Port 2 (p2), Port 5 (p5), Port 5 (p5) port 2 (p2) – Maxim Integrated High-Speed Microcontroller Users Guide: Network Microcontroller Supplement User Manual
Page 43
High-Speed Microcontroller User’s
Guide: Network Microcontroller
Supplement
43
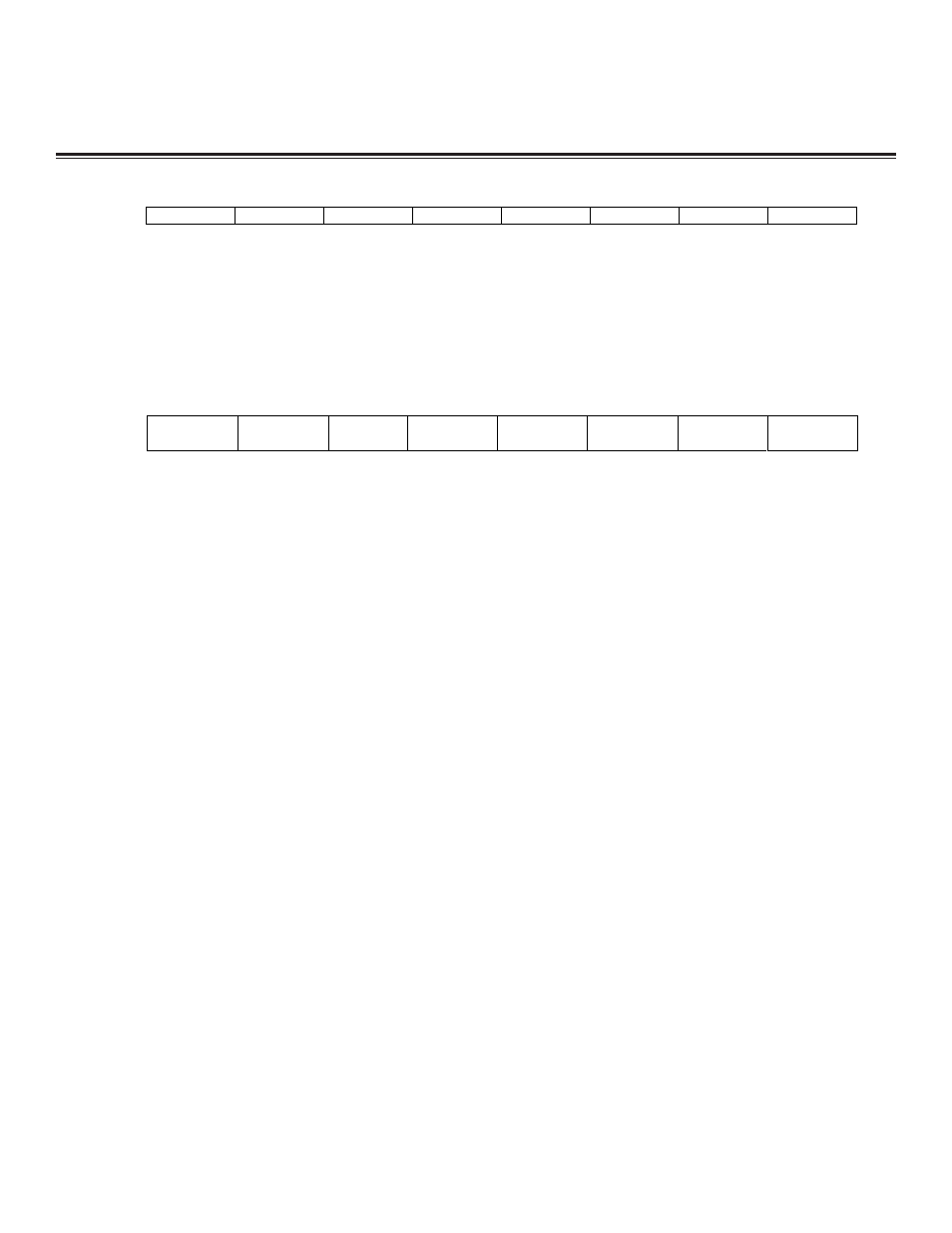
Port 5 (P5)
Port 2 (P2)
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
SFR A0h
A15/P2.7
A14/P2.6
A13/P2.5
A12/P2.4
A11/P2.3
A10/P2.2
A9/P2.1
A8/P2.0
RW-1
RW-1
RW-1
RW-1
RW-1
RW-1
RW-1
RW-1
R = Unrestricted read, W = Unrestricted write, -n = Value after reset
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
SFR A1h
P5.7
PCE3
P5.6
PCE2
P5.5
PCE1
P5.4
PCE0
P5.3
—
P5.2
T3
P5.1
C0RX
P5.0
C0TX
RW-1
RW-1
RW-1
RW-1
RW-1
RW-1
RW-1
RW-1
R = Unrestricted read, W = Unrestricted write, -n = Value after reset
P2.7–0
Bits 7–0
Port 2. This port functions as an address bus during external memory access and as a general-purpose
I/O port on devices that incorporate internal program memory. During external memory cycles, this port
contains the MSB of the address. The only instructions to access the P2 SFR are MOVX A, @Ri and
MOVX @Ri, A when port 2 is used as the MSB of an external address.
P5.7–0
Bits 7–0
PCE3
Bit 7
PCE2
Bit 6
PCE1
Bit 5
PCE0
Bit 4
Bit 3
T3
Bit 2
C0RX
Bit 1
C0TX
Bit 0
Port 5. This port can function as a programmable parallel I/O port, a CAN interface, timer 3 input, and/or
peripheral enable signals. Data written to the port latch serves to set both logic level and direction of the
data on the pin. A 1 written to a port latch, previously programmed low (0), activates a high-current, one-
shot pullup on the corresponding pin. This is followed by a static, low-current pullup that remains on until
the port is changed again. The final high state of the port pin is considered a pseudo-input mode and
can be easily overdriven from an external source. Port latches previously in a high-output state do not
change, nor does the high-current one-shot fire when a 1 is loaded. Loading a 0 to a port latch results
in a static, high-current pulldown on the corresponding pin. This mode is termed the I/O output state,
since no weak devices are used to drive the pin.
Writes to P5.1–P5.0 are disabled when the P5CNT.3 bit in the port 5 control SFR is programmed to a 1.
These bits read as a 1 when assigned to the CAN processor. The P5.2 latch bit must be set to 1 before
the pin can be used for the alternate function of T3. The value of the port latch is not altered by a read
operation, except the read-modify-write instructions that perform a read followed by a write. See P5CNT
SFR (A2h) for more details.
Peripheral chip enable 3. When enabled by the P5CNT register, this pin asserts the fourth chip-enable
signal.
Peripheral chip enable 2. When enabled by the P5CNT register, this pin asserts the third chip-enable
signal.
Peripheral chip enable 1. When enabled by the P5CNT register, this pin asserts the second chip-
enable signal.
Peripheral chip enable 0. When enabled by the P5CNT register, this pin asserts the first chip-enable
signal.
Reserved.
Timer/counter 3 external input. This pin functions as an external input to timer 3 when configured as
such with the T3CM SFR. A 1-to-0 transition on this pin increments timer 3.
CAN 0 receive. This pin is connected to the receive data-output pin of the CAN 0 transceiver device.
CAN 0 transmit. This pin is connected to the transmit data-input pin of the CAN 0 transceiver device.
Maxim Integrated
