Casio ClassPad II fx-CP400 User Manual
Page 87
Chapter 2: Main Application
87
Important!
See “Important!” under “invBinomialCDf” on page 86.
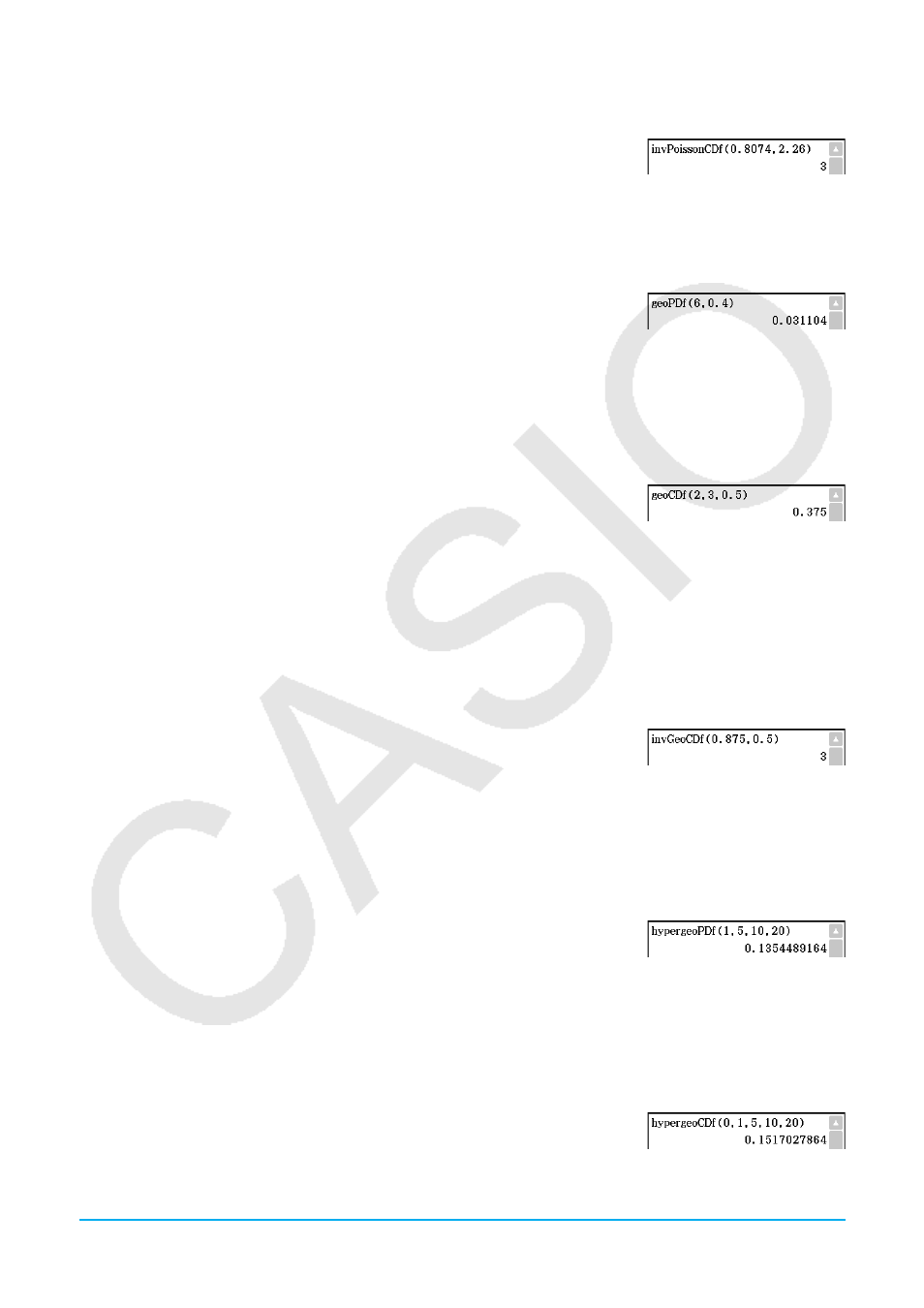
Example: To determine the minimum number of trials when
prob
= 0.8074,
= 2.26
u geoPDf [Action][Distribution/Inv.Dist][Discrete][geoPDf]
Function: Returns the probability in a geometric distribution that the success will occur on a specified trial.
Syntax: geoPDf(
x
,
pos
[ ) ]
Calculation Result Output:
prob
Example: To determine the geometric probability when
x
= 6,
pos
= 0.4
u geoCDf [Action][Distribution/Inv.Dist][Discrete][geoCDf]
Function: Returns the cumulative probability in a geometric distribution that the success will occur between
specified lower value and upper value.
Syntax: geoCDf(lower value, upper value,
pos
[ ) ]
Calculation Result Output:
prob
Example: To determine the geometric probability when lower value = 2,
upper value = 3,
pos
= 0.5
u invGeoCDf [Action][Distribution/Inv.Dist][Inverse][invGeoCDf]
Function: Returns the minimum number of trials of a geometric cumulative probability distribution for specified
values.
Syntax: invGeoCDf(
prob
,
pos
[ ) ]
Calculation Result Output:
x
Inv,
½
x
Inv
Important!
See “Important!” under “invBinomialCDf” on page 86.
Example: To determine the minimum number of trials when
prob
= 0.875,
pos
= 0.5
u hypergeoPDf [Action][Distribution/Inv.Dist][Discrete][hypergeoPDf]
Function: Returns the probability in a hypergeometric distribution that the success will occur on a specified
trial.
Syntax: hypergeoPDf(
x
,
n
,
M
,
N
[ ) ]
Calculation Result Output:
prob
Example: Determine the hypergeometric probability when
x
= 1,
n
= 5,
M
= 10,
N
= 20.
u hypergeoCDf [Action][Distribution/Inv.Dist][Discrete][hypergeoCDf]
Function: Returns the cumulative probability in a hypergeometric distribution that the success will occur
between specified lower value and upper value.
Syntax: hypergeoCDf(lower value, upper value,
n
,
M
,
N
[ ) ]
Calculation Result Output:
prob
Example: Determine the hypergeometric cumulative distribution when lower
value = 0, upper value = 1,
n
= 5,
M
= 10,
N
= 20.
