechanism
shows the operation procedure of the Request_Response mechanism, which applies only to
peer-to-peer delay measurement. It shows an example of the Request_Response mechanism in two-step
mode.
1.
The master clock sends a Sync message to the member clock, and records the sending time t1.
Upon receiving the message, the member clock records the receiving time t2.
2.
After sending the Sync message, the master clock immediately sends a Follow_Up message
carrying time t1.
3.
The member clock sends a Delay_Req message to calculate the transmission delay in the reverse
direction, and records the sending time t3. Upon receiving the message, the master clock records
the receiving time t4.
4.
The master clock returns a Delay_Resp message carrying time t4.
From the above process, the member clock collects four timestamps, t1 to t4, and obtains the round-trip
delay to the master clock by using the following calculation:
•
[(t2 – t1) + (t4 – t3)]
The member clock also obtains the one-way delay by using the following calculation:
•
[(t2 – t1) + (t4 – t3)] / 2
The offset between the member and master clocks is obtained by using the following calculation:
•
(t2 – t1) – [(t2 – t1) + (t4 – t3)] / 2
•
[(t2 – t1) – (t4 – t3)] / 2
Depending on whether to send Follow_Up messages, the Request_Response mechanism includes two
modes: single-step and two-step.
•
In single-step mode, t1 is carried in the Sync message, and no Follow_Up message is sent.
•
In two-step mode, t1 is carried in the Follow_Up message.
Master clock
Member clock
(1) Sync
(2) Follow_Up
(4) Delay_Resp
t1
t2
t3
t4
Timestamps
known by
member clock
t2
t1, t2
t1, t2, t3
t1, t2, t3, t4
