Elenco 130-in-1 Electronics Playground User Manual
Page 151
-151-
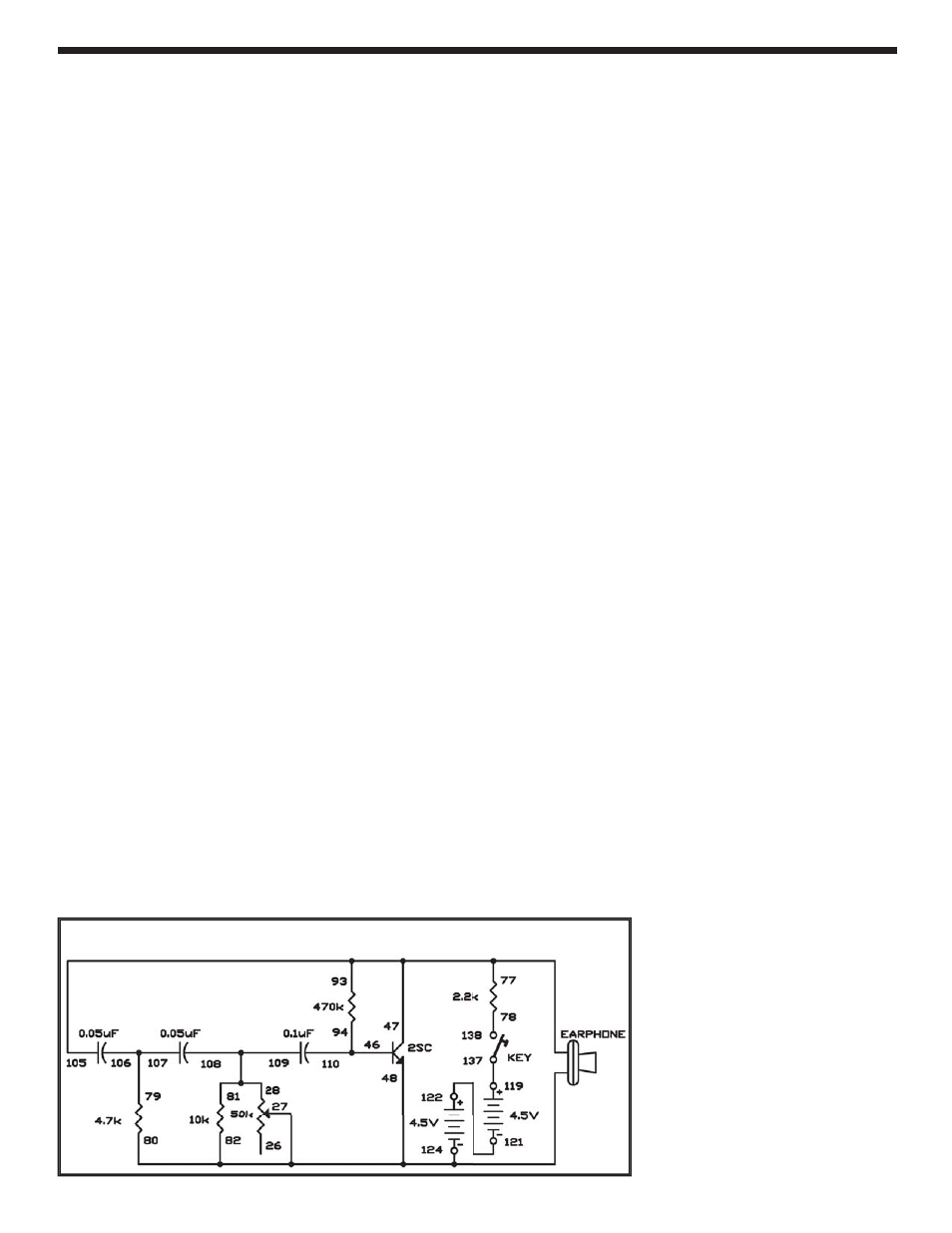
In this experiment, you build and study a low-distortion
sine wave oscillator. Build this experiment after you
have built and studied the previous experiment
because this one has no transformer; transformers
are likely to cause distortion because of their non-
linear characteristics.
As in the previous experiment, you should listen to the
tone of this oscillator and modify the control for the
clearest-sounding single tone (the one with the least
distortion). Again, start with the control near
maximum. The operating frequency is about 300Hz at
the minimum distortion setting of the control.
We call this circuit an RC phase shift oscillator, and it
is considered a basic sine wave oscillator. The positive
feedback of the signal causes oscillations to occur.
The resistors (R) and capacitors (C) make up the path
for the signal to the transistor base. Every time the
signals pass the RC circuits, a slight time lag occurs.
In other words, the rise and fall of the wave (the
phase) shifts slightly. That’s why we call it phase shift.
After the signal has traveled through the circuit, the
phase shifts 180 degrees. When the collector voltage
rises, this rise is fed back to the collector with the
phase shifted. When the base voltage rises, the
collector voltage falls. This repeating cycle causes the
transistor to oscillate.
The frequency changes when you change the control
setting, because the degrees of phase shift changes.
The tonal quality also changes. Set the control to the
point where you can hear the purest tone; at this point
a clear sine wave is generated.
Notes:
EXPERIMENT #129: SINE WAVE OSCILLATOR WITH LOW DISTORTION
Wiring Sequence:
124-27-48-82-80-EARPHONE
47-105-93-77-EARPHONE
81-109-108-28
94-110-46
78-138
79-106-107
119-137
121-122
Schematic
