Oampdu types – Allied Telesis AT-S70 User Manual
Page 92
Chapter 8: Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM)
92
One important aspect of the IEEE 802.3ah OAM spec is that an OAM
entity may be in either Active or Passive mode.
Active Mode – Active-mode stations forward OAM communications
and can send queries and commands to a remote station.
Passive Mode – Passive-mode stations wait for the peer station to
forward OAM communications and then respond to commands and
queries. Generally, passive-mode do not initiate communications.
By default, the Converteon™ line card should come up in Passive mode
for OAM discovery (as per the IEEE 802.3ah). In order to initiate OAM
discovery, the line card needs to be configured in the Active mode by the
AT-CV5M01 CPM card. Therefore, if a line card is in a chassis with no
CPM card, it will come up in Passive mode.
The difference between the modes is that an OAM active-mode station
has more control on its peer than an OAM passive-mode station. For
example, an active-mode station can put a passive-mode station into
loopback mode, but not vice versa.
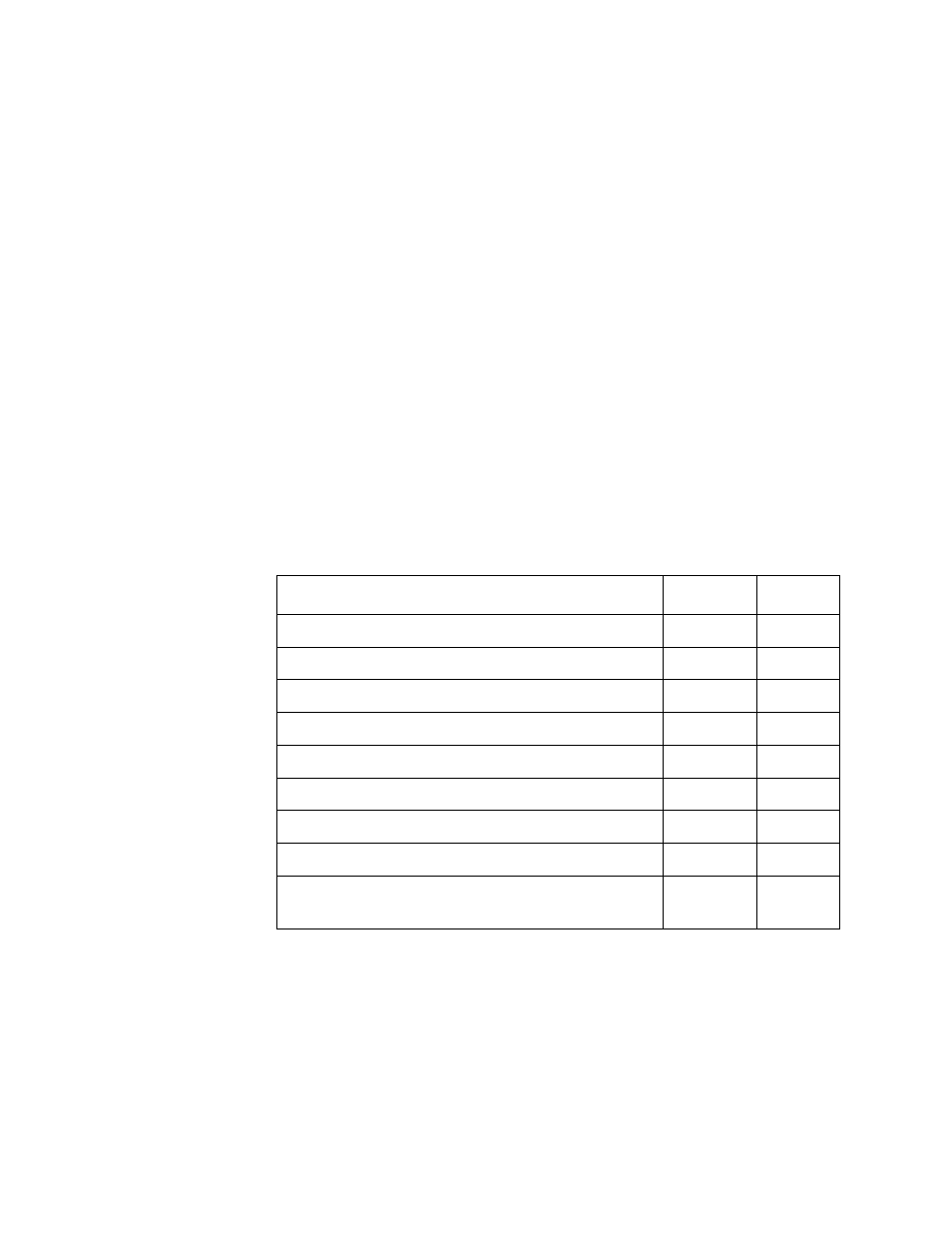
Table 3 lists the OAM Active and OAM Passive mode behaviors.
OAMPDU Types
Two Ethernet ports use OAMPDU to exchange the OAM protocol. The
OAMPDUs use a specific multicast destination address and EtherType.
Most of the OAMPDU types are used to define a set of standard type-
length-value (TLV) encoding of attributes within the type.
Table 3. OAM Active and Passive Mode Behaviors
Capability
Active
Passive
Initiates OAM Discovery process
Yes
No
Reacts to OAM Discovery process initiation
Yes
Yes
Required to send Information OAMPDUs
Yes
Yes
Permitted to send Event Notification OAMPDUs
Yes
Yes
Permitted to send Variable Request OAMPDUs
Yes
No
Permitted to send Variable Response OAMPDUs
Yes*
Yes
Permitted to send Loopback Control OAMPDUs
Yes
No
Reacts to Loopback Control OAMPDUs
Yes*
Yes
Permitted to send Organization Specific
OAMPDUs
Yes
Yes
* Requires the peer station to be in Active mode.
