Before you start the fun, Installation of batteries, Remember – Elenco 130-in-1 Electronics Playground User Manual
Page 4
-157-
Electric Field
The region of electric attraction
or repulsion around a constant
voltage. This is usually
associated with the dielectric in
a capacitor.
Electricity
A flow of electrons between
atoms due to an electrical
charge across the material.
Electrolytic Capacitor
A type of capacitor that has high
capacitance and is used mostly
in low frequency circuits. It has
polarity markings.
Electron
A sub-atomic particle that has
an electrical charge.
Electronics
The science of electricity and its
applications.
Emitter
The output of an NPN bipolar
junction transistor.
Encode
To put a message into a format
which is easier to transmit.
Farad, (F)
The unit of measure for
capacitance.
Feedback
To adjust the input to something
based on what its output is
doing.
Flip-Flop
A type of transistor
configuration is which the output
changes every time it receives
an input pulse.
FM
Frequency modulation. The
frequency of the radio signal is
varied depending on the
information being sent.
Forward-Biased
The state of a diode when
current is flowing through it.
Frequency
The rate at which something
repeats.
Generator
A device which uses steam or
water pressure to move a
magnet near a wire, creating an
electric current in the wire.
Germanium
A chemical element that is used
as a semiconductor.
Ground
A common term for the 0V or “–
” side of a battery or generator.
Henry (H)
The unit of measure for
Inductance.
Inductance
The ability of a wire to create an
induced voltage when the
current varies, due to magnetic
effects.
Inductor
A component that opposes
changes in electrical current.
Integrated Circuit
A type of circuit in which
transistors, diodes, resistors,
and capacitors are all
constructed on
a
semiconductor base.
Kilo- (K)
A prefix used in the metric
system. It means a thousand of
something.
Light Emitting Diode
A diode made from gallium
(LED)
arsenide that has a turn-on
energy so high that light is
generated when current flows
through it.
Magnetic Field
The region of magnetic
attraction or repulsion around a
magnet or an AC current. This is
usually associated with an
inductor or transformer.
Magnetism
A force of attraction between
certain metals. Electric currents
also have magnetic properties.
Meg- (M)
A prefix used in the metric
system. It means a million of
something.
Micro- (
μ)
A prefix used in the metric
system. It means a millionth
(0.000,001) of something.
Microphone
A device which converts sound
waves into electrical energy.
Milli- (m)
A prefix used in the metric
system. It means a thousandth
(0.001) of something.
Modulation
Methods used for encoding
radio signals with information.
Morse Code
A code used to send messages
with long or short transmit
bursts.
NAND Gate
A type of digital circuit which
gives a HIGH output if some of
its inputs are LOW.
NPN
Negative-Positive-Negative, a
type of transistor construction.
Welcome to the thrilling world of electronics! Now that
you have your Elenco
®
EP-130 Electronic Playground
Kit, you can learn about electronics while doing 130
fun experiments. In this kit we have included
everything you will need to start off on this electronics
adventure, well except the batteries that is
☺.
As you go through this manual and do the
experiments, you will notice that we have arranged
the experiments, as well as information, into a logical
progression. We will start off with easy circuits and
then work toward the more intricate ones. Take your
time and be sure to have some fun!
Each electronic component in the kit is connected to
springs, so you can do all the circuit assembly without
having to solder. To build a working project, all you
have to do is connect the wires to the terminals as
shown in each wiring sequence. There is no danger
when doing these projects because you are using low
voltage batteries, not the standard AC voltages.
Our simple instructions will show you how to operate
the circuit for each experiment. A
schematic diagram
is also included, to help you learn how the circuit
works. A
schematic is simply a blueprint that shows
how different parts are wired together. An image or
symbols for each of the components in your kit are
printed next to each piece.
As you will notice we refer to a
Volt / Ohm Meter
(VOM) for making measurements. A VOM or
multimeter is a instrument that measures voltage,
current (amperes or amps), and resistance (ohms-
Ω).
You will learn more about these in the upcoming
pages. If you really want to learn about electronic
circuits, it is vital that that you learn how to measure
circuit values - for only then will you really understand
electronic circuitry.
You do not have to have or use a VOM to do the
experiments but you will find that it helps to better
grasp how the circuits work. The VOM is a good
investment if you plan to stay interested in electricity
and electronics.
-4-
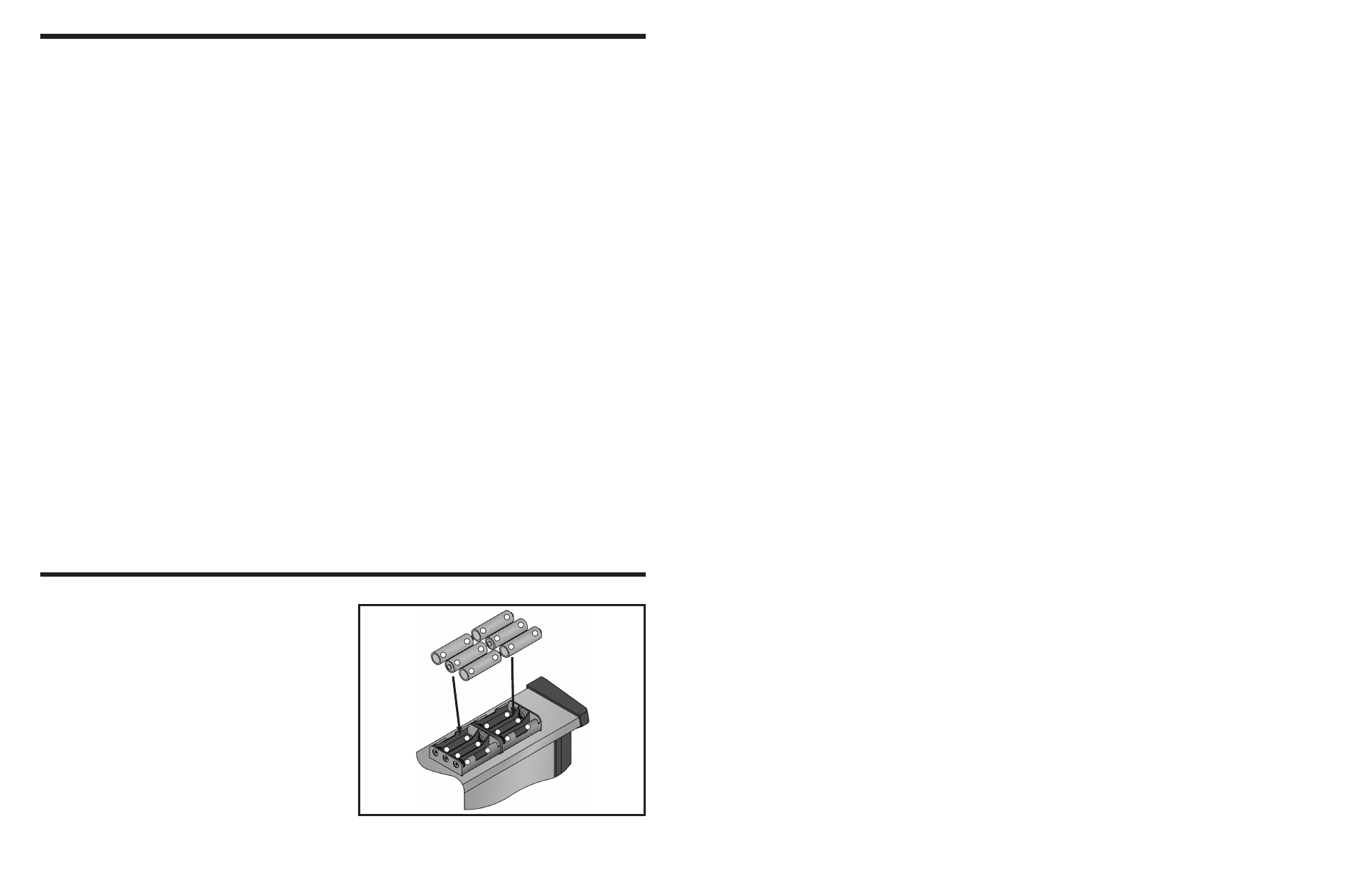
BEFORE YOU START THE FUN!
This kit requires six (6) “AA” batteries. To install the
batteries to the back of your kit make sure to install
them in the corresponding compartments. Put the +
end and the – end correctly into the kit, the + end for
the battery is the side that has the metal cap.
Remember:
Never leave a dying battery or dead
battery in your kit. Even if they are “leak-proof”, they
still have the potential to leak damaging chemicals.
INSTALLATION OF BATTERIES
+
–
–
+
–
+
+
–
–
+
–
+
+
–
–
+
–
+
+
–
–
+
–
+
