Protocols and standards – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 365
13-14
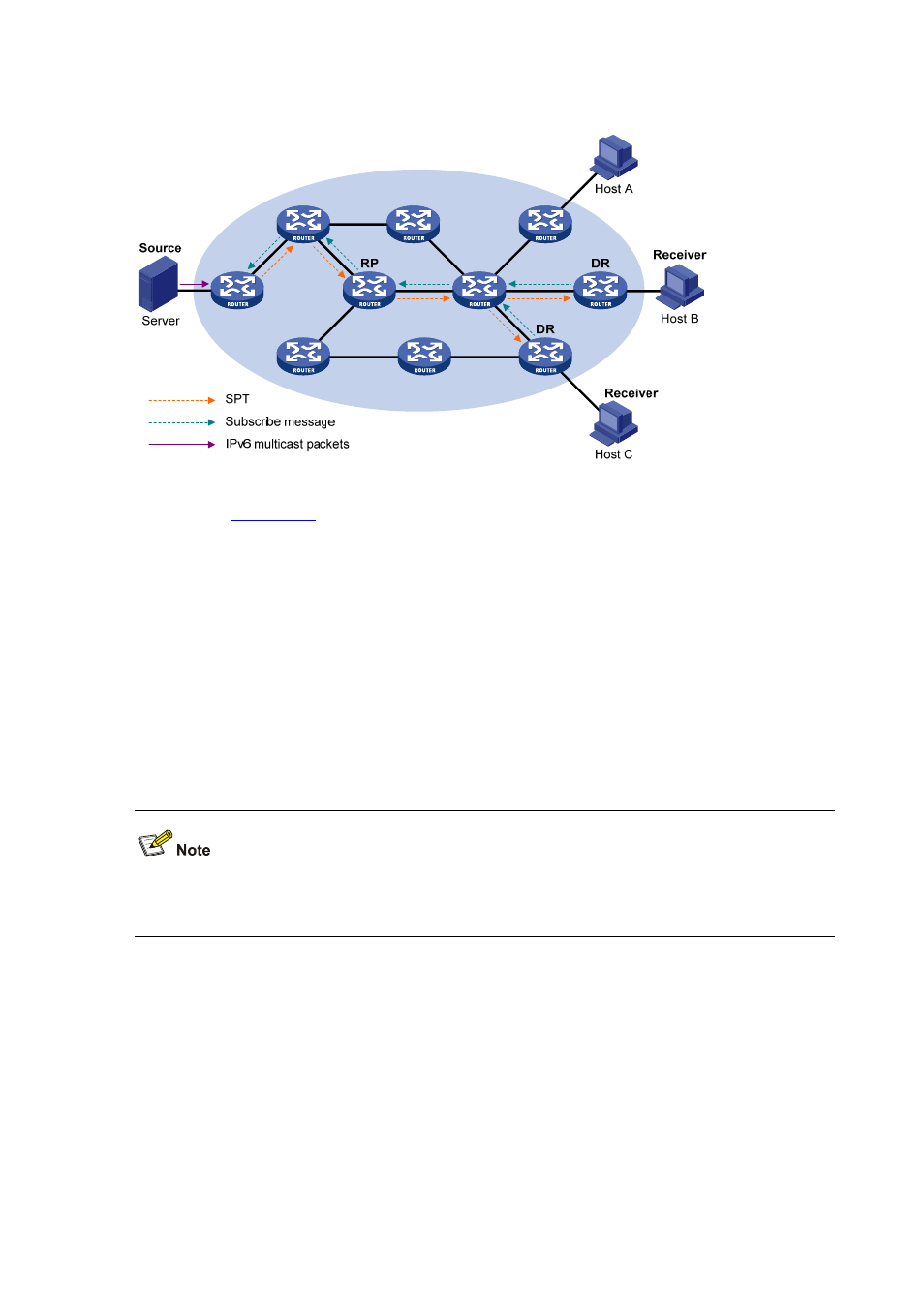
Figure 13-7 Building an SPT in IPv6 PIM-SSM
As shown in
, Hosts B and C are IPv6 multicast information receivers. They send an
MLDv2 report message to the respective DRs to announce that they are interested in the
information of the specific IPv6 multicast source S and that sent to the IPv6 multicast group G.
The DR that has received the report first checks whether the IPv6 group address in this
message falls in the IPv6 SSM group range:
z
If so, the IPv6 PIM-SSM model is built: the DR sends a channel subscription message hop
by hop toward the IPv6 multicast source S. An (S, G) entry is created on all routers on the
path from the DR to the source. Thus, an SPT is built in the network, with the source S as
its root and receivers as its leaves. This SPT is the transmission channel in IPv6 PIM-SSM.
z
If not, the IPv6 PIM-SM process is followed: the DR needs to send a (*, G) join message to
the RP, and an IPv6 multicast source registration process is needed.
In IPv6 PIM-SSM, the “channel” concept is used to refer to an IPv6 multicast group, and the
“channel subscription” concept is used to refer to a join message.
Protocols and Standards
IPv6 PIM–related specifications are as follows:
z
RFC 4601: Protocol Independent Multicast-Sparse Mode (PIM-SM): Protocol Specification
(Revised)
z
RFC 3973: Protocol Independent Multicast-Dense Mode(PIM-DM):Protocol
Specification(Revised)
z
RFC 3956: Embedding the Rendezvous Point (RP) Address in an IPv6 Multicast Address
z
RFC 4607: Source-Specific Multicast for IP
