Endec operation – Maxim Integrated High-Speed Microcontroller Users Guide: Network Microcontroller Supplement User Manual
Page 175
High-Speed Microcontroller User’s
Guide: Network Microcontroller
Supplement
175
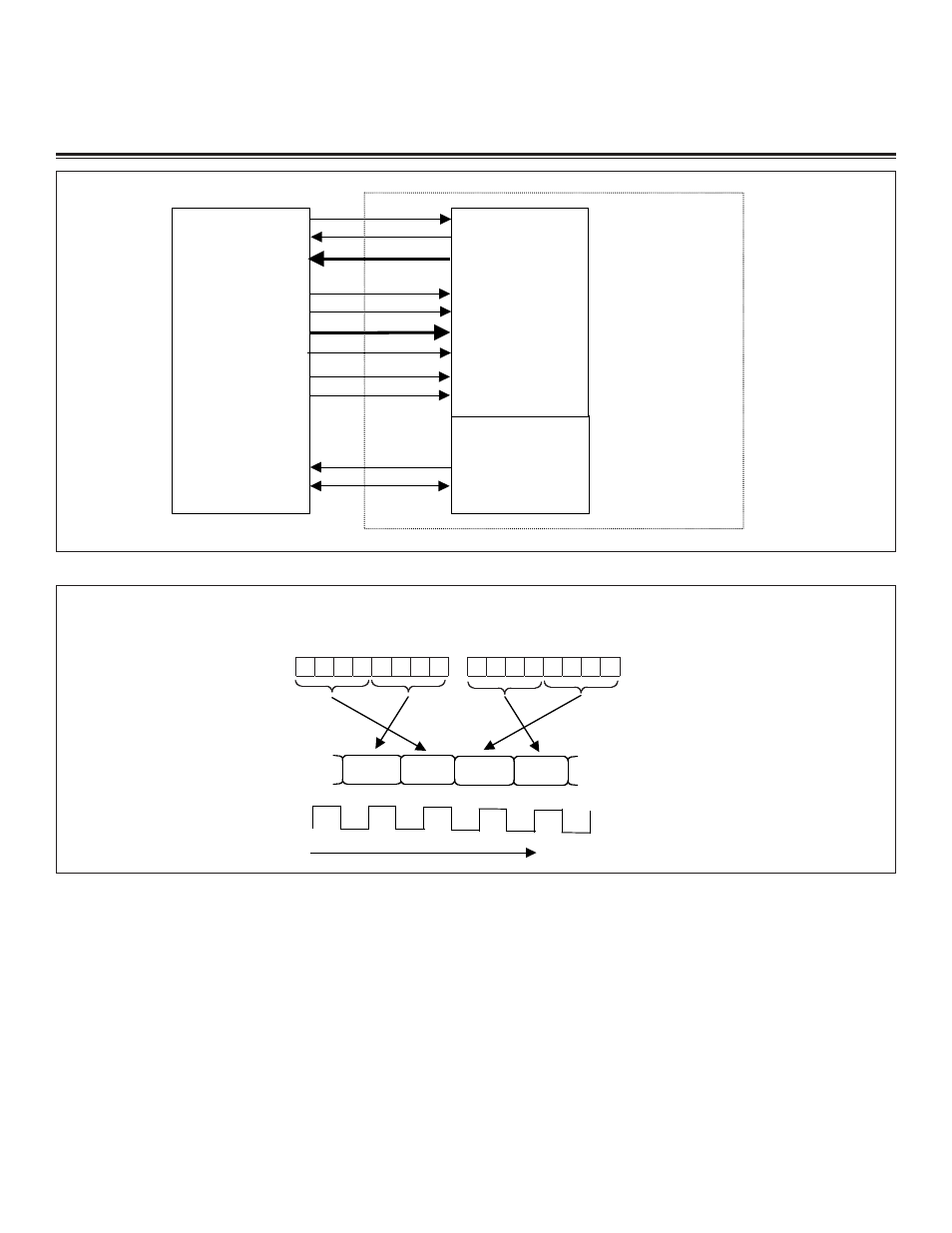
Figure 22-2. MII Signal Diagram
Figure 22-3. MII Mode–Byte/Bit Transmit and Receive Order
ENDEC OPERATION
The DS80C400 supports a serial ENDEC mode of operation, which is a subset of the MII mode of operation. The ENDEC mode can
be used to support communication through GPSI (general-purpose serial interface) or SNI (serial network interface). The ENDEC mode
of operation is selected by setting the port select bit (bit 27) of the MAC control CSR register. When ENDEC mode has been selected,
only the lowest bit of each RXD3:0 and TXD3:0 nibble, RXD.0 and TXD.0, respectively, are used for data transactions. The only outputs
generated by the DS80C400 are the TXEN and TXD.0 signals. All other signals are sourced from the PHY, including the TXCLK and
RXCLK clocks, which must run at 10MHz to provide 10Mbps bandwidth. The RX_ER input signal is not used for ENDEC mode and
should be connected in the inactive state (logic low). Figure 22-4 shows an example ENDEC interface. Serial data transactions con-
ducted between the DS80C400 MAC and the external PHY over the TXD.0 and RXD.0 lines are done least significant bit first, as shown
in Figure 22-4. The MII serial management bus (MDC, MDIO pins) operates no differently in ENDEC mode than MII mode and can still
be used for external PHY configuration.
RXD[3:0]
RXCLK
MDC
MII
MANAGEMENT
BLOCK
(Serial interface bus
to PHY)
MDIO
MII I/O BLOCK
(Transmit, receive,
and flow control)
EXTERNAL
PHY
DEVICE
TX_EN
TXD[3:0]
RX_DV
RX_ER
CRS
COL
TXCLK
DS80C400
7
0
7
0
1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0
Bytes transmitted by the MAC
A1h E6h
TXD[3:0]
(to PHY)
E
1
6
A
TXCLK
(from PHY)
Increasing time
Maxim Integrated
