Figure 18 – Rockwell Automation 20-COMM-ER 20-COMM-ER Dual-Port EtherNet/IP Communication Adapter User Manual User Manual
Page 76
76
Rockwell Automation Publication 20COMM-UM015B-EN-P - July 2013
Chapter 4 Configuring the I/O
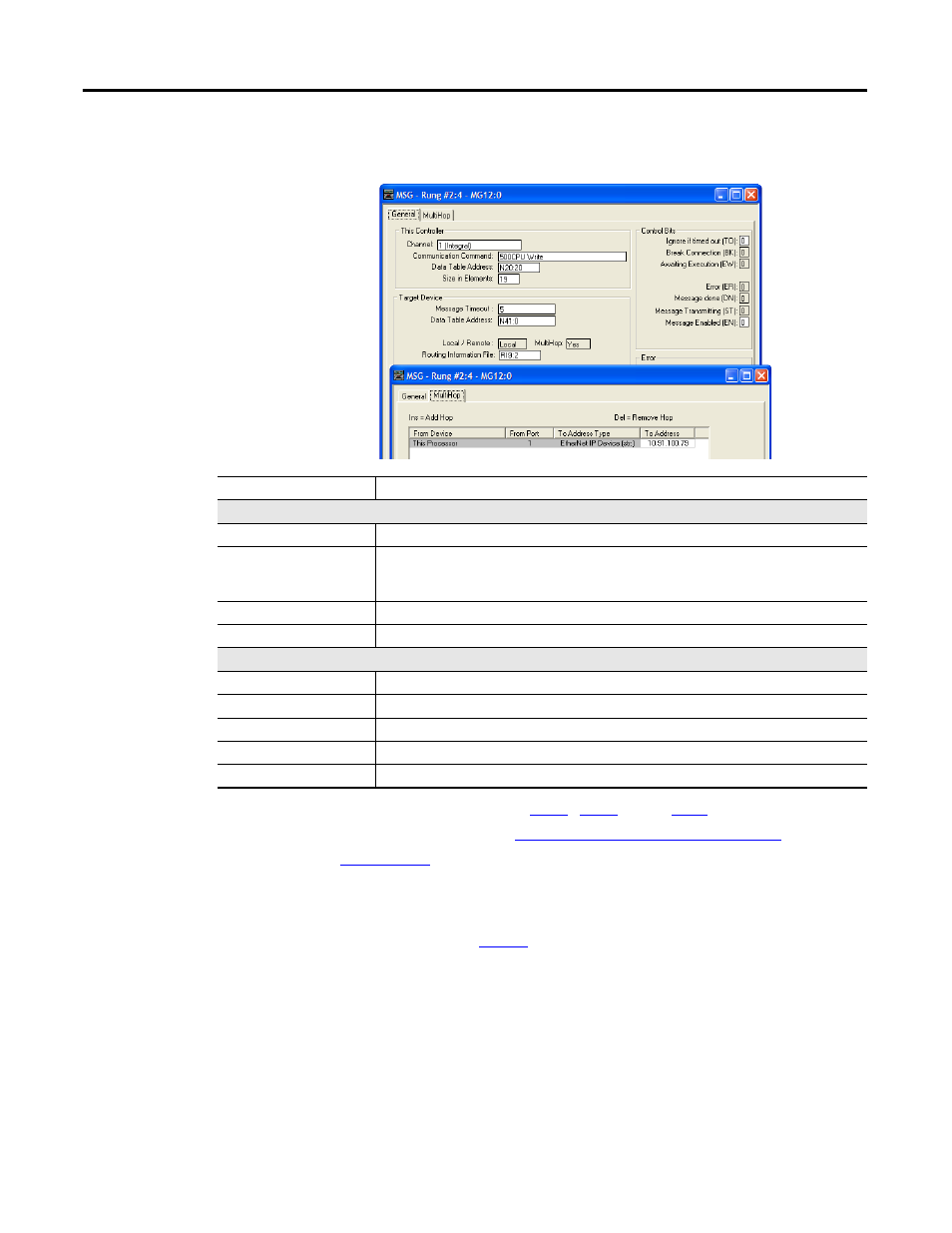
Figure 18 - MicroLogix 1100/1400 Message Configuration Screens for the Logic
Command, Reference, and Datalink In
General Tab BoxSetting
This Controller (data for MicroLogix 1100)
Channel
1 (integral). Controller port to which the network is connected.
Communication Command
500CPU Write. The controller type and command type for the controller to read or write data.
Because the MicroLogix 1100 is part of the SLC-500 controller family, the ‘500CPU’ controller
type was selected. The ‘Write’ command type was selected to write data to the drive.
Data Table Address
(1)
N20:20. An unused controller data table address containing the data to be written to the drive.
Size in Elements
(2)
19. Number of elements (words) to be transferred. Each element size is a 16-bit integer.
Target Device (data for adapter/drive)
Message Timeout
5. Message timeout duration in seconds.
Data Table Address
(3)
N41:0. Specific starting address of the destination file in the drive.
Routing Information File
RI9:2. An unused routing information file for the controller.
MultiHop Tab BoxSetting
To Address
10.91.100.79. The IP address of the adapter connected to the drive.
(1) For details on data table addresses for this example project, see
starting on
(2) For details to determine element size for a specific drive, see
Understanding Controller Data Table Addresses on page 97
(3) For N-File details, see
TIP
This message will error out if the Control Timeout value is not changed from a non-
zero value. Refer to
for writing a value to the Control Timeout.
TIP
If the controller is controlling more than one drive, it is recommended to
intersperse the control I/O messaging for each drive to conserve network
bandwidth and decrease response time. That is, sequence the message
instructions for each drive so that its group of messages will occur at a different
time than those for another drive.
