Appendix f: rtd module – B&B Electronics ZZ24D-NA(NB,NC,ND)-SR - Manual User Manual
Page 91
Appendix F: RTD Module
Manual Documentation Number: pn7515_Zlinx IO0712m
85
A
A
p
p
p
p
e
e
n
n
d
d
i
i
x
x
F
F
:
:
R
R
T
T
D
D
M
M
o
o
d
d
u
u
l
l
e
e
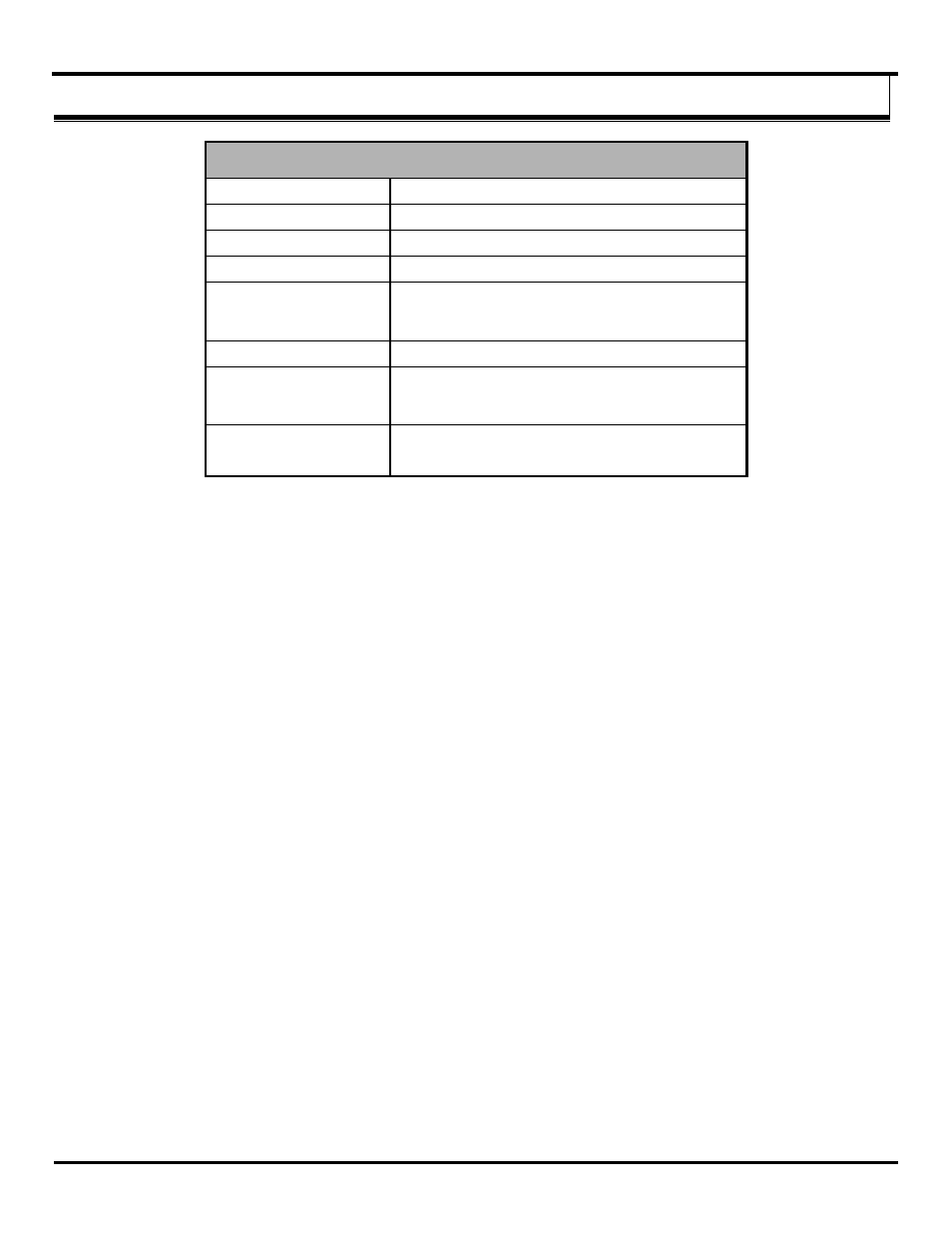
RTD Module ZZ-4RTD1
Number of RTD: 4
Modbus mode: Resolution – 16 bits
Peer-to-Peer mode: Resolution – 12 bits
Wire Configuration: 2, 3, and 4 wire
Type: Pt100, optimized for temperature coefficient of 385
Pt1000, optimized for temperature coefficient of 385
Cu10, optimized for temperature coefficient of 427
Input connection: 3.5 mm removable terminal block (4 per output)
RTD Module
Temperature range:
Pt100 = -200 to 650ºC
Pt1000 = -200 to 100ºC
Cu 10 = -100 to 260ºC
Resolution: 16 Bit resolution for Modbus mode
12 Bit resolution for Peer-to-Peer mode
RTD Calculations
Converting 0 to 65535 discrete voltage levels to degrees ºC in Modbus mode:
1. A Pt100 RTD has a temperature range of -200ºC to +650ºC which equals a range of 850 degrees.
2. A resolution of 65535 / 850 degrees equals 77.1 steps per 1 degree ºC.
3. To convert a reading of 15420 to degrees (ºC) perform the following calculation:
15420 (reading) / 77.1 (steps) = 200 (degrees)
200 degree reading with a -200 to 650 range equals 0ºC
Another way to look at it:
D = # of degrees across the entire RTD module range
-200 to 650 = 850 for PT100
D = 850
N = # of steps per degree - 65535/D = N
65535/850 = 77.1
N = 77.1
Current reading/N = D
15420/77.1 = 200 degrees
200 degrees is applied across the completer RTD module range. To calculate the true temperature start at the lowest reading
and scale up 200 degrees.
-200 + 200 degrees = 0ºC
