6 process alarm block (pa) – Micromod MOD: 1800P - MOD 30ML Identity Module (Version 2) Algorithms, Tables and Sequential Logic Functions User Manual
Page 51
Logic Functions - Book 2
PROCESS ALARM BLOCK
8-43
8.6
PROCESS ALARM BLOCK (PA)
The process alarm block is used to initiate a discrete alarm signal to advise the operator of an
irregular process condition. The alarm is calculated by comparing an alarm source with a trip
value. The alarm source is usually a value in some other block that the operator wishes to
monitor. The type of comparison made is specified by the trip condition. Depending on the
result of the comparison, the alarm is considered active or clear (inactive). The user can
acknowledge the existence of an alarm by one of several methods. This block has two
discrete outputs that can be checked to see whether or not the alarm is active or
acknowledged. These outputs can be used to initiate logic in other blocks throughout the
database.
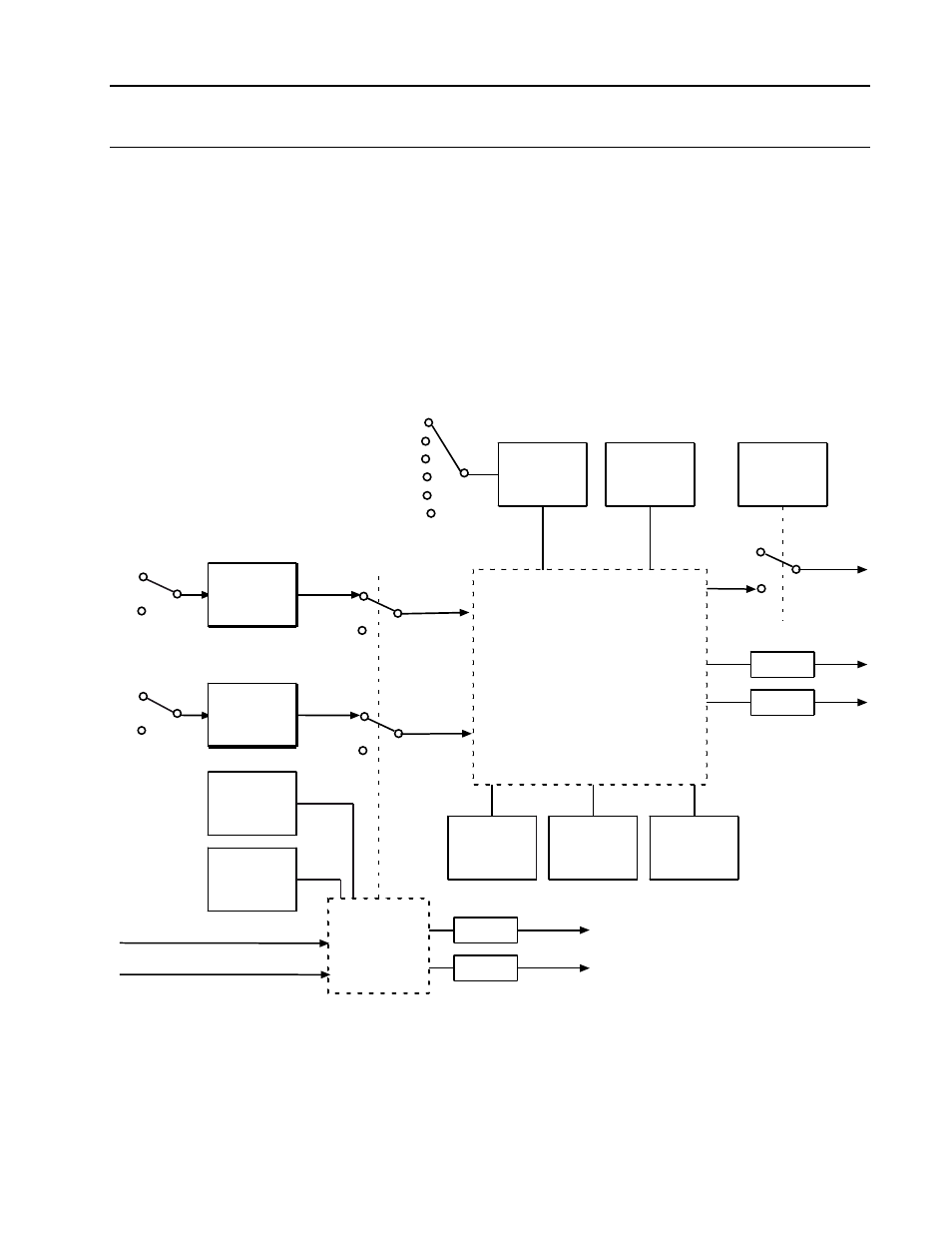
Available to the user as block outputs are the active alarm calculation status and the
unacknowledged status. A functional block diagram of the block is shown in Figure 8-22. The
process alarm block display, which is used to configure the block, is shown in Figure 8-23.
Alarm Input LSP Quality
Acknowledge Input LSP Quality
Bad Inputs
Accepted
(YES, NO)
YES
NONE
Value
Discrete
LSP
Alarm
Input
Process Alarm Calculation
(See example diagram)
Acknowledge
Input
Trip
Condition
State
(RUN, HOLD,
OFF, DEBUG)
Hysteresis
(Floating Point
Alarm)
* Data Type may be:
Count, Discrete, Short State,
Long State, Floating Point,
Msec Time, or Date
NO
Report
Events
LSP *
BAD
GOOD
BAD
GOOD
Trip Value *
Priority
(0 to 255)
Less
Less Equal
Greater
Greater Equal
Equal
Not Equal
Suppress
Calculation
(YES, NO)
Quality Check
AQ
UQ
U
A
Figure 8-22. Functional Block Diagram, Process Alarm Block
