H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 263
9-7
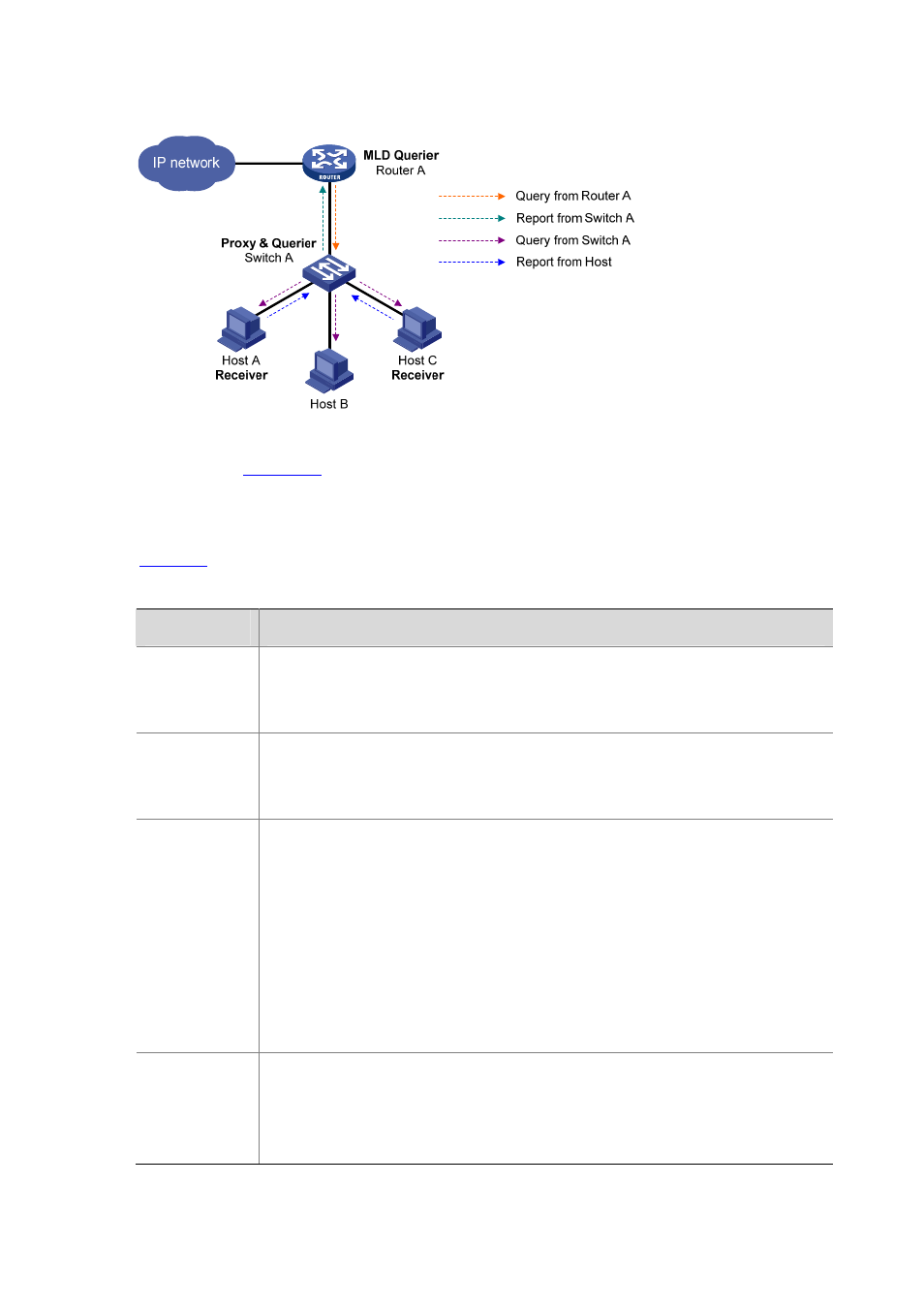
Figure 9-3 Network diagram for MLD snooping proxying
As shown in
, Switch A works as an MLD Snooping proxy. As a host from the
perspective of the querier Router A, Switch A represents its attached hosts to send their
membership reports and done messages to Router A.
describes how an MLD Snooping proxy processes MLD messages.
Table 9-2 MLD message processing on an MLD snooping proxy
MLD message
Actions
General query
When receiving an MLD general query, the proxy forwards it to all ports but the
receiving port. In addition, the proxy generates a report according to the group
memberships it maintains and sends the report out all router ports.
Multicast-addre
ss-specific
query
In response to the MLD group-specific query for a certain IPv6 multicast group, the
proxy sends the report to the group out all router ports if the forwarding entry for the
group still contains a member port.
Report
When receiving a report for an IPv6 multicast group, the proxy looks up the multicast
forwarding table for the entry for the multicast group. If the forwarding entry is found
with the receiving port contained as a dynamic port in the outgoing port list, the
proxy resets the aging timer for the entry. If the forwarding entry is found but the
outgoing port list does not include the receiving port, the proxy adds the port to the
outgoing port list as a dynamic member port and starts an aging timer for it. If no
forwarding entry is found, the proxy creates the entry, adds the receiving port to the
outgoing port list as a dynamic member port and starts an aging timer for the port,
and then, sends a report to the group out all router ports.
Done
In response to a done message for an IPv6 multicast group, the proxy sends a
multicast-address-specific query for the group out the receiving port. After making
sure that no member port is contained in the forwarding entry for the IPv6 multicast
group, the proxy sends a done message for the group out all router ports.
