1 zero or tare (option 0), Figure 50: zero (option 0), Table 24. calibration report for air rh sensor – Campbell Scientific CR3000 Micrologger User Manual
Page 159
Section 7. Installation
159
"offset" = "y‐ intercept" = "zero"
"multiplier" = "slope" = "gain"
7.8.1.5.1 Zero or Tare (Option 0)
Zero option simply adjusts a sensor's output to zero. It does not affect the
multiplier.
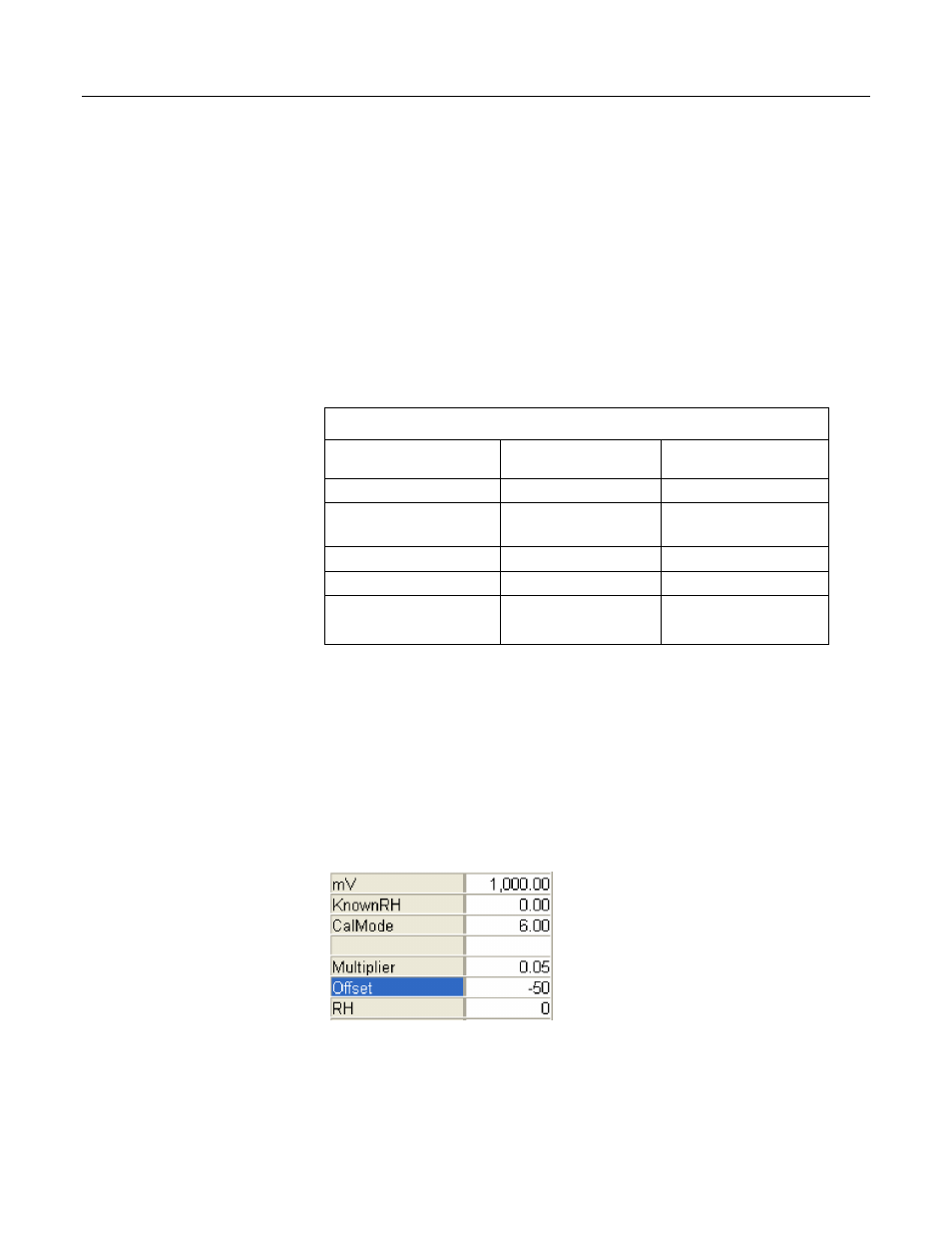
Case: A sensor measures the relative humidity (RH) of air. Multiplier is known to
be stable, but sensor offset drifts and requires regular zeroing in a desiccated
chamber. The following procedure zeros the RH sensor to obtain the calibration
report shown. Use the integrated keyboard / display or software numeric monitor
to change variable values as directed.
Table 24. Calibration Report for Air RH Sensor
Parameter Argument
at
Deployment
Argument at 30-Day
Service
mV output
1000 mV
1050 mV
KnownRH (desiccated
chamber)
0 %
0 %
Multiplier
0.05 % / mV
0.05 % / mV
Offset
-50 %
-52.5 %
RH reading
0 %
0 %
1. Send CRBasic example FieldCal Zeroing Demonstration Program
(p. 160)
to the
CR3000. An excitation channel has been programmed to simulate a sensor
output.
2. To place the simulated RH sensor in a simulated-calibration condition (in the
field it would be placed in a desiccated chamber), place a jumper wire between
channels VX1/EX1 and SE6 (3L). Set variable mV to 1000. Set variable
KnownRH to 0.0.
3. To simulate a calibration, change the value in variable CalMode to 1 to start
calibration. When CalMode increments to 6, zero calibration is complete.
Calibrated Offset will equal -50% at this stage of this example.
Figure 50: Zero (Option 0)
4. To continue this example and simulate a zero-drift condition, change variable
mV to 1050.
