HP Radio Frequency Planner Software Series User Manual
Page 65
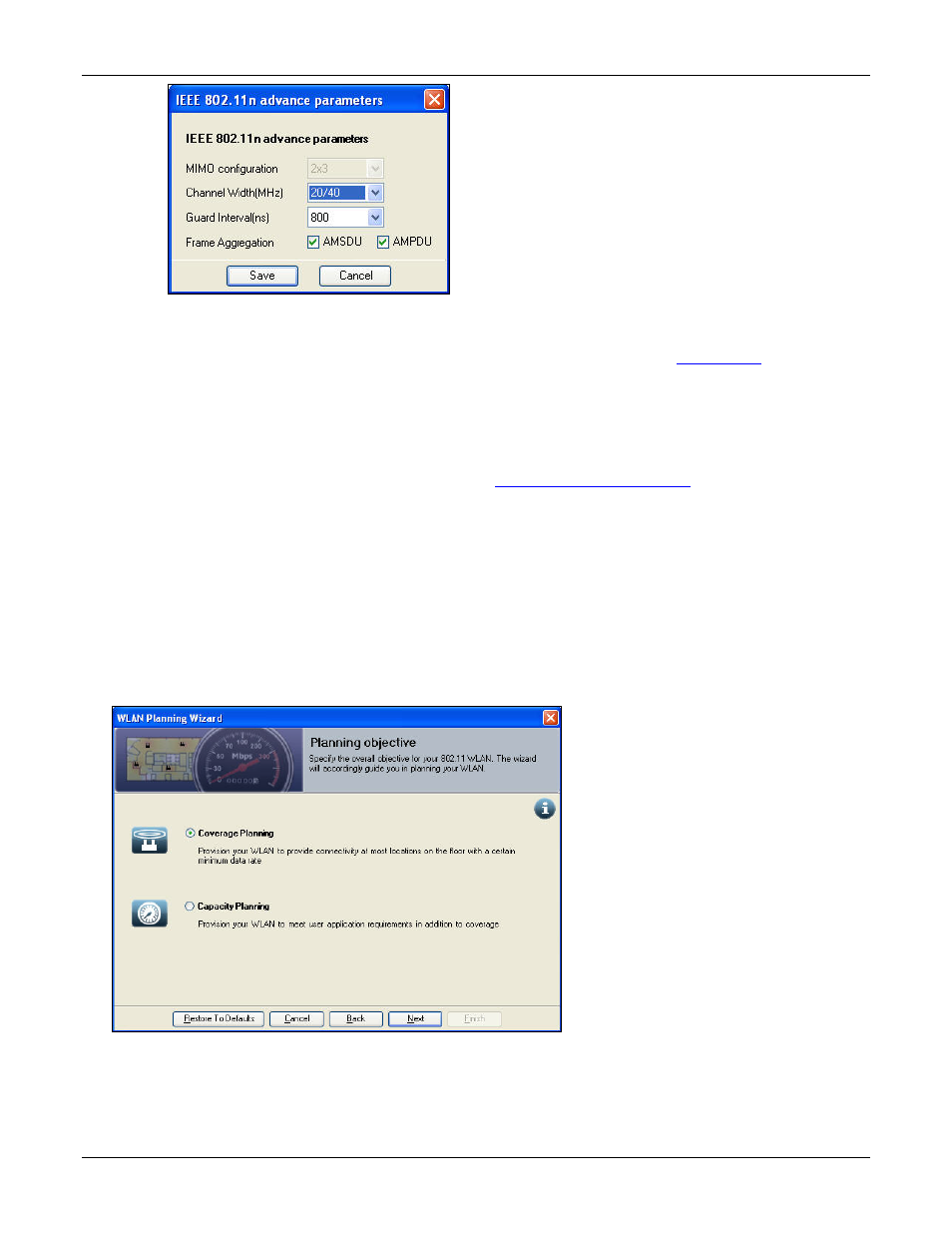
Table of Contents
HP RF Planner User Guide
58
Figure 70.
802.11n Advance Parameters
Set the IEEE 802.11n Advance parameters:
MIMO configuration: Displays the MIMO configuration you specified while
. This field is
disabled and cannot be modified. You must go to the AP properties screen to modify the same.
Channel Width (MHz): Specify the desired channel width.
Guard Interval (ns): Specify the desired guard interval.
Frame Aggregation: Select either AMSDU or AMPDU, or both checkboxes for the desired frame
aggregation.
For more details on the advance parameters, refer to
•
Channel Allocation Strategy: Due to limited available frequency spectrum for 802.11 WLANs, dense AP deployment
often requires spatial reuse of frequencies. The strategy you chose determines the set of available channels. Planner
assigns channels to minimize interference. During on-site planning, interference from the existing APs is considered.
Select either of the options for channel allocation strategy.
Only non overlapping channels: These are channels that do not interfere with each other. For example, in the
US, 2.4 GHz band offers three non-overlapping channels – 1, 6, and 11.
All available channels: All channels are considered. For example, in the US 2.4 GHz band offers 11 channels.
Using partially overlapping channels (say 1, 4, 7, 11) can improve overall WLAN capacity.
3 The WLAN Planning Wizard: Planning Objective screen helps you specify the planning objective for the 802.11 WLAN,
while also guiding you in planning.
Figure 71.
WLAN Planning – Planning Objective
Planner allows you to choose the focus of WLAN planning. Based on the focus, Planner considers different factors for
populating the number of APs required and their placement.
