Protocols and standards, Bgp path attributes – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 189
175
300B
BGP path attributes
BGP uses the following path attributes in update messages for route filtering and selection:
•
ORIGIN
The ORIGIN attribute specifies the origin of BGP routes. This attribute has the following types:
{
IGP—Has the highest priority. Routes generated in the local AS have the IGP attribute.
{
EGP—Has the second highest priority. Routes obtained through EGP have the EGP attribute.
{
INCOMPLETE—Has the lowest priority. The source of routes with this attribute is unknown.
Routes redistributed from other routing protocols have the INCOMPLETE attribute.
•
AS_PATH
The AS_PATH attribute identifies the ASs through which a route has passed. Before advertising a
route to another AS, BGP adds the local AS number into the AS_PATH attribute, so the receiver can
determine ASs to route the message back.
The AS_PATH attribute has the following types:
{
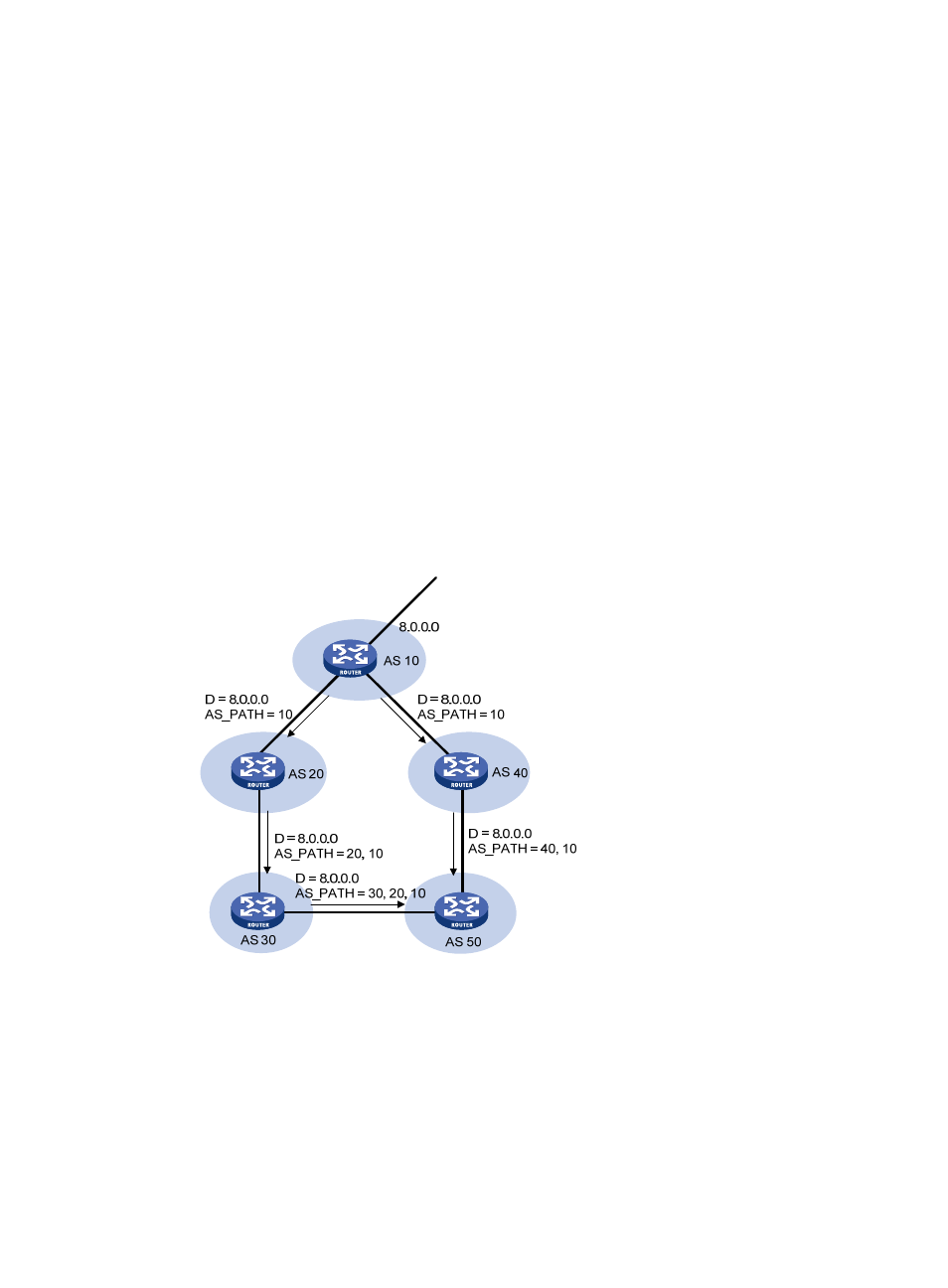
AS_SEQUENCE—Arranges AS numbers in sequence. As shown in
1052H
Figure 46
, the number of the
AS closest to the receiver's AS is leftmost.
{
AS_SET—Arranges AS numbers randomly.
Figure 46 AS_PATH attribute
BGP uses the AS_PATH attribute to implement the following functions:
{
Avoid routing loops—A BGP router does not receive routes containing the local AS number to
avoid routing loops.
{
Affect route selection—BGP gives priority to the route with the shortest AS_PATH length if other
factors are the same. As shown in
1053H
Figure 46
, the BGP router in AS 50 gives priority to the route
passing AS 40 for sending data to the destination 8.0.0.0. In some applications, you can apply
a routing policy to control BGP route selection by modifying the AS_PATH length. For more
information about routing policy, see "
1054H
Configuring routing policies
."
