4 pt100 in four-wire full-bridge, Figure 82: pt100 in three-wire half-bridge – Campbell Scientific CR3000 Micrologger User Manual
Page 266
Section 7. Installation
266
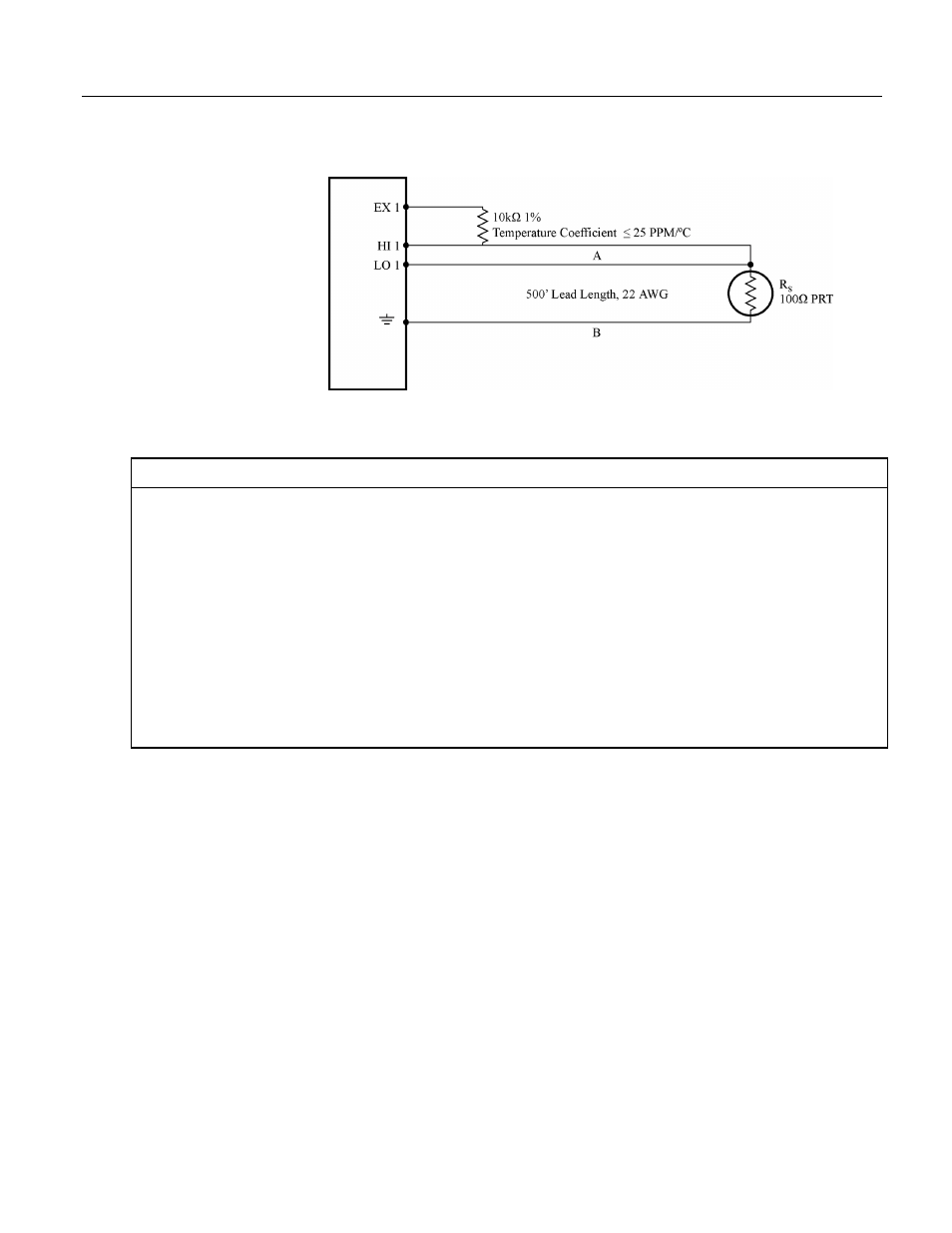
Figure 82: PT100 in three-wire half-bridge
CRBasic Example 60. PT100 in Three‐wire Half‐bridge
'See FIGURE. PT100 in Three-Wire Half-Bridge
for wiring diagram.
Public
Rs_Ro
Public
Deg_C
BeginProg
Scan
(1,Sec,0,0)
'BrHalf3W(Dest,Reps,Range1,SEChan,ExChan,MPE,Ex_mV,True,0,250,100.93,0)
BrHalf3W
(Rs_Ro,1,mV50,1,Vx1,1,4400,True,0,250,100.93,0)
'PRTCalc(Destination,Reps,Source,PRTType,Mult,Offset)
PRTCalc
(Deg_C,1,Rs_Ro,1,1.0,0)
NextScan
EndProg
7.8.18.2.4 PT100 in Four-Wire Full-Bridge
Example Shows:
• How to measure a PRT in a four-wire full-bridge
Advantages:
• Uses half as many input channels as four-wire half-bridge.
Example PRT Specifications:
• Alpha = 0.00392 (PRTType 2)
This example measures a 100 ohm PRT in a four-wire full-bridge, as shown in
figure PT100 in Four-Wire Full-Bridge
(p. 268),
using CRBasic instruction
BRFull(). In this example, the PRT is in a constant-temperature bath and the
measurement is to be used as the input for a control algorithm.
As described in table Resistive Bridge Measurements with Voltage Excitation (
p.
), the result of BRFull() is X,
X = 1000 V
S
/V
X
