Timer block events, 6 timer block events – Micromod MOD: 1800P - MOD 30ML Identity Module (Version 2) Algorithms, Tables and Sequential Logic Functions User Manual
Page 70
Logic Functions - Book 2
TIMER BLOCK
8-62
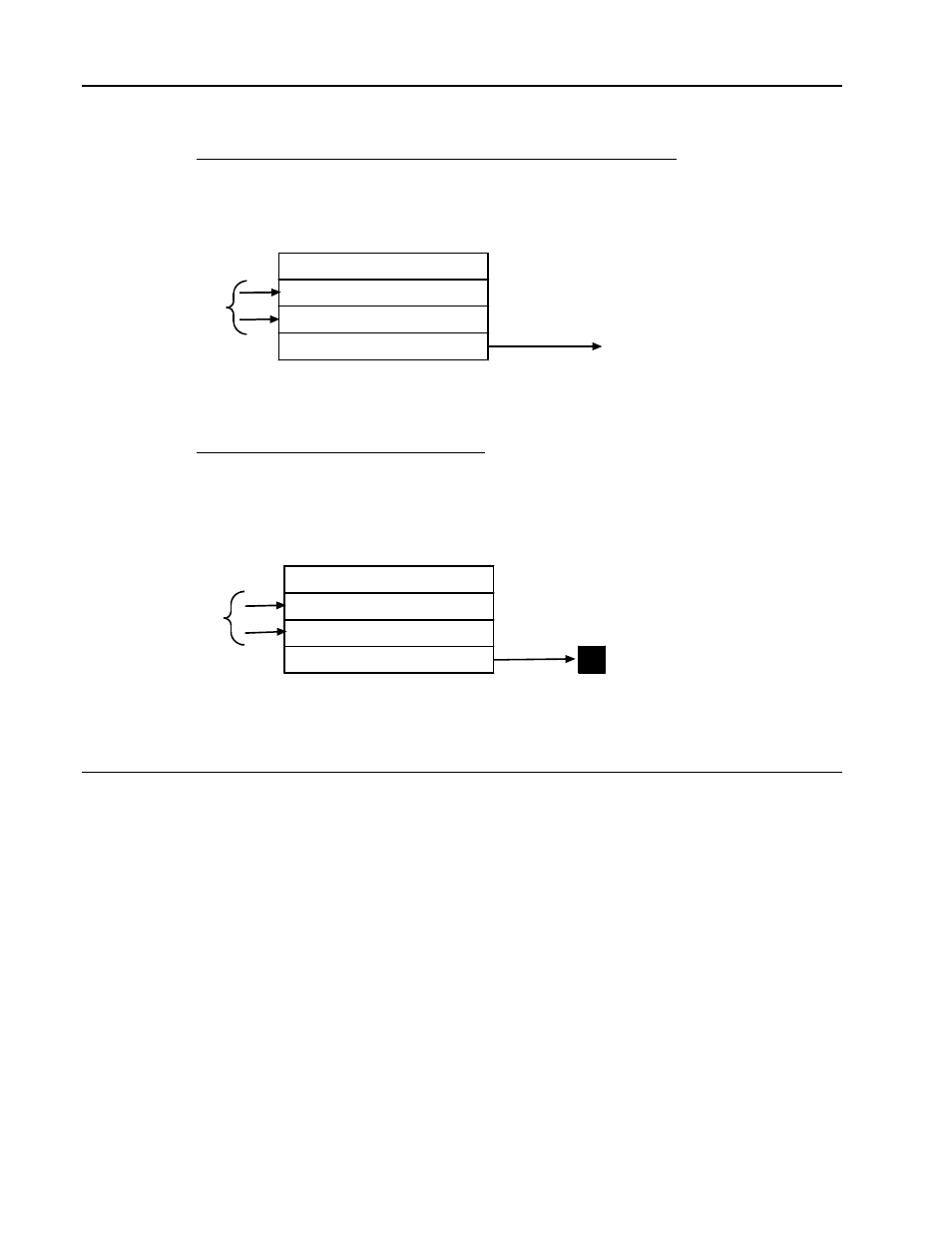
EXAMPLE 3 Timing Only When Disable Source is False (Figure 8-34)
When disable source is false, timer will time towards its limit from the current time value. If
disable source becomes true, timer will stop and hold the elapsed time. Then, when disable
source becomes false, the timer will start to time from the held value and continue to time until
the limit is reached.
HLSTAT
Disable
Reset
High Limit Status
Discrete Output to
Another Function Block
TM3
Discrete
Inputs
Figure 8-34. Softwiring Drawing for Timer Block, Example 3
EXAMPLE 4 Running Timer (Figure 8-35)
A running timer is used to display time into a process or operation. If the total process time is
uncertain, the reset input/limit can be set at the maximum value of approximately 1193 hours.
The disable source is set at false when the timer is to become active and true when inactive.
The total time is the time value when the process or operation is complete. The reset source
is put through a false to true transition when the timer is required again.
TIME
Timer Disable
Timer Reset
Time
Operator Indication of
Timer Value
TM4
Discrete
Inputs
Figure 8-35. Softwiring Drawing for Timer Block, Example 4
8.7.6
Timer Block Events
The event codes (and their suggested text messages) for the timer block are given below.
See database attributes descriptions for additional information. See System Event Block,
LOGIC FUNCTIONS - BOOK 1, IB-23G600 for a description of event transitions.
0
BLOCK STATE SET TO RUN
1
BLOCK STATE SET TO HOLD
2
BLOCK STATE SET TO OFF
3
BLOCK STATE SET TO DEBUG
