Micromod MOD: 1800P - MOD 30ML Identity Module (Version 2) Algorithms, Tables and Sequential Logic Functions User Manual
Page 53
Logic Functions - Book 2
PROCESS ALARM BLOCK
8-45
Alarm Clear
Time
(Group Scan Cycles)
750
500
250
0.000000
0
30
25
20
15
10
5
35
1000
TRUE
FALSE
Alarm
Active
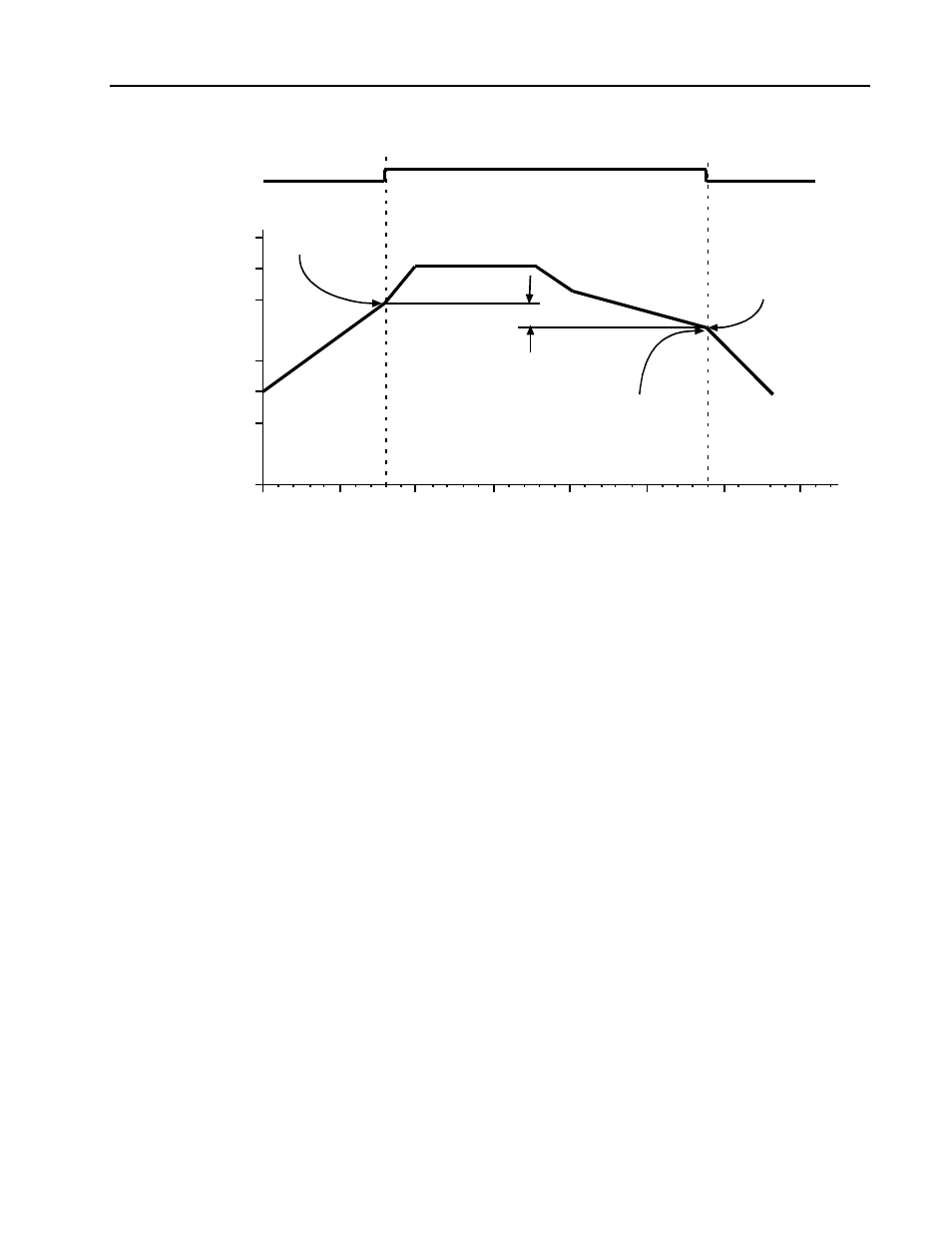
HIGH ALARM CALCULATION
Process Input
Floating Point
Value
Hysteresis Value (50)
Configured Trip Condition is >=
Alarm Value >= Trip Value
Alarm Value < Trip Value - Hysteresis
Figure 8-24. Example of Process Alarm Tripping (Floating Point Data)
An alarm can be acknowledged in 1 of 6 ways:
•
By using the Alarm Acknowledge discrete input. This acknowledgment is edge triggered
so that a value of 0 (FALSE) followed by a value of 1 (TRUE) acknowledges the alarm.
The quality of this input is ignored if bad inputs are accepted.
•
By using the Process Alarm Acknowledge discrete input to the System Event block. This
acknowledges all process alarms.
•
By using the Global Acknowledge discrete input to the System Event block. This
acknowledges all diagnostic alarms, process alarms, and notification/request messages.
The System Event block handles global acknowledgement if the block or its loop are in
HOLD or OFF. Global acknowledgement will not occur if the block or its loop is in
DEBUG.
•
By setting the Suppress Alarm Calculation to YES.
•
By receiving an alarm acknowledge message into this block’s message handler from
some other device which causes a FALSE value to be written to the Unacknowledged
field of this block.
•
By writing the value FALSE to the Unacknowledged field of this block.
