Host failover software, Remote copy operations, Figure 5 remote copy operations – HP StorageWorks XP Remote Web Console Software User Manual
Page 26: Initial copy operations, 5 remote copy operations
26
Overview of Continuous Access XP Journal
Host failover software
Host failover software, which transfers information between host servers at the primary and remote sites,
is a critical component of any disaster recovery effort. Host failover is configured using the desired host
failover software product for the platform (for example, Microsoft Cluster Server or HP Serviceguard),
depending on your installation requirements and standards. The Command View XP or XP Remote Web
Console software products do not provide host failover functions.
When using Continuous Access XP Journal as a data migration tool, host failover is recommended but not
required. When using Continuous Access XP Journal as a disaster recover tool, host failover is required to
ensure effective disaster recovery operations. When a Continuous Access XP Journal pair is suspended
due to an error condition, the primary array generates sense information that should be transferred to the
remote site using the host failover software for effective disaster detection and recovery.
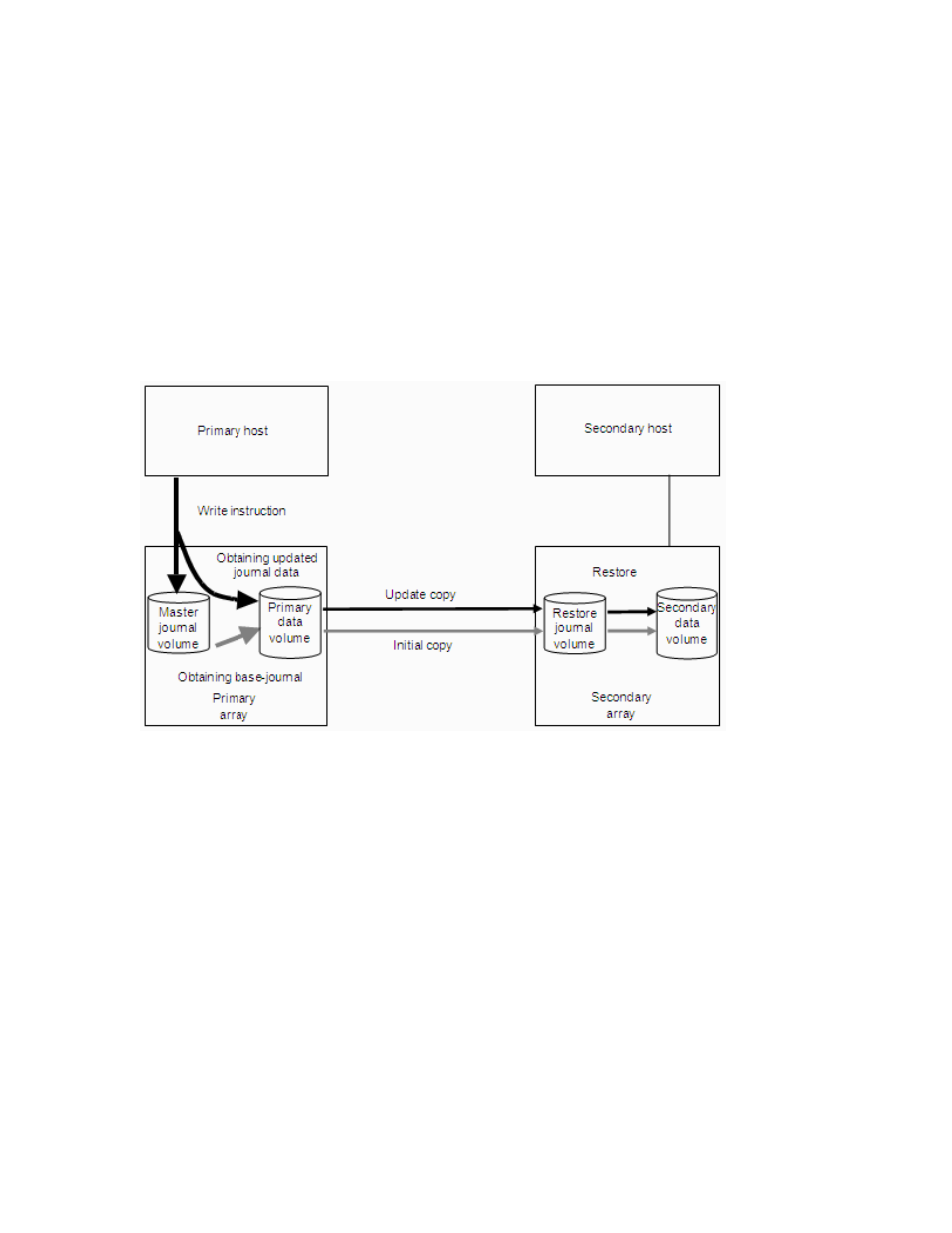
Remote copy operations
illustrates the types of Continuous Access XP Journal remote copy operations: initial copy and
update copy.
Figure 5
Remote copy operations
Initial copy operations
Initial copy operations synchronize data in the primary data volume with data in the secondary data
volume. Initial copy operations are performed independently from host I/Os. Initial copy operations are
performed when creating a data volume pair or resynchronize a suspended pair. The initial copy
operation copies base-journal data obtained from the primary data volume at the primary array to the
secondary array, and then restores the base-journal to the secondary data volume.
If the journal-obtain operation starts at the primary data volume, the primary array uses all of the primary
data volume’s data as base-journal data, in sequence. The base-journal contains a replica of the entire
data volume and a replica of data volume updates. The base-journal is copied from the primary array to
the secondary array after the secondary array issues a read-journal command. After the base-journal is
copied to the secondary array, the base-journal is stored in a restore journal volume in a restore journal
group to which the secondary data volume belongs. After that, data in the restore journal volume is
restored (destaged) to the secondary data volume, so data in the secondary data volume is coherent and
synchronized with data in the primary data volume.
Base-journal data reflects the entire data volume plus updates. The difference area within the base-journal
is used during differential resynchronization operations. Journal data for the entire data volume is created
when the data volume pair is created. Difference journal data is used when the data volume’s pair status
changes from Suspended to Pairresync. Merging difference bitmaps recorded on the primary and
secondary data volumes allows you to obtain journal data for only what changed while the pair was
