Bit timing – Maxim Integrated High-Speed Microcontroller Users Guide: Network Microcontroller Supplement User Manual
Page 162
High-Speed Microcontroller User’s
Guide: Network Microcontroller
Supplement
162
Bit Timing
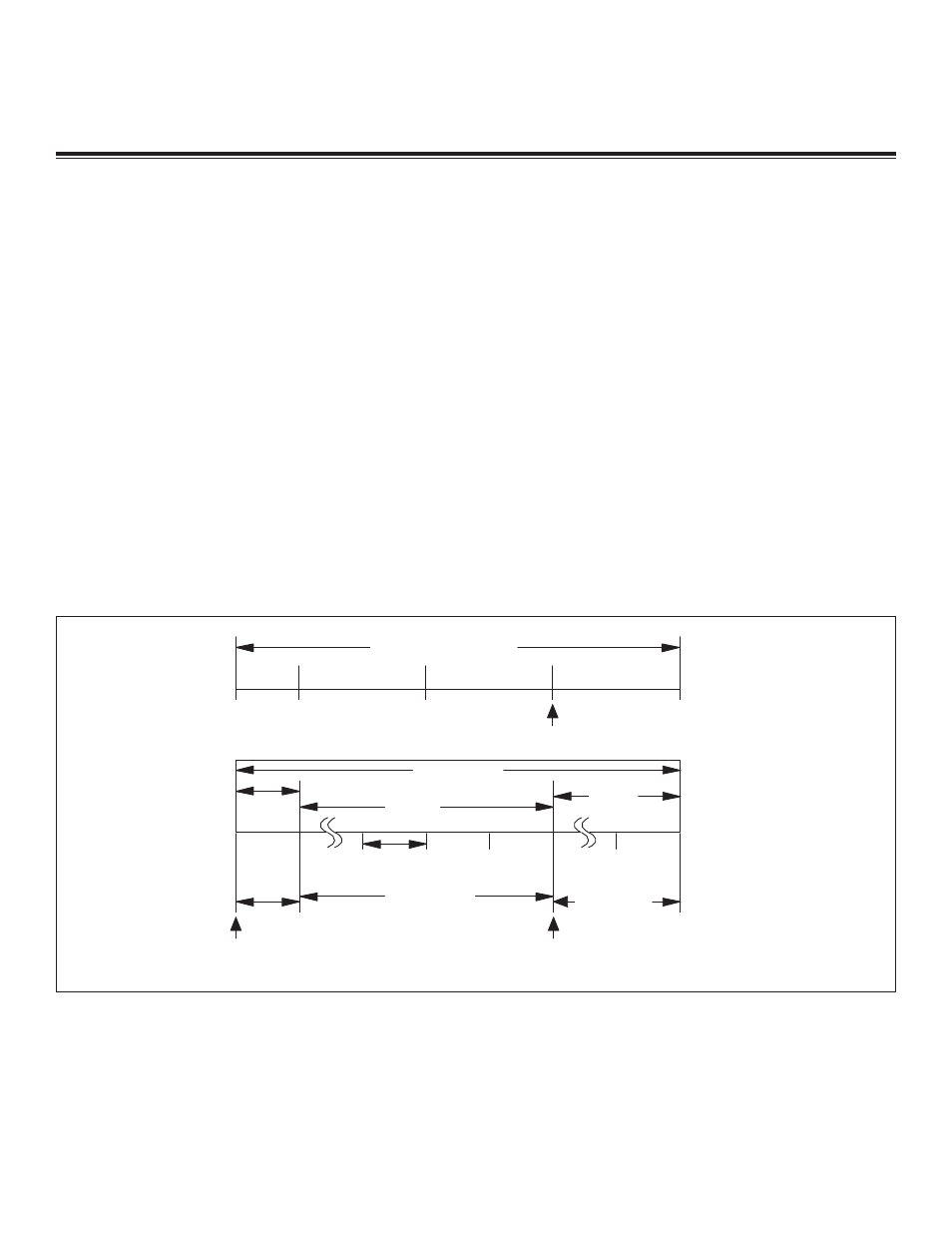
Bit timing in the CAN 2.0B specification is based on a unit called the nominal bit time. The nominal bit time is further subdivided into
four specific time periods.
1. The SYNC_SEG time segment is where an edge is expected when synchronizing to the CAN bus.
2. The PROP_SEG time segment is provided to compensate for the physical times associated with the CAN bus network.
3. The PHASE_SEG1 and PHASE_SEG2 time segments compensate for edge-phase errors.
4. The PHASE_SEG1 and PHASE_SEG2 time segments can be lengthened or shorted through the use of the SJW1 and SJW0
bits in the CAN 0 bus timing register 0.
The CAN bus bit data is evaluated at a specific sample point. A time quantum (t
QU
) is a unit of time derived from the division of the
microcontroller system clock by both the baud-rate prescaler (programmed by the BPR7–BPR0 bits of the clock output register and
CAN 0 bus timing register) and the system clock divider (programmed by the CD1:0 and 4X/2X bits of the PMR register). Combining
the PROP_SEG and PHASE_SEG1 time segments into one time period termed t
TSEG1
and equating the SYNC_SEG time segment to
t
SYNC_SEG
and PHASE_SEG2 to t
TSEG2
provides the basis for the time segments outlined in Figure 19-11 and the CAN bus timing SFR
register descriptions.
The CAN 0 bus timing register 0 (C0BT0) contains the control bits for the PHASE_SEG1 and PHASE_SEG2 time segments as well as
the baud-rate prescaler (BPR5–0) bits. CAN 0 bus timing register 1 (C0BT1) controls the sampling rate, the time segment 2 bits that
control the number of clock cycles assigned to the phase segment 2 portion, and the time segment 1 bits that determine the number
of clock cycles assigned to the phase segment 1 portion. The value of both of the bus timing registers are automatically loaded into
the CAN module following each software change of the SWINT bit from a 1 to a 0 by the microcontroller. The bit timing parameters must
be configured before starting operation of the CAN module. These registers can be modified only during a software initialization (SWINT
= 1), when the CAN module is NOT in a bus-off mode, and after the removal of a system reset or a CAN reset. To avoid unpredictable
behavior of the CAN module, the bus timing registers should never be written with all zeros. To prevent this, the SWINT is forced to 0
when TSEG1 = TSEG2 = 00h.
1 Bit Time
1 t
QU
Time Quanta
TRANSMIT
SAMPLE
POINT
SYNC_SEG
PROP_SEG
PHASE_SEG1
PHASE_SEG2
Nominal Bit Time
t
TSEG2
t
TSEG1
t
SYNC-SEG
SAMPLE
POINT
1 t
QU
Time Quanta
2 t
QU
– 16 t
QU
2 t
QU
– 8 t
QU
Figure 19-11. Bit Timing
Maxim Integrated
