Campbell Scientific CR3000 Micrologger User Manual
Page 304
Section 8. Operation
304
• Offset = 3 x Basic Resolution + 5.0 µV if the measurement is of a single-
ended input channel
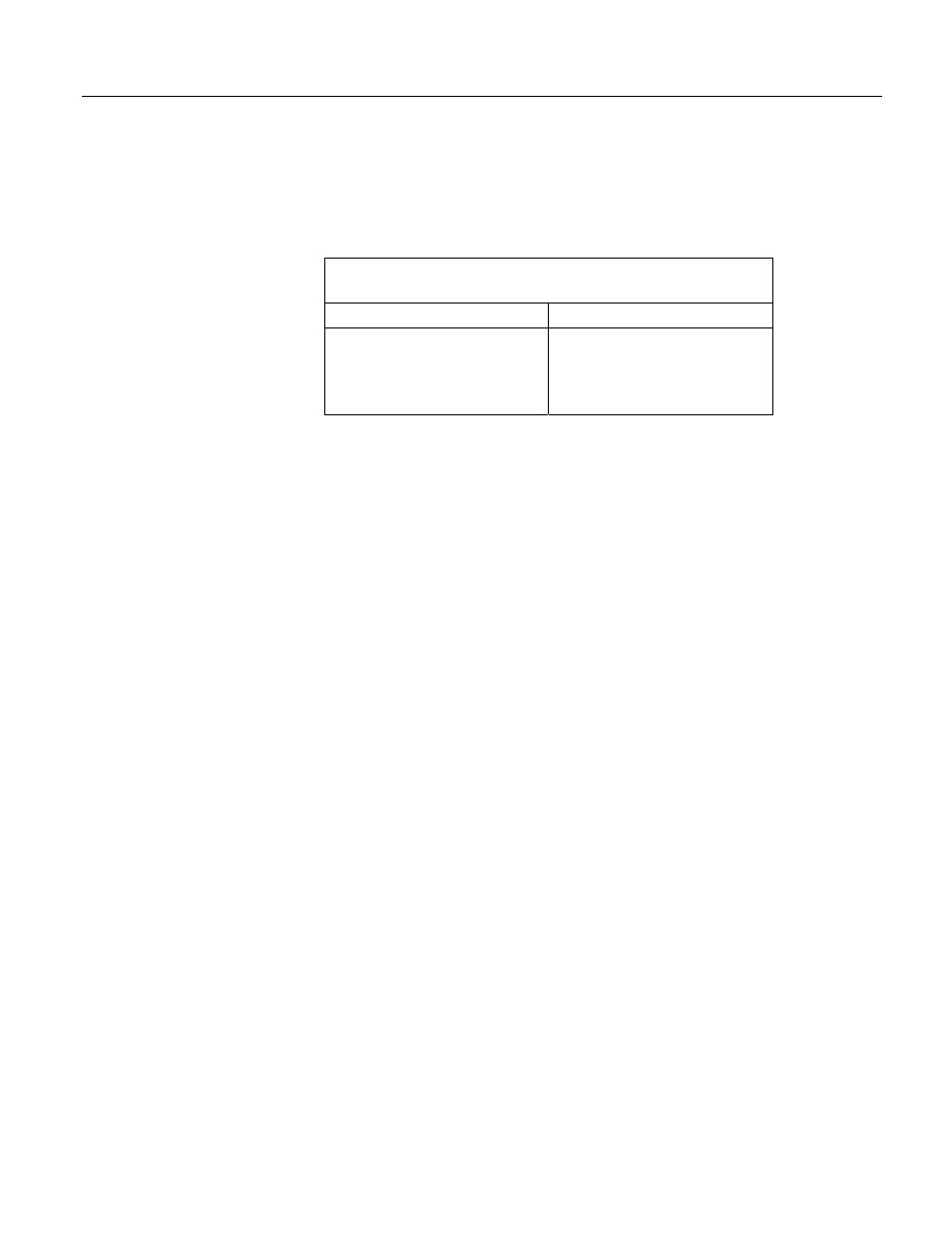
The following table lists basic resolution values.
Table 65. Analog Input-Voltage Range and Basic
Resolution
Range (mV)
Basic Resolution (µV)
±5000
±1000
±200
±50
±20
167
33.3
6.67
1.67
0.67
Assumptions that support the ratiometric-accuracy specification include:
•
• Excitation voltages less than 500 mV and excitation currents less than 500
µA are reversed during the excitation phase of the measurement.
• Effects due to the following are not included in the specification:
o Bridge-resistor errors
o Sensor noise
o Measurement noise
The ratiometric-accuracy specification is applied to a three-wire half-bridge
measurement that uses the BrHalf() instruction as follows:
The relationship defining the BrHalf() instruction is X = V1/Vx, where V1
is the voltage measurement and Vx is the excitation voltage. The
estimated accuracy of X is designated as ∆X, where ∆X = ∆V1/Vx. ∆V1 is
derived using the following method.
The ratiometric-accuracy specification is applied to a four-wire full-bridge
measurement that uses the BrFull() instruction as follows:
The relationship defining the BrFull() instruction is X = 1000*V1/Vx,
where V1 is the voltage measurement and Vx is the excitation voltage.
Result X is expressed as mV/V. Estimated accuracy of X is ∆X, where ∆X
= 1000*∆V1/Vx. ∆V1 is derived using the following method.
∆V1 is derived using the ratiometric‐accuracy equation. The derivation
is illustrated in this example, which is supported by the assumption that
the measurement is differential with input reversal, datalogger
temperature is between 0° to 40°C, analog‐input range is ±200 mV, V1 =
110 mV, and excitation is reversed during the excitation phase of the
measurement. The effect each assumption has on the magnitude of
∆V1 in this example is noted in the following figure.
In the case of the Resistance() instruction, sensor resistance is determined from
Vs/Ix, where excitation current Ix is measured across a 1000 Ω, ±0.005% @ 25
˚C, 2 ppm/˚C TCR internal resistor.
