Joining an ipv6 multicast group – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 323
12-3
Joining an IPv6 multicast group
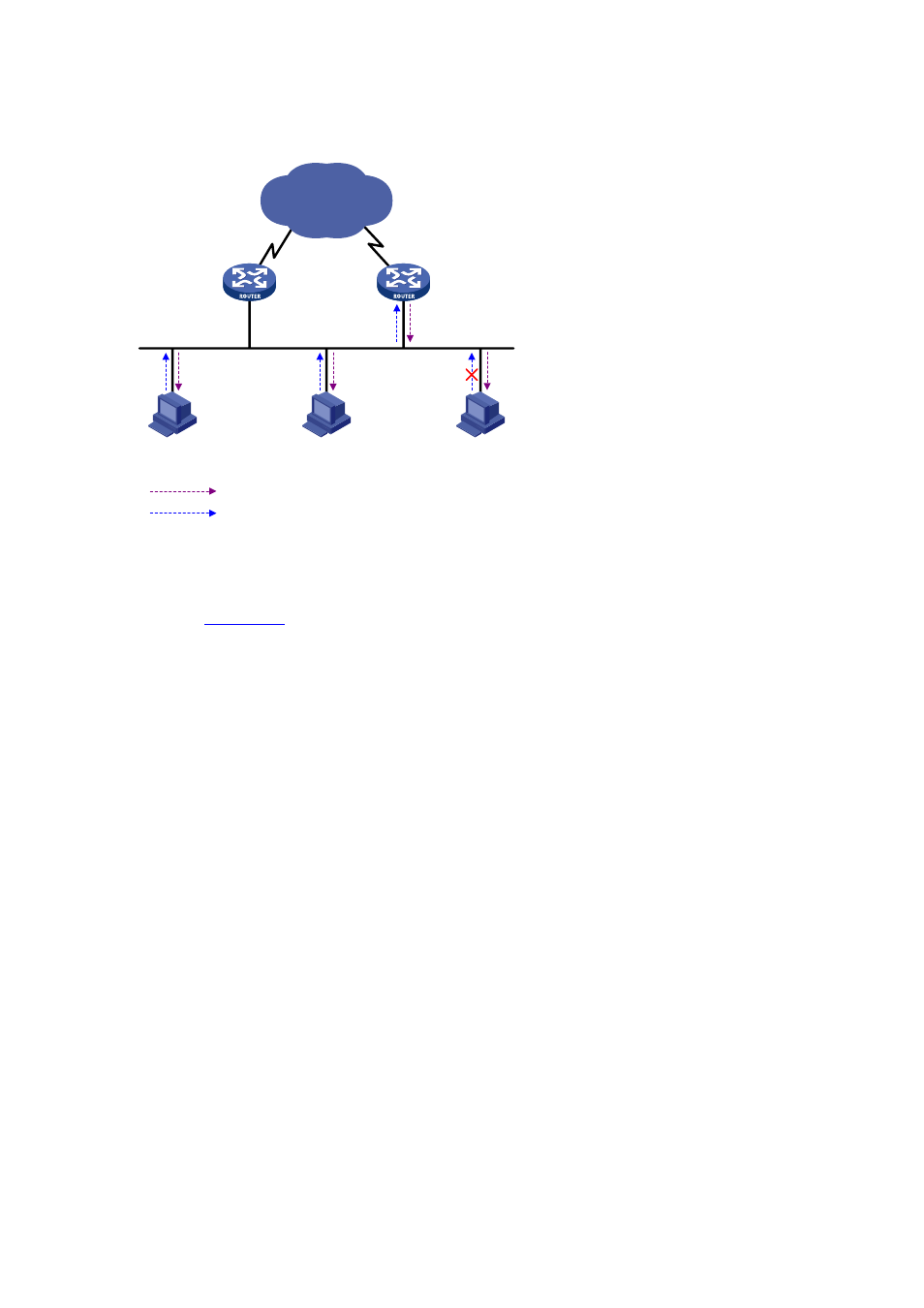
Figure 12-1 MLD queries and reports
Query
Report
Querier
Host A
(G2)
Host B
(G1)
Host C
(G1)
Ethernet
Router A
Router B
IPv6 network
Assume that Host B and Host C are expected to receive IPv6 multicast data addressed to IPv6
multicast group G1, while Host A is expected to receive IPv6 multicast data addressed to G2, as
shown in
. The following describes how the hosts join the IPv6 multicast groups and the
MLD querier (Router B in the figure) maintains the IPv6 multicast group memberships:
1) The hosts send unsolicited MLD reports to the addresses of the IPv6 multicast groups that they
want to join, without having to wait for the MLD queries from the MLD querier.
2) The MLD querier periodically multicasts MLD queries (with the destination address of FF02::1) to
all hosts and routers on the local subnet.
3) Upon receiving a query message, Host B or Host C (the delay timer of whichever expires first)
sends an MLD report to the IPv6 multicast group address of G1, to announce its membership for
G1. Assume it is Host B that sends the report message. Upon hearing the report from Host B,
Host C, which is on the same subnet with Host B, suppresses its own report for G1, because the
MLD routers (Router A and Router B) already know that at least one host on the local subnet is
interested in G1. This mechanism, known as MLD report suppression, helps reduce traffic on the
local subnet.
4) At the same time, because Host A is interested in G2, it sends a report to the IPv6 multicast group
address of G2.
5) Through the above-mentioned query/report process, the MLD routers learn that members of G1
and G2 are attached to the local subnet, and the IPv6 multicast routing protocol (IPv6 PIM for
example) running on the routers generates (*, G1) and (*, G2) multicast forwarding entries, which
will be the basis for subsequent IPv6 multicast forwarding, where * represents any IPv6 multicast
source.
6) When the IPv6 multicast data addressed to G1 or G2 reaches an MLD router, because the (*, G1)
and (*, G2) multicast forwarding entries exist on the MLD router, the router forwards the IPv6
multicast data to the local subnet, and then the receivers on the subnet receive the data.
