Openflow network, Openflow instance – H3C Technologies H3C Intelligent Management Center User Manual
Page 12
2
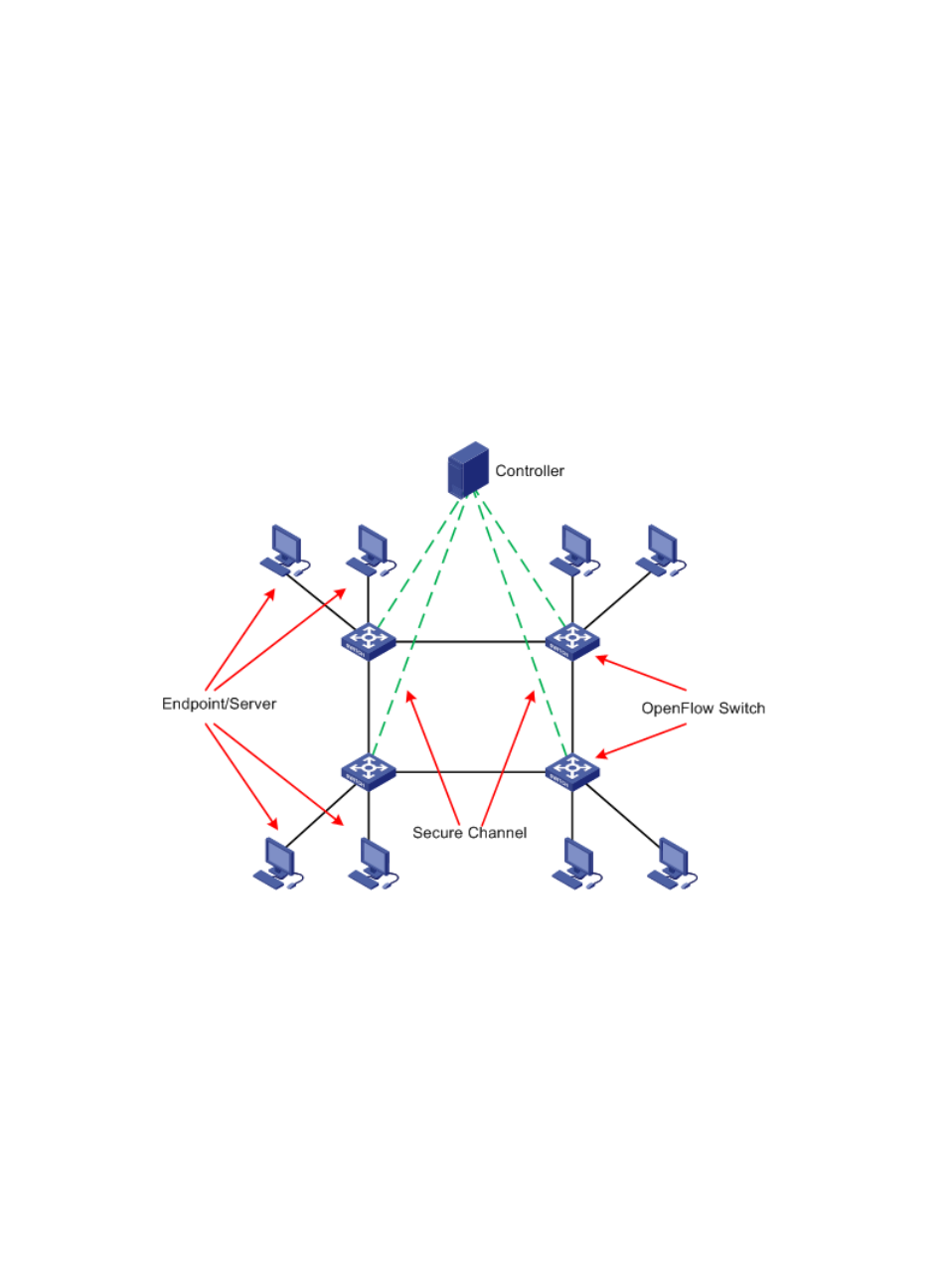
OpenFlow network
In an OpenFlow network, as shown in
, the controller directly controls the packet forwarding for
OpenFlow switches. The control packets (defined by the OpenFlow protocol) between OpenFlow
switches and controller are transmitted through a secure channel.
The controller provides centralized control on the data plane of OpenFlow switches through the
OpenFlow protocol.
An OpenFlow switch can communicate with multiple controllers. The OpenFlow channel between the
OpenFlow switch and each controller can have only one main connection.
An OpenFlow switch communicates with the controller through a secure channel and the connection must
use TCP or SSL.
An OpenFlow switch forwards packets between endpoints and servers according forwarding rules
deployed by the controller.
Figure 1 OpenFlow Network
OpenFlow instance
For OpenFlow switches that support multiple OpenFlow instances, each OpenFlow instance is
considered as a separate logical OpenFlow switch and is identified by a unique DataPath ID (DPID).
For OpenFlow switches that does not support multiple OpenFlow instances, such as vSwitches, the
OpenFlow switch itself is considered as an OpenFlow instance and is identified by a unique DPID.
A DPID is 64 bits in length. By default, the lower 48-bits are for the MAC address of the network bridge
of the device to which the OpenFlow instance belongs, and the upper 16-bits are vendor-defined.
