3 performing basic statistical calculations, Performing basic statistical calculations, Calculating statistical values – Casio ClassPad II fx-CP400 User Manual
Page 136
Chapter 7: Statistics Application
136
7-3
Performing Basic Statistical Calculations
Mean, standard deviation, and other statistical values can be obtained from single-variable data and paired-
variable data. Regression calculation can also be performed on paired-variable data. All of these calculations
are performed using [Calc] menu commands.
Calculating Statistical Values
You can use the procedure below to display a lists of various single-variable and paired-variable statistical
values.
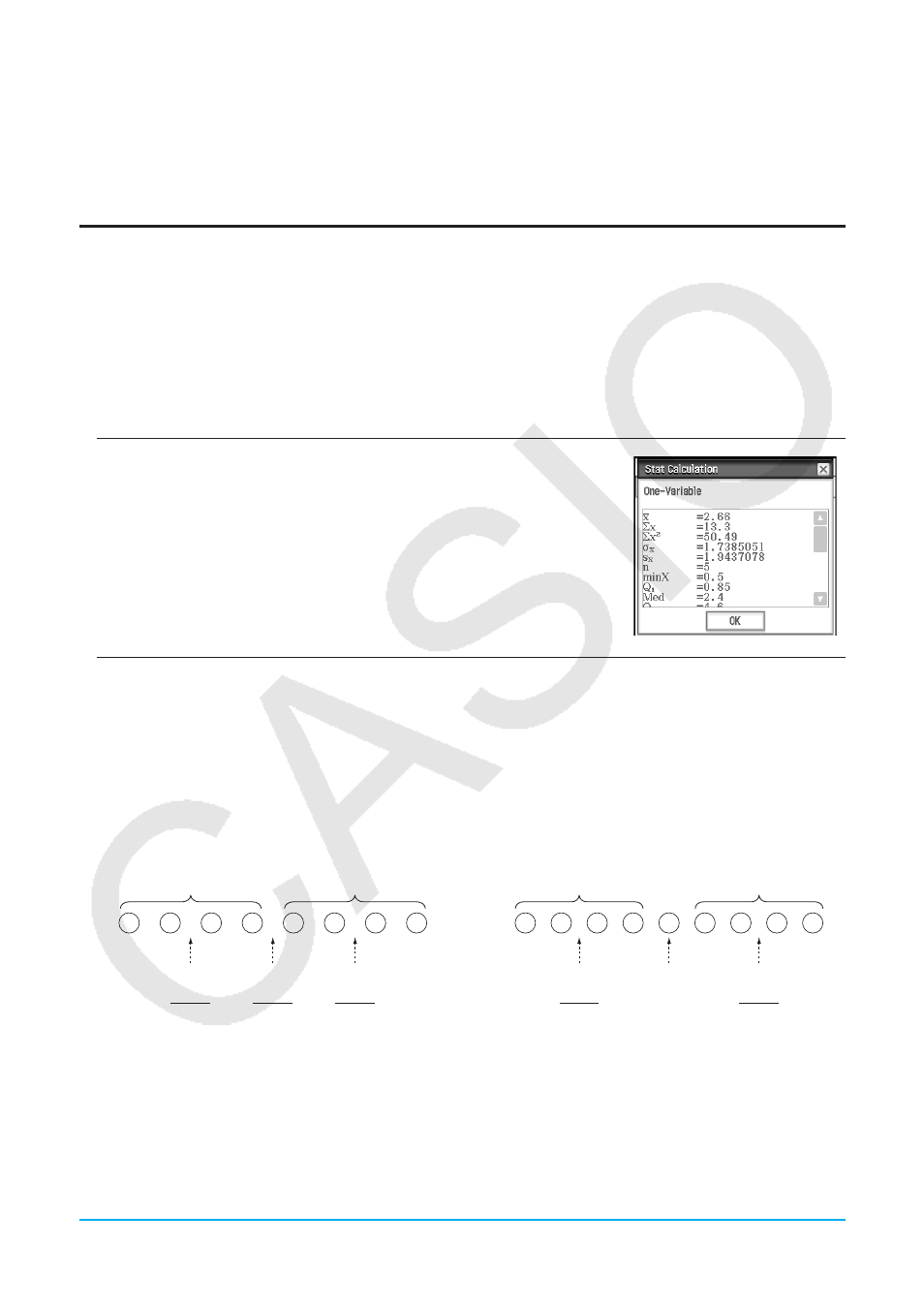
u To display single-variable calculation results
1. On the Stat Editor window or Stat Graph window, tap [Calc] - [One-Variable].
2. On the dialog box that appears, specify the [XList] name, select the [Freq] setting, and then tap [OK].
• This displays the dialog box with the single-variable statistical calculation results described below.
o: sample
mean
Σ
x
:
sum of data
Σ
x
2
: sum of squares
σ
x
:
population standard deviation
s
x
:
sample standard deviation
n
: sample
size
minX: minimum
Q
1
: first
quartile
Med: median
Q
3
: third
quartile
maxX: maximum
Mode: mode*
ModeN: number of data mode
items
ModeF: data mode frequency
* If “Mode =
'ModeStat” is displayed, it means that solutions are stored in the “ModeStat” system variable.
To view the “ModeStat” contents, tap any list name cell on the Stat Editor window, input “ModeStat”, and
then press E.
Calculation Methods for Q
1
and Q
3
Q
1
and Q
3
can be calculated in accordance with the [Q
1
, Q
3
on Data] setting on the Basic Format dialog box
(page 34) as described below.
[Q
1
, Q
3
on Data] unchecked (default): With this calculation method, processing depends on whether the
number of elements
n
in the population is an even number or odd number.
Example:
n
= 8
Example:
n
= 9
Lower half group
Upper half group
Lower half group
Upper half group
2
4 + 5
Median
Q
1
Q
3
2
2 + 3
2
6 + 7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Median
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Q
3
2
7 + 8
Q
1
2
2 + 3
When
n
is an even number, using the center point of the total population as the reference, the population
elements are divided into two groups: a lower half group and an upper half group. Q
1
and Q
3
then become
the values described below.
Q
1
= {median of the group of
n
/2 items from the bottom of the population}
Q
3
= {median of the group of
n
/2 items from the top of the population}
