Linear network introduction – Rockwell Automation 284E ArmorStart with EtherNet/IP - User Manual User Manual
Page 61
Rockwell Automation Publication 280E-UM001B-EN-P - July 2012
61
Introduction to EtherNet/IP and Device Level Ring Technology Chapter 3
Linear Network Introduction
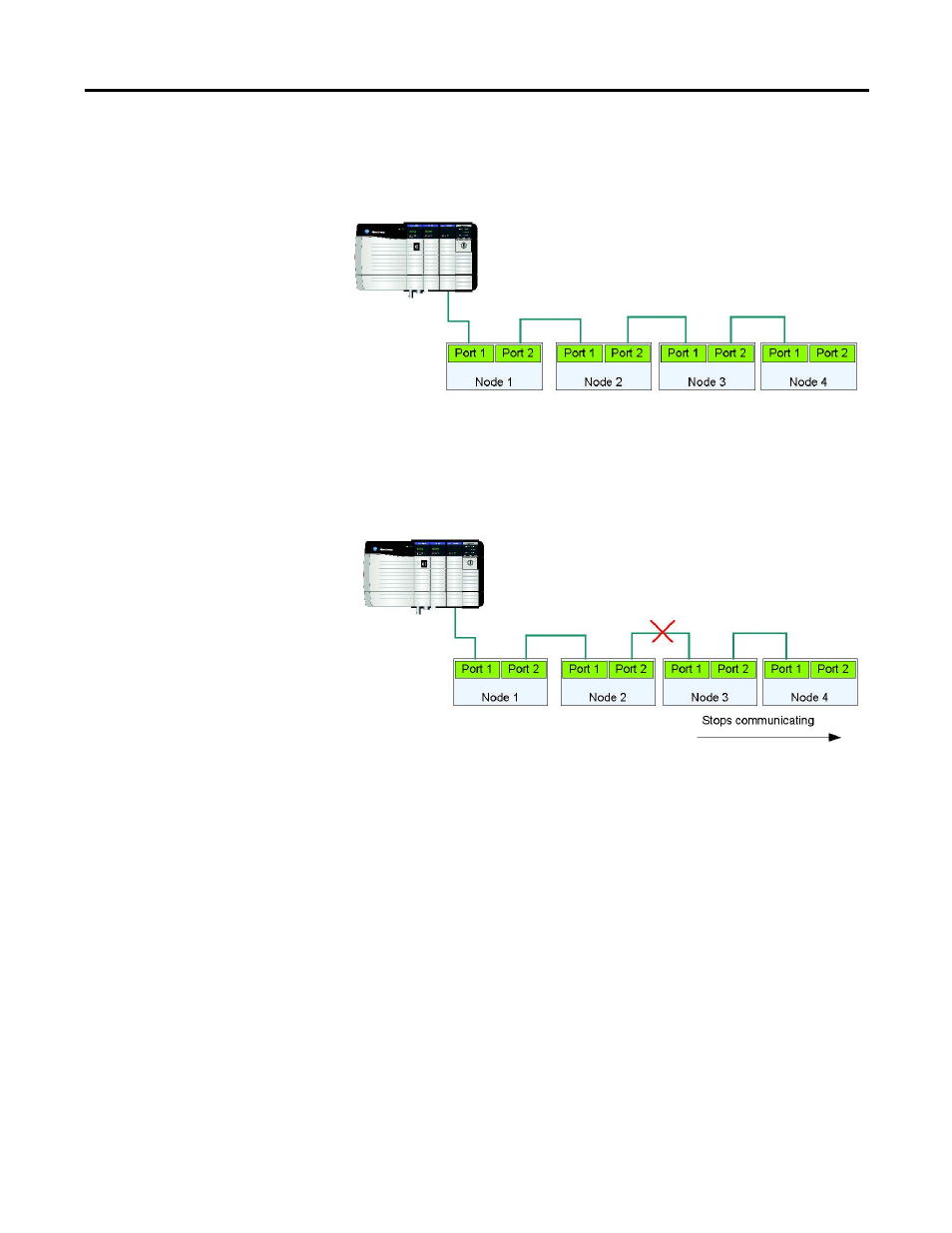
A linear network is a collection of devices that are daisy-chained together.
Figure 42 - Linear Network Collection of Devices
In this topology a communication issue in the media or device will prevent nodes
downstream from communicating.
Figure 43 - Communication Issue in the Media or Device Line
The EtherNet/IP embedded switch technology allows this topology to be
implemented at the device level. No additional switches are required.
These are the primary advantages of a linear network:
• The network simplifies installation and reduces wiring and installation
costs.
• The network requires no special software configuration.
• Embedded switch products offer improved CIP Sync application
performance on linear networks.
The primary disadvantage of a linear network is that any break of the cable
disconnects all devices downstream from the break from the rest of the network.
