Lethal arrhythmia analysis option: events detected – Welch Allyn Acuity and Mobile Acuity LT Central Monitoring Systems - User Manual User Manual
Page 59
Directions for use
Chapter 4 Adjust monitoring settings and patient information
55
Lethal Arrhythmia Analysis option: events detected
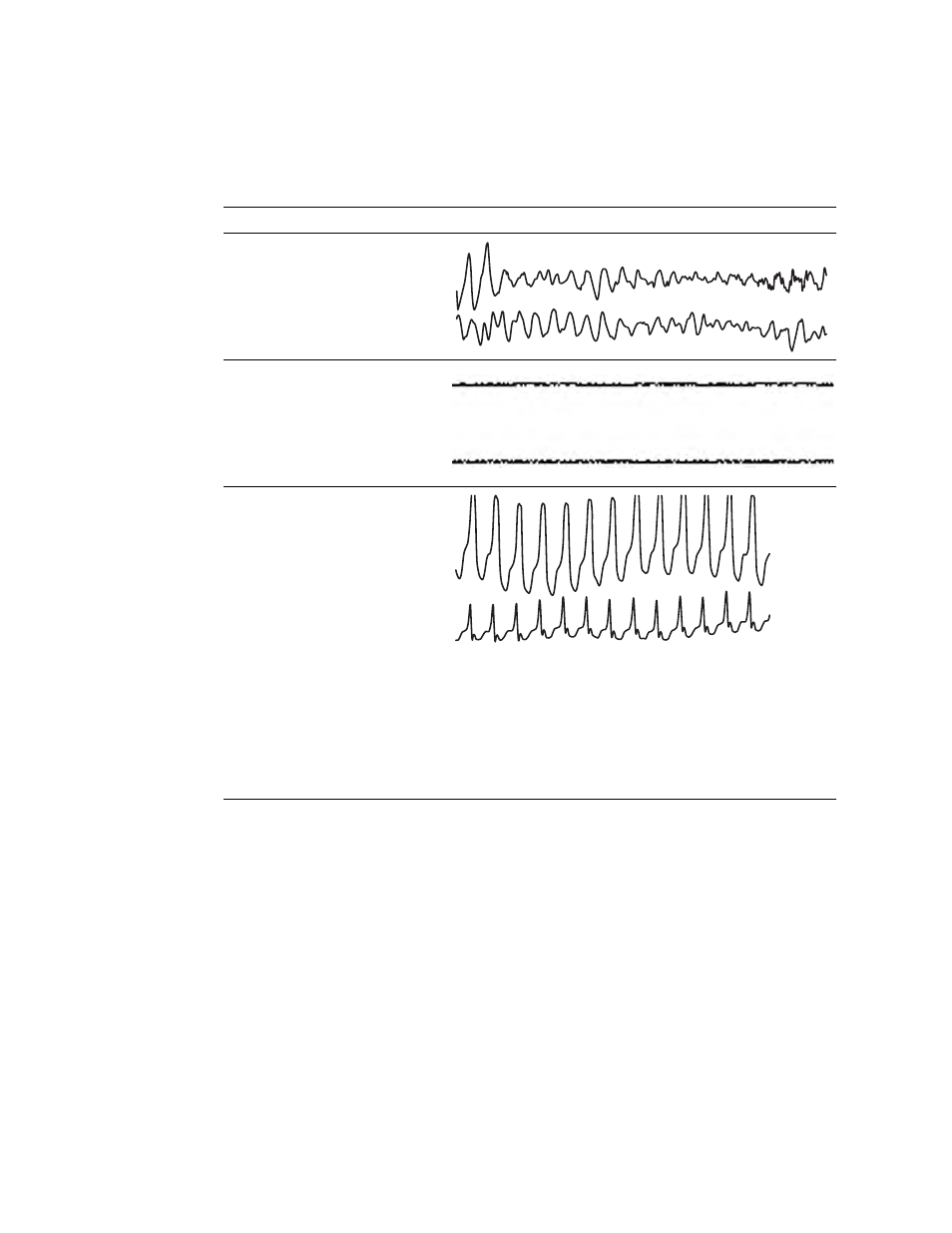
Table 4. Definitions of lethal arrhythmia events
a
a.
Alarming for lethal arrhythmias cannot be turned off.
Arrhythmia event and definition
Waveform example
VFib
b
(ventricular fibrillation)
Chaotic quivering of the ventricles
accompanied by rapid irregular waves but
no formed QRS complexes.
b.
VFib is detected within 6 seconds if the waveform fulfills these conditions:
Absence of fast slew-rate activity (QRS-like activity)
Wave rate higher than 130 bpm
Average peak-to-peak wave amplitude higher than 200 µV
Wave period variance higher than a specific threshold
Asystole
Absence of any detected beat for 4 or
more seconds.
VTach (ventricular tachycardia)
A run of premature ventricular beats that
exceeds the PVC run alarm limit and that
meets or exceeds the patient’s VTach
alarm limit.
Note: The American Heart Association
describes sustained and nonsustained
ventricular tachycardia as follows:
Ventricular tachycardia can be referred to
as sustained or nonsustained. Sustained
refers to an episode that lasts at least 30
seconds and generally requires
termination by antiarrhythmia drugs,
antitachycardia pacing techniques or
electrical cardioversion. Nonsustained
ventricular tachycardia suggests that the
episodes are short (three beats or longer)
and terminate spontaneously.
