Casio ClassPad II fx-CP400 User Manual
Page 133
Chapter 7: Statistics Application
133
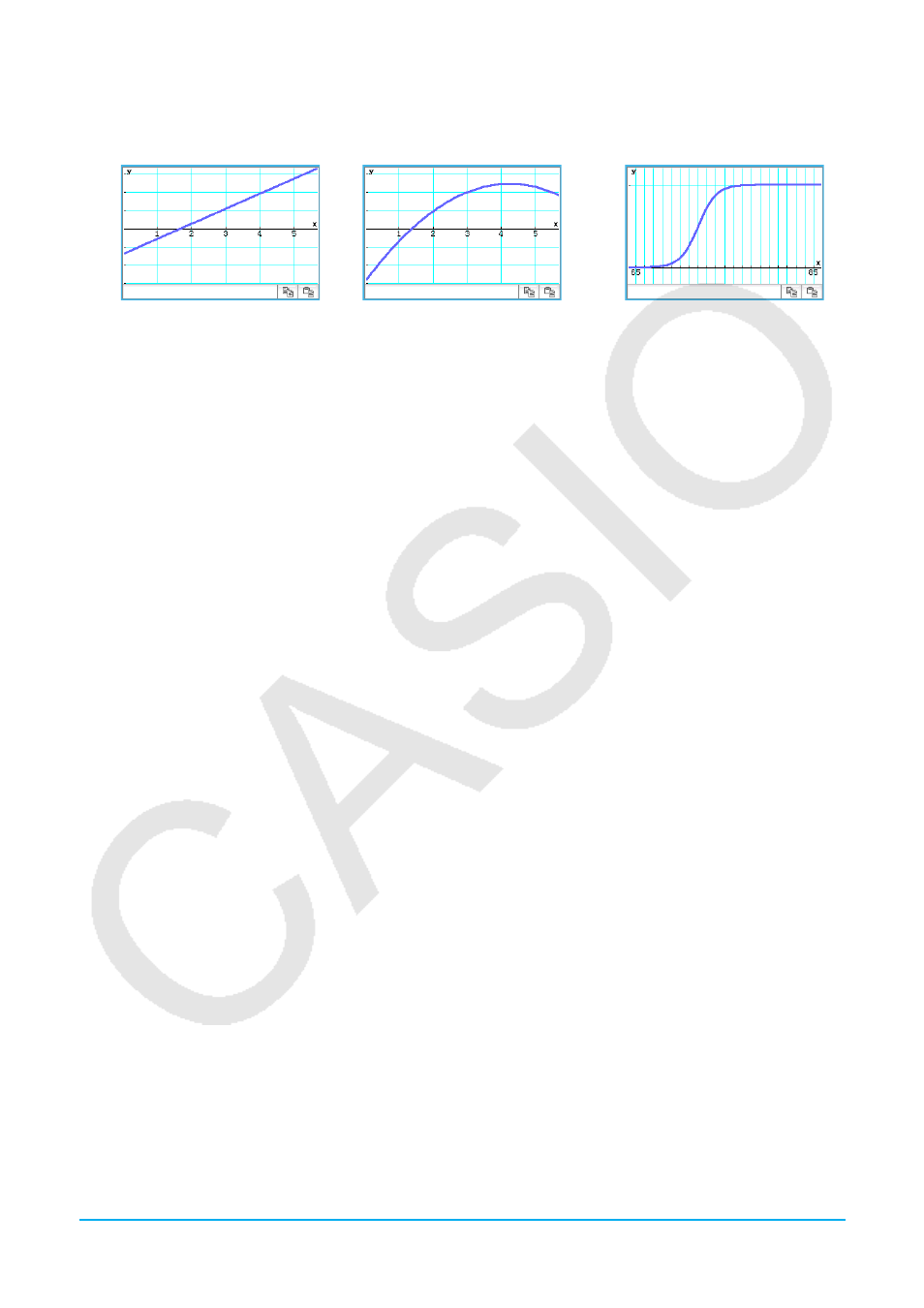
k Regression graphs
Regression graphs of each of the paired-variable data can be drawn according to the model formulas under
“Regression types” below.
Linear regression graph
Quadratic regression graph
Logistic regression graph
Regression types:
Linear regression (LinearR) [Linear Reg] ..............................................................
y
=
a
ؒ
x
+
b
,
y
=
a
+
b
ؒ
x
Linear regression uses the method of least squares to determine the equation that best fits your data
points, and returns values for the slope and
y
-intercept. The graphic representation of this relationship is a
linear regression graph.
Med-Med line (MedMed) [MedMed Line] ...................................................................................
y
=
a
ؒ
x
+
b
When you suspect that the data contains extreme values, you should use the Med-Med graph (which
is based on medians) in place of the linear regression graph. Med-Med graph is similar to the linear
regression graph, but it also minimizes the effects of extreme values.
Quadratic regression (QuadR) [Quadratic Reg] .............................................................
y
=
a
ؒ
x
2
+
b
ؒ
x
+
c
Cubic regression (CubicR) [Cubic Reg] ................................................................
y
=
a
ؒ
x
3
+
b
ؒ
x
2
+
c
ؒ
x
+
d
Quartic regression (QuartR) [Quartic Reg] .................................................
y
=
a
ؒ
x
4
+
b
ؒ
x
3
+
c
ؒ
x
2
+
d
ؒ
x
+
e
Quadratic, cubic, and quartic regression graphs use the method of least squares to draw a curve that
passes the vicinity of as many data points as possible. These graphs can be expressed as quadratic, cubic,
and quartic regression expressions.
Logarithmic regression (LogR) [Logarithmic Reg] ....................................................................
a
+
b
ؒln(
x
)
Logarithmic regression expresses
y
as a logarithmic function of
x
. The normal logarithmic regression
formula is
y
=
a
+
b
ؒln(
x
). If we say that X = ln(
x
), then this formula corresponds to the linear regression
formula
y
=
a
+
b
ؒX.
a
ؒ
e
b
Ⴇ
x
Exponential regression (ExpR) [Exponential Reg].............................................................
y
=
a
ؒ
e
b
ؒ
x
Exponential regression can be used when
y
is proportional to the exponential function of
x
. The normal
exponential regression formula is
y
=
a
ؒ
e
b
ؒ
x
. If we obtain the logarithms of both sides, we get ln(
y
) = ln(
a
) +
b
ؒ
x
. Next, if we say that Y = ln(
y
) and A = In(
a
), the formula corresponds to the linear regression formula Y
= A +
b
ؒ
x
.
a
ؒ
b
x
Exponential regression (abExpR) [abExponential Reg] ........................................................
y
=
a
ؒ
b
x
Exponential regression can be used when
y
is proportional to the exponential function of
x
. The normal
exponential regression formula in this case is
y
=
a
ؒ
b
x
. If we take the natural logarithms of both sides, we
get ln(
y
) = ln(
a
) + (ln(
b
))
ؒ
x
. Next, if we say that Y = ln(
y
), A = ln(
a
) and B = ln(
b
), the formula corresponds to
the linear regression formula Y = A + B
ؒ
x
.
Power regression (PowerR) [Power Reg] ......................................................................................
y
=
a
ؒ
x
b
Power regression can be used when y is proportional to the power of
x
. The normal power regression
formula is
y
=
a
ؒ
x
b
. If we obtain the logarithms of both sides, we get ln(
y
) = ln(
a
) +
b
ؒln(
x
). Next, if we say
that X = ln(
x
), Y = ln(
y
), and A = ln(
a
), the formula corresponds to the linear regression formula Y = A +
b
ؒX.
Sinusoidal regression (SinR) [Sinusoidal Reg] ........................................................
y
=
a
ؒsin(
b
ؒ
x
+
c
) +
d
Sinusoidal regression is best for data that repeats at a regular fixed interval over time.
