Ntp security, Ntp access control, Ntp authentication – H3C Technologies H3C S6300 Series Switches User Manual
Page 25
12
NTP security
To improve time synchronization security, NTP provides the access control and authentication functions.
NTP access control
You can control NTP access by using an ACL. The access rights are in the following order, from least
restrictive to most restrictive:
•
Peer—Allows time requests and NTP control queries (such as alarms, authentication status, and time
server information) and allows the local device to synchronize itself to a peer device.
•
Server—Allows time requests and NTP control queries, but does not allow the local device to
synchronize itself to a peer device.
•
Synchronization—Allows only time requests from a system whose address passes the access list
criteria.
•
Query—Allows only NTP control queries from a peer device to the local device.
The device processes an NTP request as follows:
•
If no NTP access control is configured, peer is granted to the local device and peer devices.
•
If the IP address of the peer device matches a permit statement in an ACL for more than one access
right, the least restrictive access right is granted to the peer device. If a deny statement or no ACL is
matched, no access right is granted.
•
If no ACL is created for a specific access right, the associated access right is not granted.
•
If no ACL is created for any access right, peer is granted.
This feature provides minimal security for a system running NTP. A more secure method is NTP
authentication.
NTP authentication
Use this feature to authenticate the NTP messages for security purposes. If an NTP message passes
authentication, the device can receive it and get time synchronization information. If it does not, the
device discards the message. This function makes sure the device does not synchronize to an
unauthorized time server.
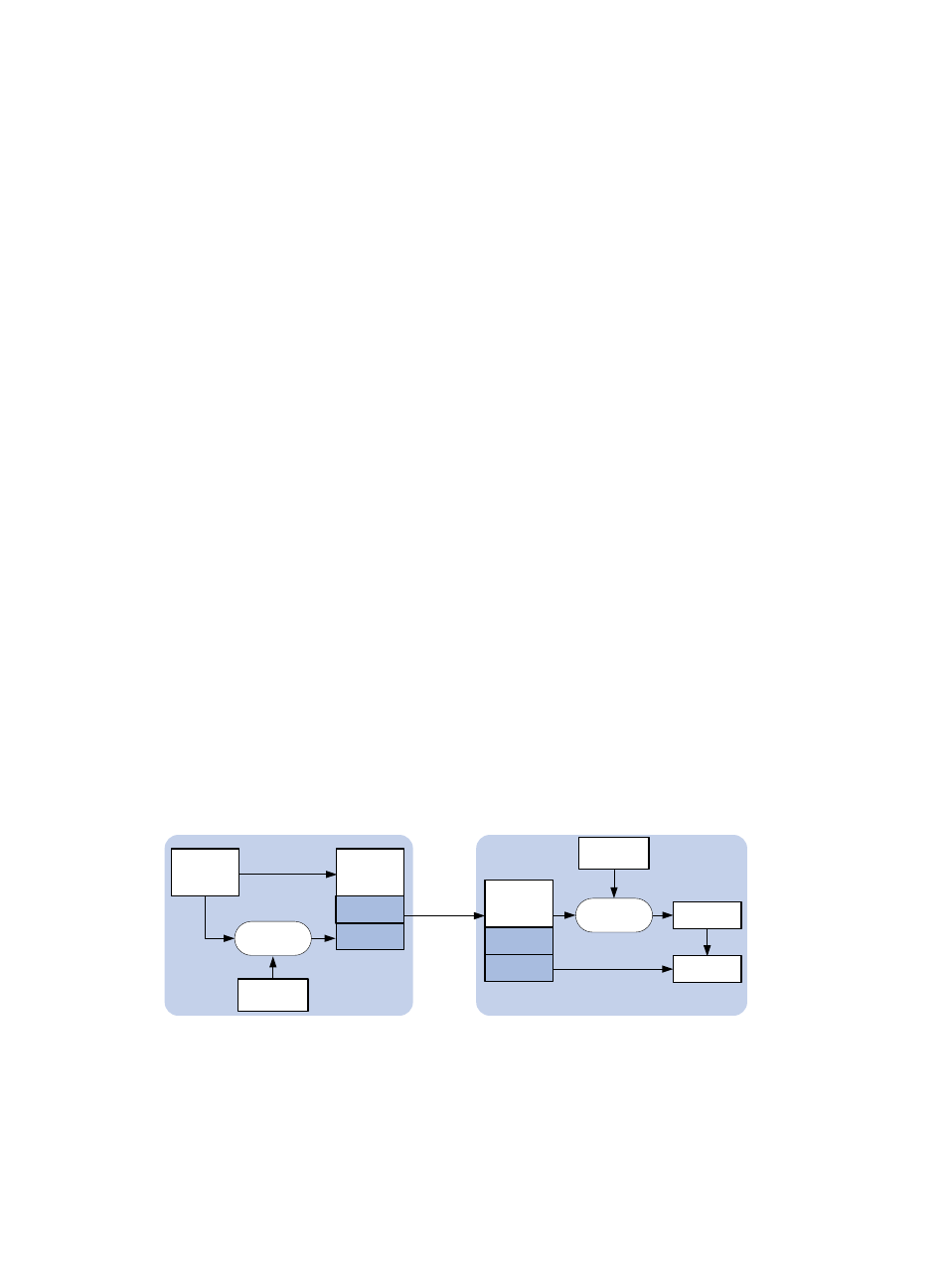
Figure 7 NTP authentication
As shown in
, NTP authentication works as follows:
1.
The sender uses the MD5 algorithm to calculate the NTP message according to the key identified
by a key ID, and sends the calculated digest together with the NTP message and key ID to the
receiver.
2.
Upon receiving the message, the receiver performs the following operations:
Key value
Message
Sender
Message
Sends to the
receiver
Digest
Receiver
Compare
Compute the
digest
Compute the
digest
Digest
Key ID
Message
Digest
Key ID
Key value
