10 ospf authentication – CANOGA PERKINS 9175 Configuration Guide User Manual
Page 109
CanogaOS Configuration Guide
17-10
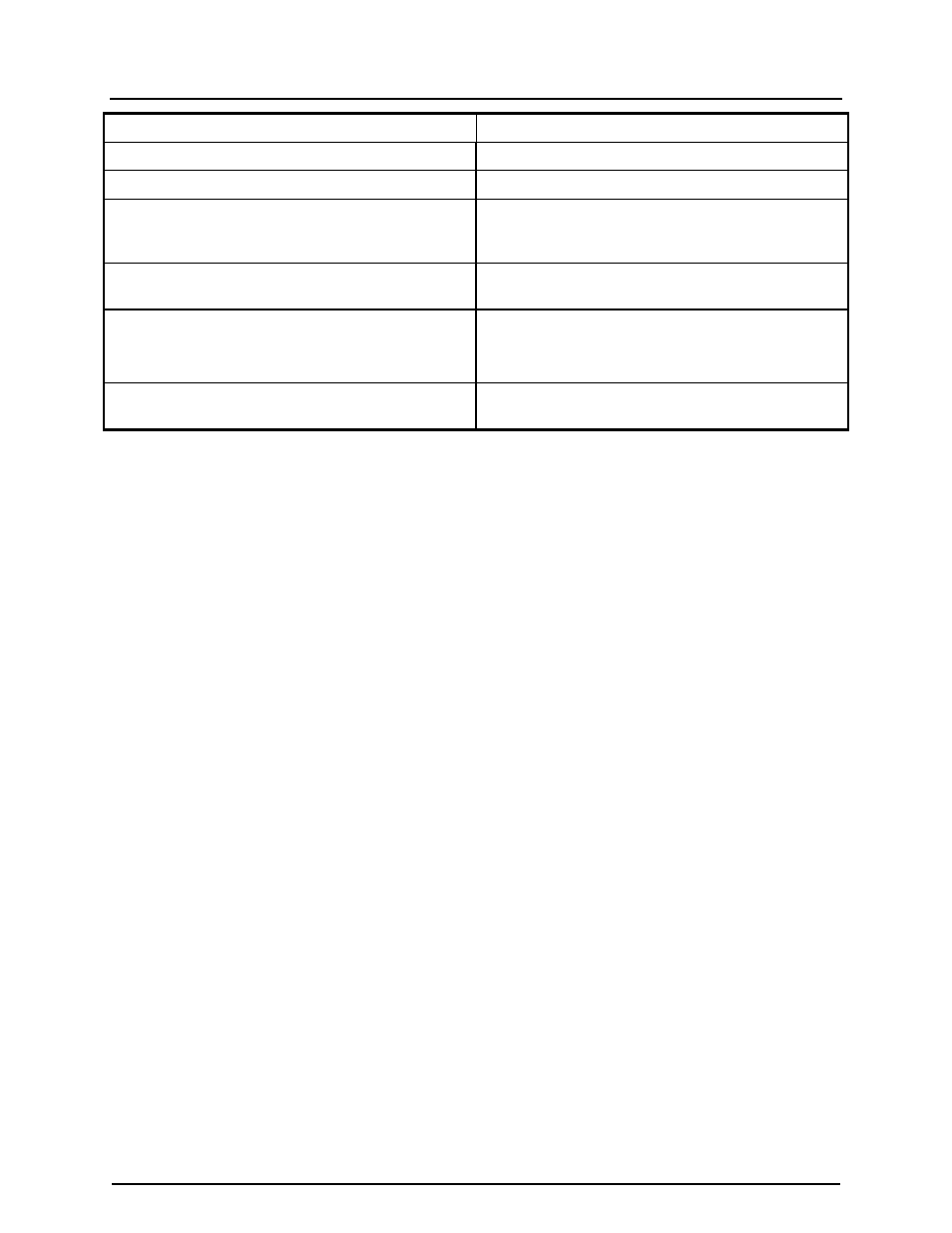
DUT(config)# interface loopback 20
Specify loopback as the interface you want to configure
DUT(config-if)# ip address 192.168.2.63/32
Configure the IP address on this interface.
DUT(config-if)# exit
Exit the Interface mode and return to Configure mode.
DUT(config)# router ospf 100
Configure the Routing process and specify the Process
ID (100). The Process ID should be a unique positive
integer identifying the routing process.
DUT(config-router)# router-id 192.168.2.63
Configure OSPF Router ID (192.168.1.63) for this
router.
DUT(config-router)# network 10.10.23.0/24 area 1
DUT(config-router)# network 10.10.24.0/24 area 2
DUT(config-router)# network 192.168.2.63/32 area 2
Define interfaces on which OSPF runs and associate the
area IDs (1 and 2) with the interface.
DUT(config-router)# area 1 virtual-link 192.168.1.62
Configure a virtual link between this router R2 and
R1(Router ID 192.168.2.62) through transit area 1.
Validation Commands
show ip ospf virtual link, show ip ospf neighbor, show ip ospf, show ip ospf route
17.10 OSPF Authentication
In our implementation there are three types of OSPF authentications--Null authentication
(Type 0), Simple Text (Type 1) authentication and MD5 (Type 2) authentication. With null
authentication, routing exchanges over the network are not authenticated. In Simple Text
authentication, the authentication type is the same for all routers that communicate using
OSPF in a network. For MD5 authentication, you configure a key and a key-id on each
router. The router generates a message digest on the basis of the key, key ID and the
OSPF packet and adds it to the OSPF packet.
The Authentication type can be configured on a per-interface basis or a per-area basis.
Additionally, Interface and Area authentication can be used together. Area authentication
is used for an area and interface authentication is used for a specific interface in the area.
If the Interface authentication type is different from Area authentication type, Interface
authentication type overrides the Area authentication type. If the Authentication type is
not specified for an interface, the Authentication type for the area is used. The
authentication command descriptions contain details of each type of authentication.
Refer to the OSPF Command Reference for OSPF authentication commands.
In the example below, R1 and R2 are configured for both the interface and area
authentications. The authentication type of interface eth1 on R1 and interface eth0 on R2
is md5 mode and is defined by the area authentication command; however, the
authentication type of interface eth2 on R1 and interface eth1 on R2 is plain text mode
and is defined by the ip ospf authentication command. This interface command overrides
the area authentication command.
Topology
