Casio ClassPad II fx-CP400 User Manual
Page 205
Chapter 12: Program Application
205
Chapter 12: Program Application
205
HypergeoCD
k
Syntax: HypergeoCD
ⅪLower value, Upper value,
n
value,
M
value,
N
value
Function: See “Hypergeometric Cumulative
Distribution” (page 147).
HypergeoPD
k
Syntax: HypergeoPD
Ⅺ
x
value,
n
value,
M
value,
N
value
Function: See “Hypergeometric Distribution
Probability” (page 147).
I
If~Then~ElseIf~Else~IfEnd
Ctrl - If
Syntax 1: If
Ⅺ
: IfEnd
Function 1:
• If the expression is true, the statement in the Then
block is executed. After that, execution advances to
the next statement after IfEnd.
• If the expression is false, execution advances to the
next statement after IfEnd, without executing the
statement in the Then block.
Syntax 2: If
Ⅺ
Else : [
Function 2:
• If the expression is true, the statement in the Then
block is executed. After that, execution advances to
the next statement after IfEnd.
• If the expression is false, the statement in the Else
block is executed instead of the Then block. After
that, execution advances to the next statement after
IfEnd.
Syntax 3: If
Ⅺ
ElseIf
Ⅺ
Function 3:
• If the expression is true, the statement in the If Then
block is executed. After that, execution advances to
the next statement after IfEnd.
• If the If command expression is false, the ElseIf
command expression is tested. If it is true, the
statement in the ElseIf Then block is executed.
After that, execution advances to the next statement
after IfEnd. If it is false, execution advances to the
next statement after IfEnd.
Syntax 4: If
Ⅺ
ElseIf
Ⅺ
[
Function 4:
• If the expression is true, the statement in the If Then
block is executed. After that, execution advances to
the next statement after IfEnd.
• If the If command expression is false, the ElseIf
command expression is tested. If it is true, the
statement in the ElseIf Then block is executed.
After that, execution advances to the next statement
after IfEnd. If it is false, the Else block statement is
executed. After that, execution advances to the next
statement after IfEnd.
Description:
• With all four of the syntaxes described above, you
can use a multi-statement command (:) in place
of the carriage return to separate Then block
statements.
• The If~IfEnd command can be nested.
• The If~IfEnd loop can be exited using the Break
command or Return command.
• Do not use the Goto command to exit an If~IfEnd
loop.
IfEnd
Ctrl - If
See If~Then~ElseIf~Else~IfEnd.
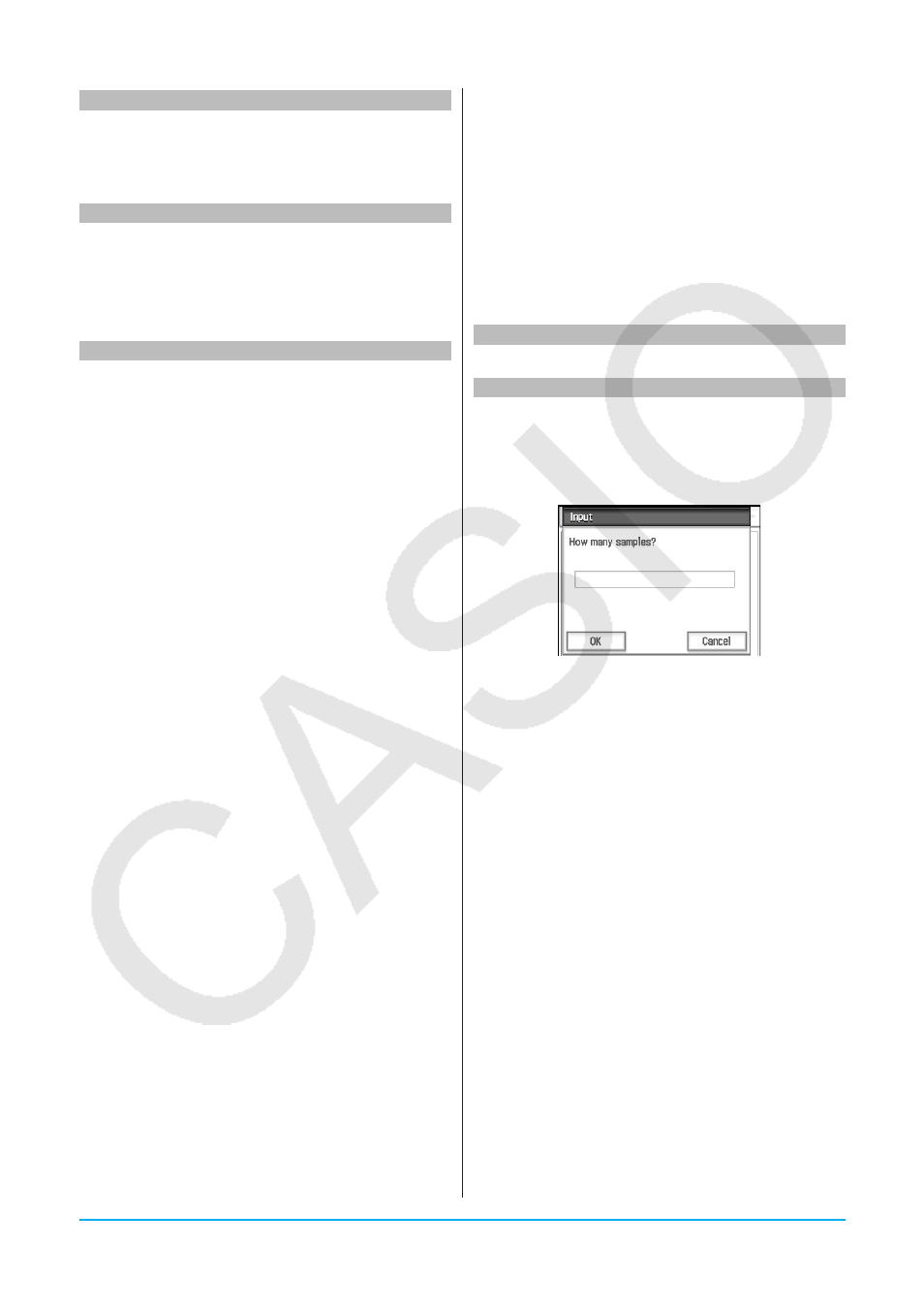
Input
I/O - Input
Syntax: Input
Ⅺ 2>"]] Function: When program execution reaches the Input Description: prompt “ • The text specified for " input dialog box title. • This command pauses program execution and displays a dialog box that contains the text string • Specifying a long text string can cause part of it to be cut off when it is displayed in the dialog box. • When the dialog box appears, input a value into the input box and then tap [OK]. This closes the • Tapping [Cancel] on the dialog box terminates program execution. Note: execution is paused for input of data. While a
command, the user is prompted for input of a value,
which is assigned to the specified variable.
• If you do not specify anything for "
indicated by "
string enclosed within quotation marks (" ") or a
variable name can be specified for "
dialog box, assigns the input value to the applicable
variable and resumes program execution.
• During execution of the Input command, program
program is paused, you can input individual
mathematical expressions only. You cannot input
commands or a series of statements joined by
colons (:).
