Ipx encapsulation types, Populating the routing table – Allied Telesis AT-8550 User Manual
Page 195
AT-9108, AT-8518, AT-8525, and AT-8550 User’s Guide
11-3
IPX
Encapsulation
Types
Novell NetWare
™
supports four types of frame encapsulation. The
ExtremeWare term for each type is described in Table 11-1.
To configure a VLAN to use a particular encapsulation type, use the
following command:
config vlan
enet_8023 | enet_8022 | enet_snap]
Populating the
Routing Table
The switch builds and maintains an IPX routing table. As in the case
of IP, the table is populated using dynamic and static entries.
Dynamic Routes. Dynamic routes are typically learned by way of
IPX/RIP. Routers that use IPX/RIP exchange information in their
routing tables in the form of advertisements. Using dynamic routes,
the routing table contains only networks that are reachable.
Dynamic routes are aged out of the table when an update for the
network is not received for a period of time, as determined by the
routing protocol.
Static Routes. Static routes are manually entered into the routing
table. Static routes are used to reach networks not advertised by
routers. You can configure up to 64 static IPX routes on the switch.
Static routes are never aged out of the routing table. Static routes are
advertised to the network using IPX/RIP.
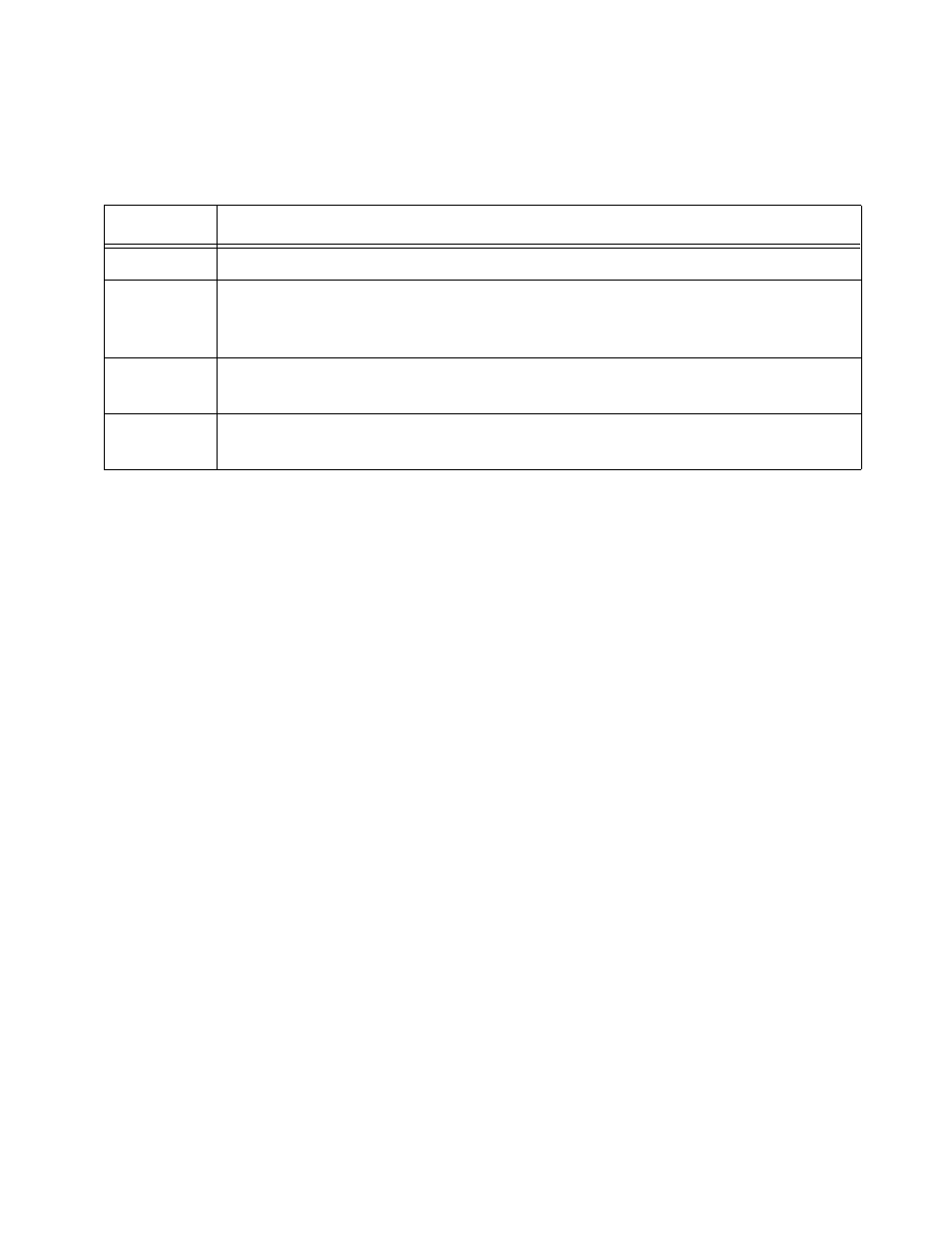
Table 11-1 IPX Encapsulation Types
Name
Description
ENET_II
The frame uses the standard Ethernet 2 header.
ENET_8023
The frame includes the IEEE 802.3 length field, but does not include the IEEE
802.2 Logical Link Control (LLC) header. This encapsulation is used by NetWare
version 2.x and the original 3.x version.
ENET_8022
The frame uses the standard IEEE format and includes the IEEE 802.2 LLC header.
This encapsulation is used by NetWare version 3.12 and 4.x.
ENET_SNAP
The frame adds a Subnetwork Access Protocol (SNAP) header to the IEEE 802.2
LLC header.
