7 configuring rstp/stp, 1 overview, 2 references – CANOGA PERKINS 9175 Configuration Guide User Manual
Page 37: 3 topology
CanogaOS Configuration Guide
7-1
7 Configuring RSTP/STP
7.1 Overview
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP, IEEE 802.1D-1998) is a Layer 2 link-management
protocol that provides path redundancy while preventing undesirable loops in the
network. For a Layer 2 Ethernet network to function properly, only one active path can
exist between any two stations. STP operation is transparent to end stations, which
cannot detect whether they are connected to a single LAN segment or a switched LAN of
multiple segments.
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP, IEEE 802.1w) can be seen as an evolution of the
802.1D standard more than a revolution. The 802.1D terminology remains primarily the
same. Most parameters have been left unchanged so users familiar with 802.1D can
rapidly configure the new protocol comfortably. RSTP was developed to decrease the
recovery time of redundant paths in Layer 2 networks as compared to the IEEE 802.1d
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) while continuing to reduce the impact of accidental
network loops. RSTP can reduce the spanning tree convergence time to 5 seconds or
less to establish a network path and reduce network downtime.
7.2 References
IEEE 802.1D (2004)
RFC 4318
RFC 4188 Bridge MIB
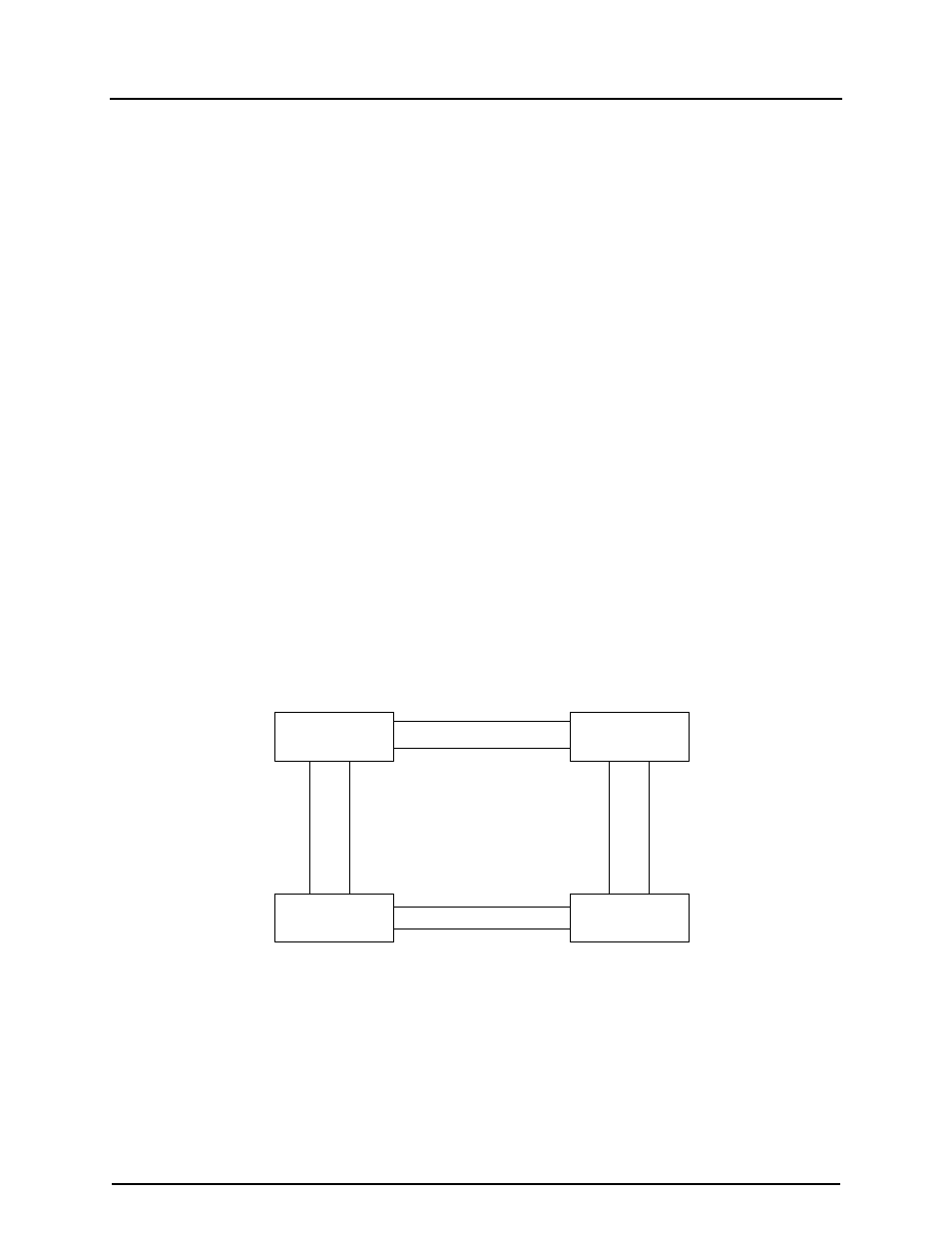
7.3 Topology
Bridge 2
Bridge 3
Bridge 4
Bridge 1
eth-0-3
eth-0-3
eth-0-4
eth-0-4
eth-0-3
eth-0-3
eth-0-3
eth-0-4
eth-0-1
eth-0-2
eth-0-1
eth-0-1
eth-0-2
eth-0-2
eth-0-1
eth-0-2
8192
12288
16384
32768
Figure 7-1: RSTP/STP Topology
Note: This configuration sample assumes that you are running the Layer-2 module. If
you are using the Layer-2 module, run the switchport command on each port to set the
switching characteristics of Layer-2 protocols.
