4 managing openflow, Managing flow tables, Pipeline processing – H3C Technologies H3C Intelligent Management Center User Manual
Page 52
42
4 Managing OpenFlow
OpenFlow uses a flow-based forwarding method. SDNM manages the elements involved in the
OpenFlow forwarding process, including flow tables, flow entries, groups, meters, and service flows.
Managing flow tables
In an OpenFlow network, each packet is processed by the OpenFlow pipeline of every OpenFlow switch
that the packet passes through. Each OpenFlow instance maintains a set of flow tables, which are
uniquely identified by their table IDs. A flow table contains one or multiple flow entries for matching and
processing packets.
To better understand OpenFlow forwarding rules, view and query flow tables by using the flow
management module of SDNM.
Pipeline processing
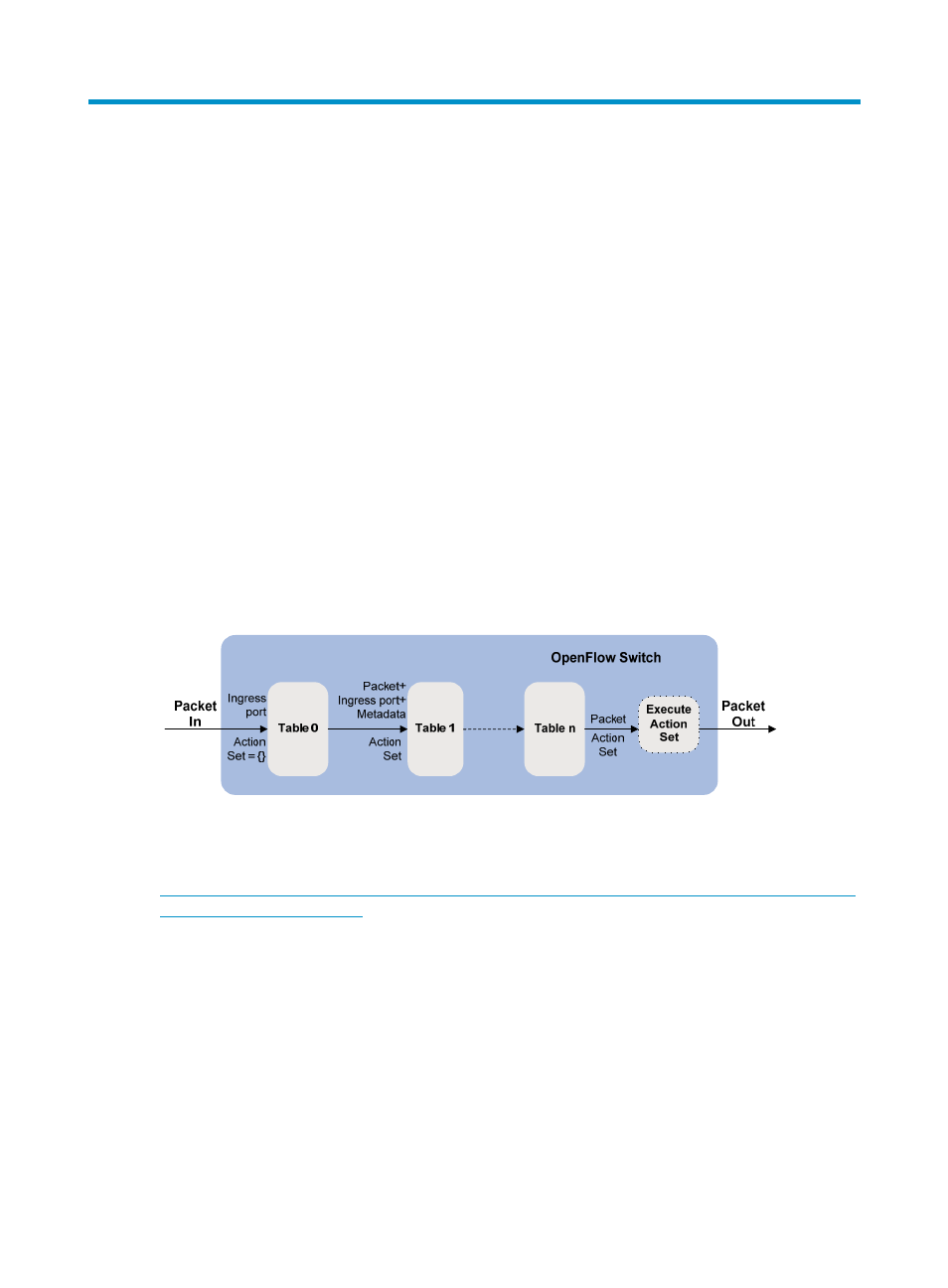
As shown in
, the pipeline of every OpenFlow switch can contain multiple flow tables. An
OpenFlow switch uses the flow entries in the flow tables to match and process received packets.
Figure 21 OpenFlow pipeline of an OpenFlow switch
For more information about the OpenFlow Switch diagram, referenced in
, see version 1.3.1 of
the Open Networking Foundation "OpenFlow Switch Specification" located at:
OpenFlow pipeline processing can only go forward. Flow tables in the OpenFlow switch are sequentially
numbered starting from 0. When a packet arrives at the switch, the pipeline starts packet matching at
table 0. The packet is first matched against the flow entries in table 0. Then the packet is forwarded to
another flow table based on the match result of table 0. A flow entry can only pass the packet to a flow
table whose ID is larger than its table ID.
The OpenFlow pipeline defines how each flow entry acts on a packet. If a packet does not match any
flow entry, a table miss happens. A table-miss flow entry defines how to process an unmatched packet.
The OpenFlow pipeline processes a packet by following these steps:
1.
Match the packet against the flow entries of a flow table in descending order of priority. The
higher the priority value, the higher the priority.
