H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 362
13-11
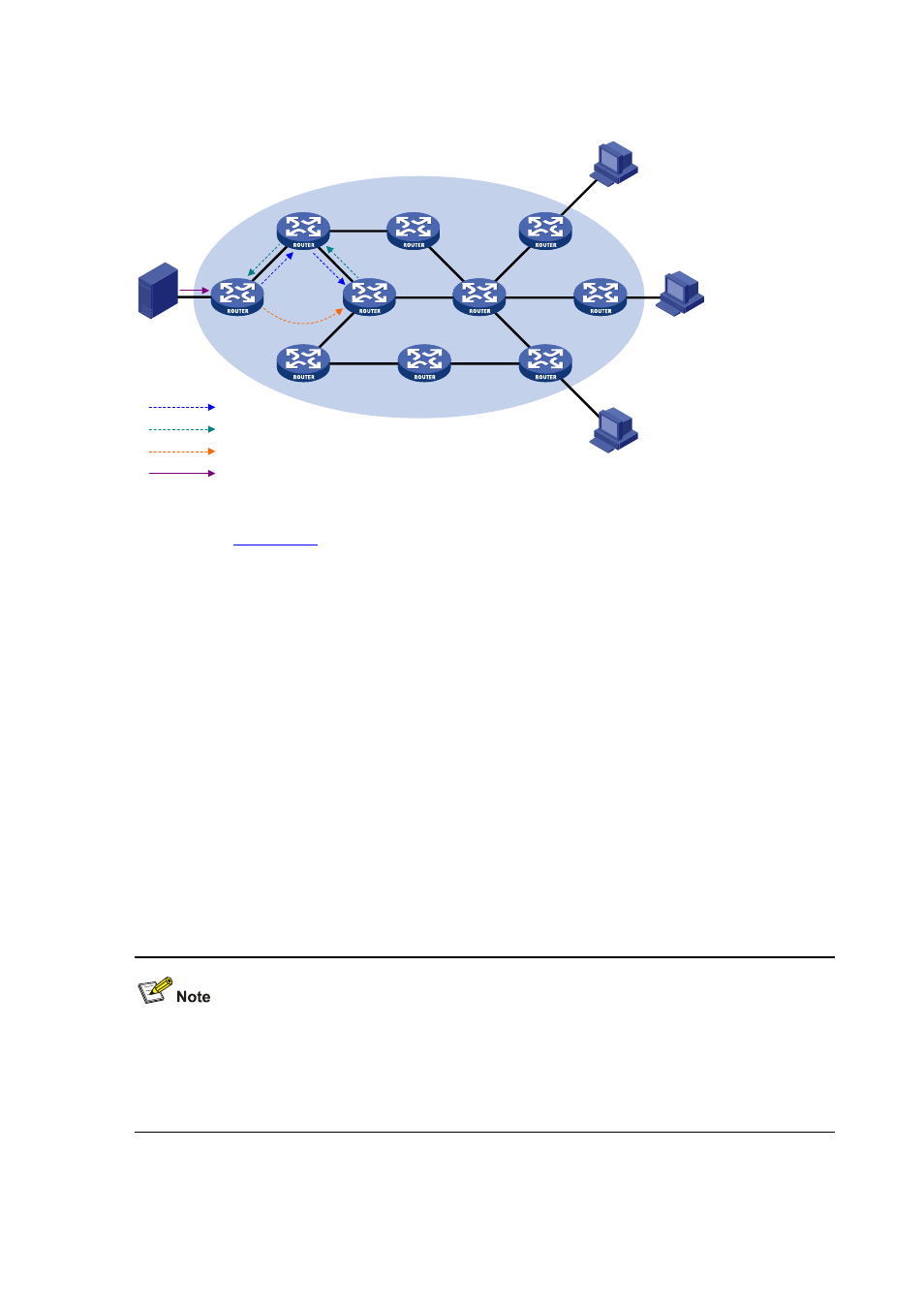
Figure 13-6 IPv6 multicast source registration
Source
Server
Host A
Host B
Host C
Receiver
Receiver
IPv6 multicast packets
SPT
Join message
Register message
RP
DR
As shown in
, the IPv6 multicast source registers with the RP as follows:
1) When the IPv6 multicast source S sends the first IPv6 multicast packet to IPv6 multicast
group G, the DR directly connected with the multicast source, upon receiving the multicast
packet, encapsulates the packet in a register message, and sends the message to the
corresponding RP by unicast.
2) When the RP receives the register message, it extracts the multicast packet from the
register message and forwards the multicast IPv6 multicast packet down the RPT, and
sends an (S, G) join message hop by hop toward the IPv6 multicast source. Thus, the
routers along the path from the RP to the IPv6 multicast source form an SPT branch. Each
router on this branch generates an (S, G) entry in its forwarding table. The DR at the IPv6
multicast source side is the root, while the RP is the leaf, of the SPT.
3) The subsequent IPv6 multicast data from the IPv6 multicast source travels along the
established SPT to the RP, and then the RP forwards the data along the RPT to the
receivers. When the IPv6 multicast traffic arrives at the RP along the SPT, the RP sends a
register-stop message to the source-side DR by unicast to stop the source registration
process.
The RP is configured to initiate an SPT switchover as described in this section. Otherwise, the
DR at the IPv6 multicast source side keeps encapsulating multicast data in register messages
and the registration process will not stop unless no outgoing interfaces exist in the (S, G) entry
on the RP.
