Route types – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 77
63
•
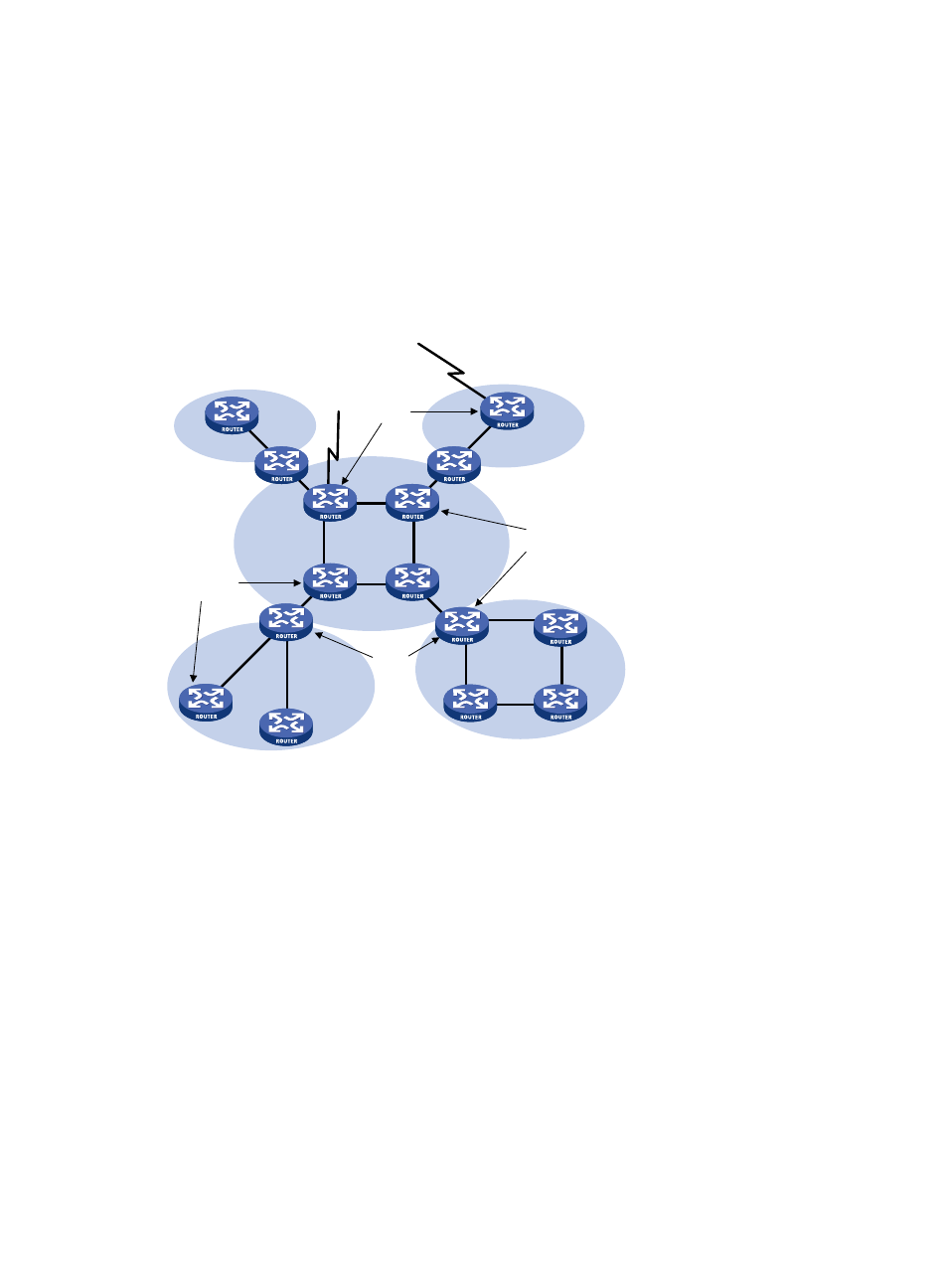
Internal router—All interfaces on an internal router belong to one OSPF area.
•
ABR—Belongs to more than two areas, one of which must be the backbone area. ABR connects the
backbone area to a non-backbone area. An ABR and the backbone area can be connected
through a physical or logical link.
•
Backbone router—At least one interface of a backbone router must reside in the backbone area.
All ABRs and internal routers in Area 0 are backbone routers.
•
ASBR—Exchanges routing information with another AS is an ASBR. An ASBR might not reside on
the border of the AS. It can be an internal router or an ABR.
Figure 19 OSPF router types
181B
Route types
OSPF prioritizes routes into the following route levels:
•
Intra-area route
•
Inter-area route
•
Type-1 external route
•
Type-2 external route
The intra-area and inter-area routes describe the network topology of the AS. The external routes describe
routes to external ASs.
A Type-1 external route has high credibility. The cost from a router to the destination of a Type-1 external
route = the cost from the router to the corresponding ASBR + the cost from the ASBR to the destination of
the external route.
A Type-2 external route has low credibility. OSPF considers the cost from the ASBR to the destination of
a Type-2 external route is much greater than the cost from the ASBR to an OSPF internal router. The cost
from the internal router to the destination of the Type-2 external route = the cost from the ASBR to the
Area 1
Area 2
Area 3
Area 4
Backbone router
ASBR
IS-IS
RIP
Internal router
ABR
Area 0
