Remote copy connections – HP XP Continuous Access Software User Manual
Page 27
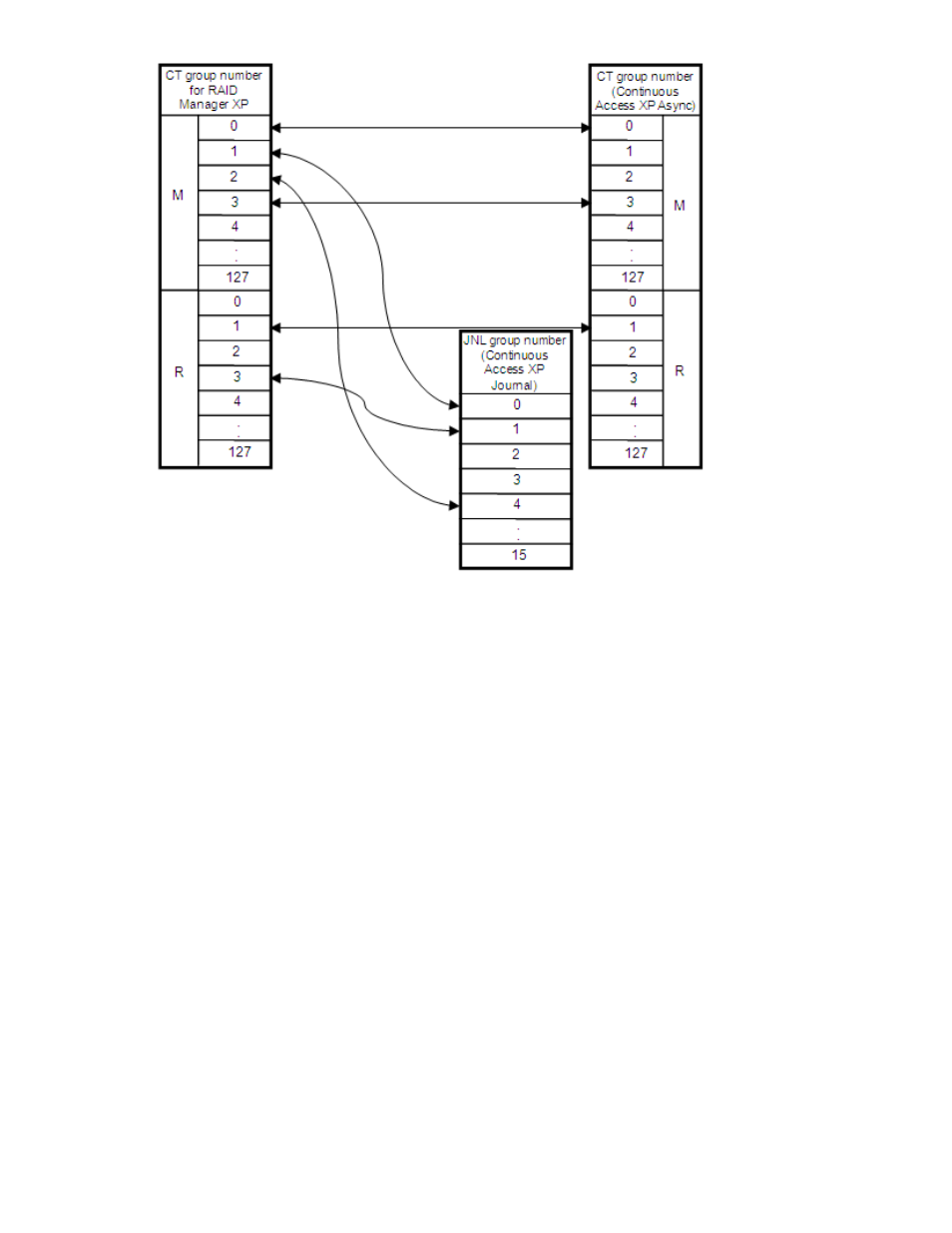
Figure 4 Corresponding consistency group and journal group numbers
Remote copy connections
Remote copy connections are the physical paths that primary arrays use to communicate with secondary
arrays. Remote copy connections enable communications between primary and secondary arrays.
Primary and secondary arrays are connected through Fibre Channel interface cables. You must establish
paths from the primary array to the secondary array, and also from the secondary array to the primary
array. You can establish up to eight paths in each direction.
When using Fibre Channel interface (optical multimode shortwave) connections, two switches are
required for distances greater than 0.5 km (1,640 feet), and distances up to 1.5 km (4,920 feet,
0.93 miles) are supported. If the distance between primary and secondary sites is greater than 1.5 km,
optical single-mode longwave interface connections are required. When using Fibre Channel interface
(single-mode longwave) connections, two switches are required for distances greater than 10 km
(6.2 miles), and distances up to 30 km (18.6 miles) are supported.
See
for more information about installing and configuring FC remote copy
connections.
The Continuous Access XP Journal remote copy configuration between the primary and secondary arrays
has the following requirements (see
•
Continuous Access XP Journal supports a 1-to-1 remote copy connection in one journal group
pair. In one journal group pair, one primary array can be connected to only one secondary
array. This configuration ensures the backup data consistency of two or more volumes (for
example, large databases) within the same array.
Continuous Access XP Journal user guide
27
