Configuring the ospf gr restarter, Is-is network types – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 141
127
passing through the Level-1-2 router might not be the best. To solve this problem, IS-IS provides the route
leaking feature.
Route leaking enables a Level-1-2 router to advertise the routes of other Level-1 areas and the Level-2 area
to the connected Level-1 area so that the Level-1 routers can select the optimal routes for packets.
252B
IS-IS network types
539B
Network types
IS-IS supports the broadcast network (for example, Ethernet and Token Ring) and the point-to-point
network (for example, PPP and HDLC).
For an NBMA interface, such as an ATM interface, you must configure point-to-point or broadcast
subinterfaces. IS-IS cannot run on P2MP links.
540B
DIS and pseudonodes
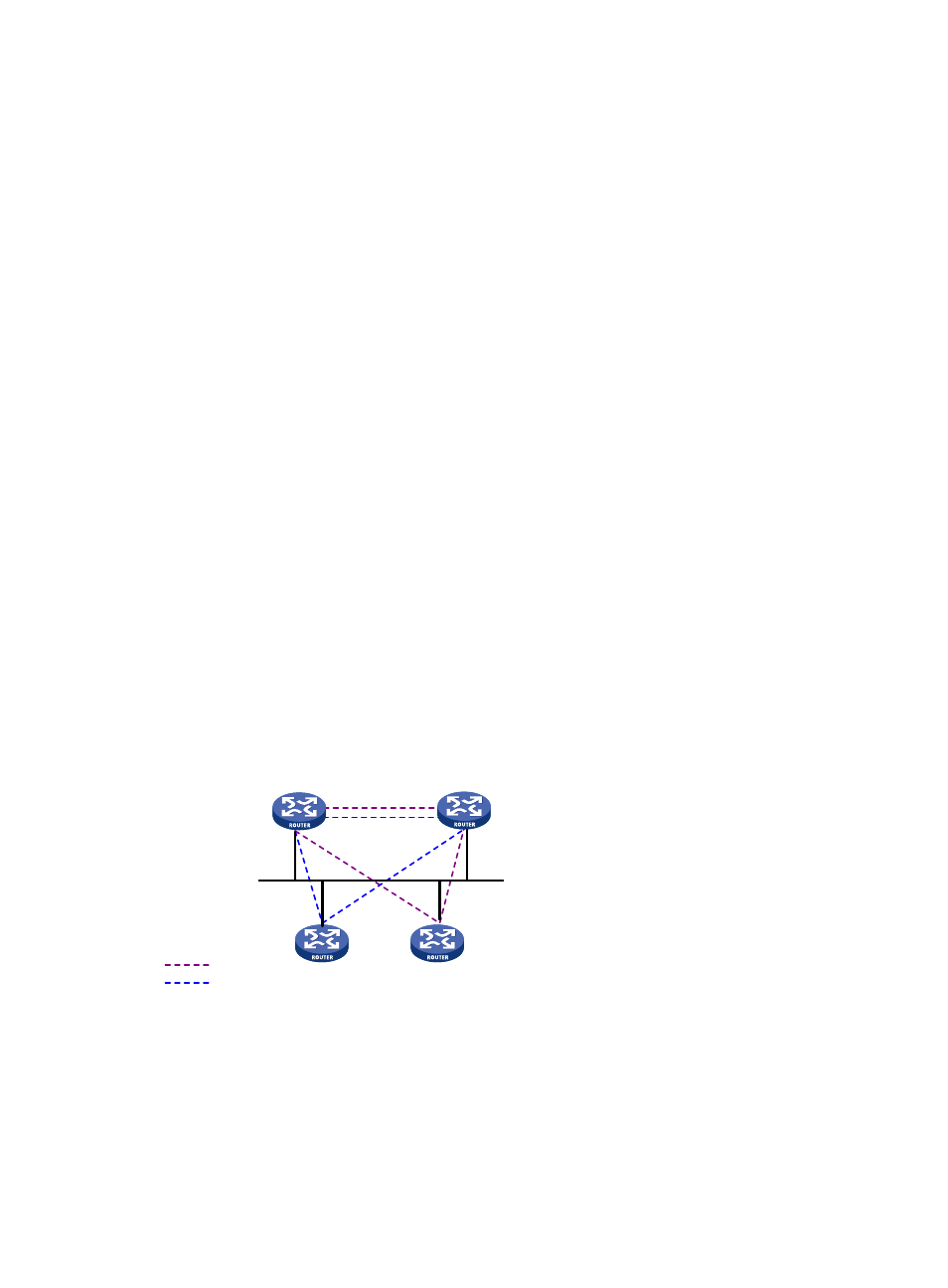
IS-IS routers on a broadcast network must elect a DIS.
The Level-1 and Level-2 DISs are elected separately. You can assign different priorities to a router for
different level DIS elections. The higher the router priority, the more likely the router becomes the DIS. If
multiple routers with the same highest DIS priority exist, the one with the highest SNPA (Subnetwork Point
of Attachment) address (MAC address on a broadcast network) will be elected. A router can be the DIS
for different levels.
IS-IS DIS election differs from OSPF DIS election in the following ways:
•
A router with priority 0 can also participate in the DIS election.
•
When a router with a higher priority is added to the network, an LSP flooding process is performed
to elect the router as the new DIS.
As shown in
1004H
Figure 35
, the same level routers on a network, including non-DIS routers, establish
adjacency with each other.
Figure 35 DIS in the IS-IS broadcast network
The DIS creates and updates pseudonodes, and generates LSPs for the pseudonodes, to describe all
routers on the network.
A pseudonode represents a virtual node on the broadcast network. It is not a real router. In IS-IS, it is
identified by the system ID of the DIS and a 1-byte Circuit ID (a non-zero value).
Using pseudonodes simplifies network topology and can reduce the amount of resources consumed by
SPF.
L1
L2
L1/L2
L1/L2
DIS
DIS
L1 adjacencies
L2 adjacencies
