3 configuring lacp, 1 overview, 2 topology – CANOGA PERKINS 9175 Configuration Guide User Manual
Page 21: 3 configurations
CanogaOS Configuration Guide
3-1
3 Configuring LACP
3.1 Overview
This chapter contains a complete sample Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
configuration. LACP is based on the 802.3ad IEEE specification. It allows bundling of
several physical interfaces to form a single logical channel providing enhanced
performance and redundancy. The aggregated interface is viewed as a single link to
each switch. The spanning tree views it as one interface and not as 2 or 3 interfaces.
When there is a failure in one physical interface, the other interfaces stay up and there is
no disruption. This implementation supports the aggregation of maximum 8 physical
Ethernet links into a single logical channel. LACP enables our device to manage link
aggregation group between other devices that conform to the 802.3ad protocol. By using
the LACP, the switch learns the identity of partners supporting LACP and the
capabilities of each port. It then dynamically groups ports with same properties into a
single logical bundle link.
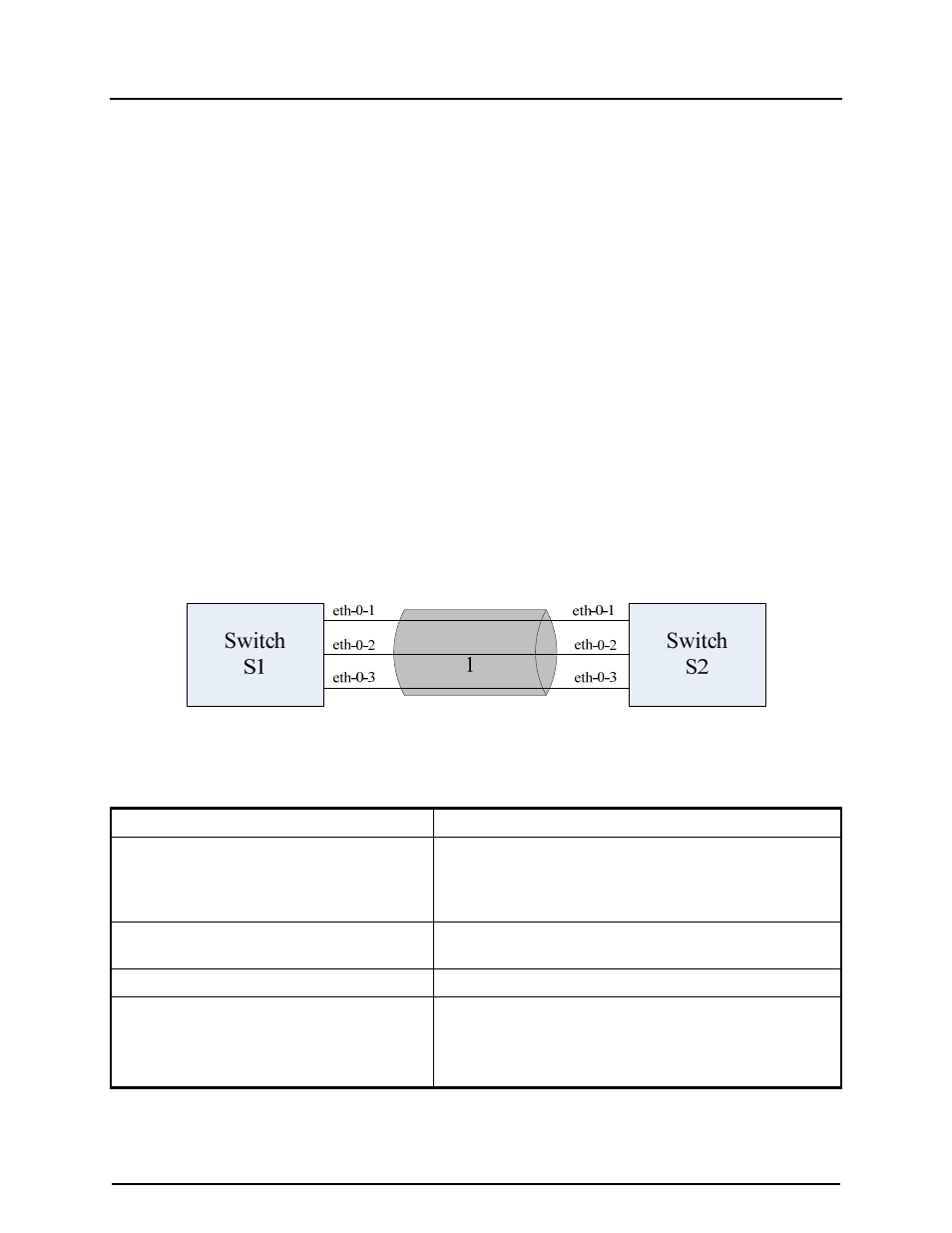
3.2 Topology
In this example, 3 links are configured between the two switches S1 and S2. These three
links are assigned the same administrative key (1) so that they aggregate to form a
single channel 1. They are viewed by the STP as one interface.
Figure 3-1: LACP
3.3 Configurations
Switch S1
DUT1#configure terminal
Enter the Configure mode.
DUT1(config)#lacp system-priority 2000
Set the system priority of this switch. This priority is used for
determining the system that is responsible for resolving
conflicts in the choice of aggregation groups. A lower
numerical value has a higher priority.
DUT1(config)#interface eth-0-1
Specify the interface (eth-0-1) to be configured and enter the
Interface mode.
DUT1(config-if)#no shutdown
Enable the interface.
DUT1(config-if)# channel-group 1 mode active
Add this interface to channel group 1 and enable link
aggregation so that it can be selected for aggregation by the
local system.
