Create service nodes and cluster controllers – Apple Compressor (4.0) User Manual
Page 222
Chapter 8
Use Apple Qmaster to set up a distributed processing system
222
Rather than actually moving segments, Apple Qmaster tells the service nodes which segments
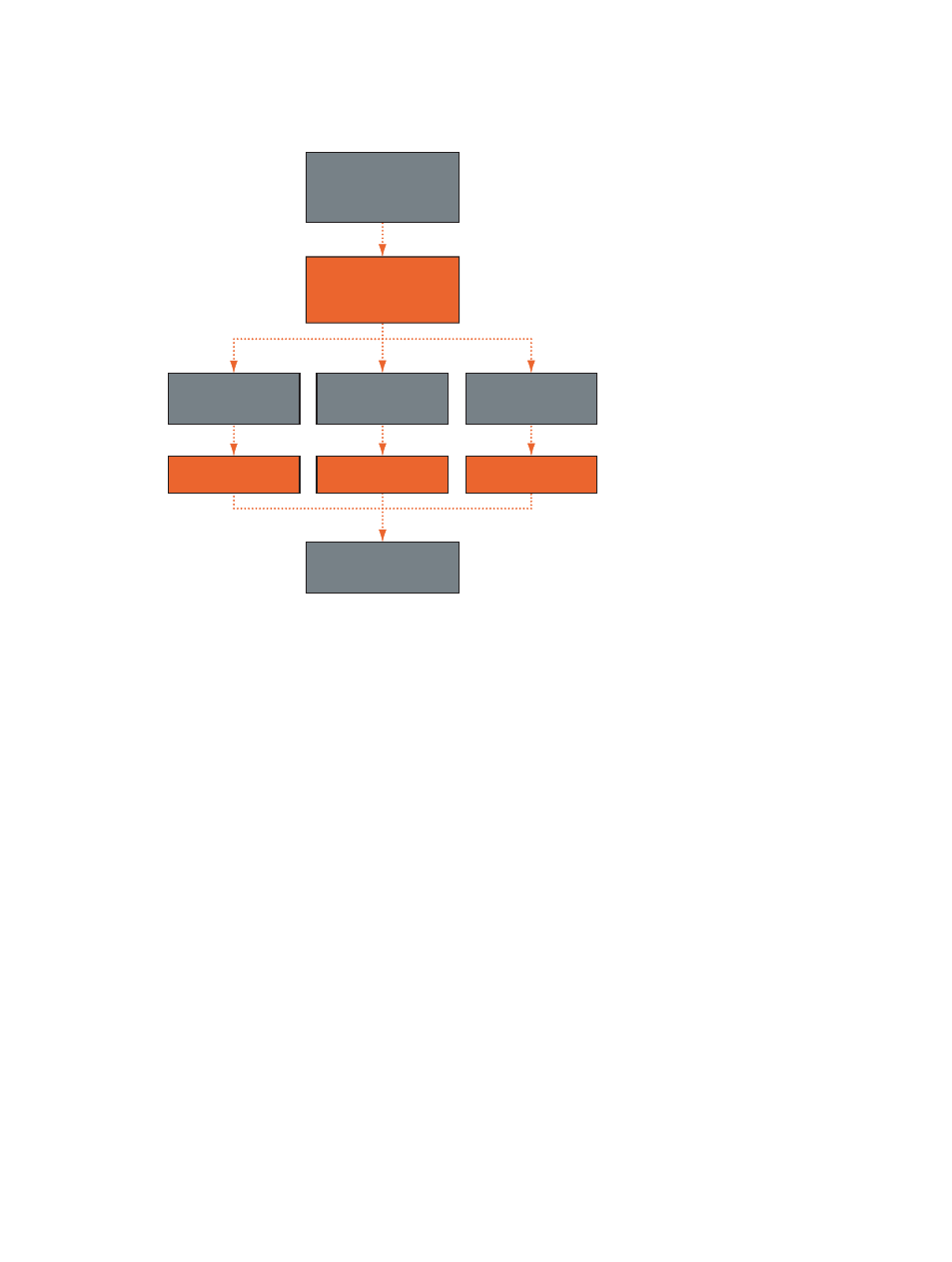
to read via the network, where to find them, and what to do with them. Below is an example of
how one batch might be processed in an Apple Qmaster system.
Batch submitted by
Compressor or
Apple Qmaster (job request
for frames 1–30)
Cluster controller
divides and distributes
job to available
service nodes
Service node 1
Service node 2
Service node 3
Instructions specifying
locations of source files
and frames 11–20
Instructions specifying
locations of source files
and frames 21–30
Instructions specifying
locations of source files
and frames 01–10
Processed file (frames 1–30)
placed in specified
destination
In distributing batches, Apple Qmaster uses the technology built in to OS X to locate services in
a cluster on the same IP subnet and to dynamically share and receive information. Because the
computers can continually transmit their current processing availability status, Apple Qmaster
can distribute the workload evenly across the cluster.
Create service nodes and cluster controllers
Creating service nodes and cluster controllers overview
Once your network is set up and you have installed the necessary components, you are ready
to create your distributed processing system. There are three ways you can set up a distributed
processing system:
•
Use This Computer Plus: The This Computer Plus option in Apple Qmaster is the easiest
approach you can take to creating a distributed processing system. You simply install
Compressor on any computers you want to perform processing duties, and then configure
the computers as service nodes. For more information, see
Quickly set up a service node using
on page 223.
•
Create a QuickCluster: You can create a QuickCluster in Apple Qmaster, configuring a single
computer to be a cluster by choosing the number of instances it supports, based on the
number of cores available. For more information, see
Set up a cluster controller using
on page 224.
•
Manually create a cluster using Apple Qadministrator: Large installations can manually create
managed clusters to be used by their clients. For more information, see
on page 258.
