Dr and bdr election, Ospf packet formats – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 78
62
The DR and BDR mechanisms can solve the problem.
•
DR—Elected to advertise routing information among other routers. If the DR fails, routers on the
network must elect another DR and synchronize information with the new DR. Using this mechanism
alone is time-consuming and prone to route calculation errors.
•
BDR—Elected along with the DR to establish adjacencies with all other routers. When the DR fails,
the BDR immediately becomes the new DR, and other routers elect a new BDR.
Routers other than the DR and BDR are called "DrOthers." They do not establish adjacencies with one
another, so the number of adjacencies is reduced.
The role of a router is subnet (or interface) specific. It might be a DR on one interface and a BDR or
DROther on another interface.
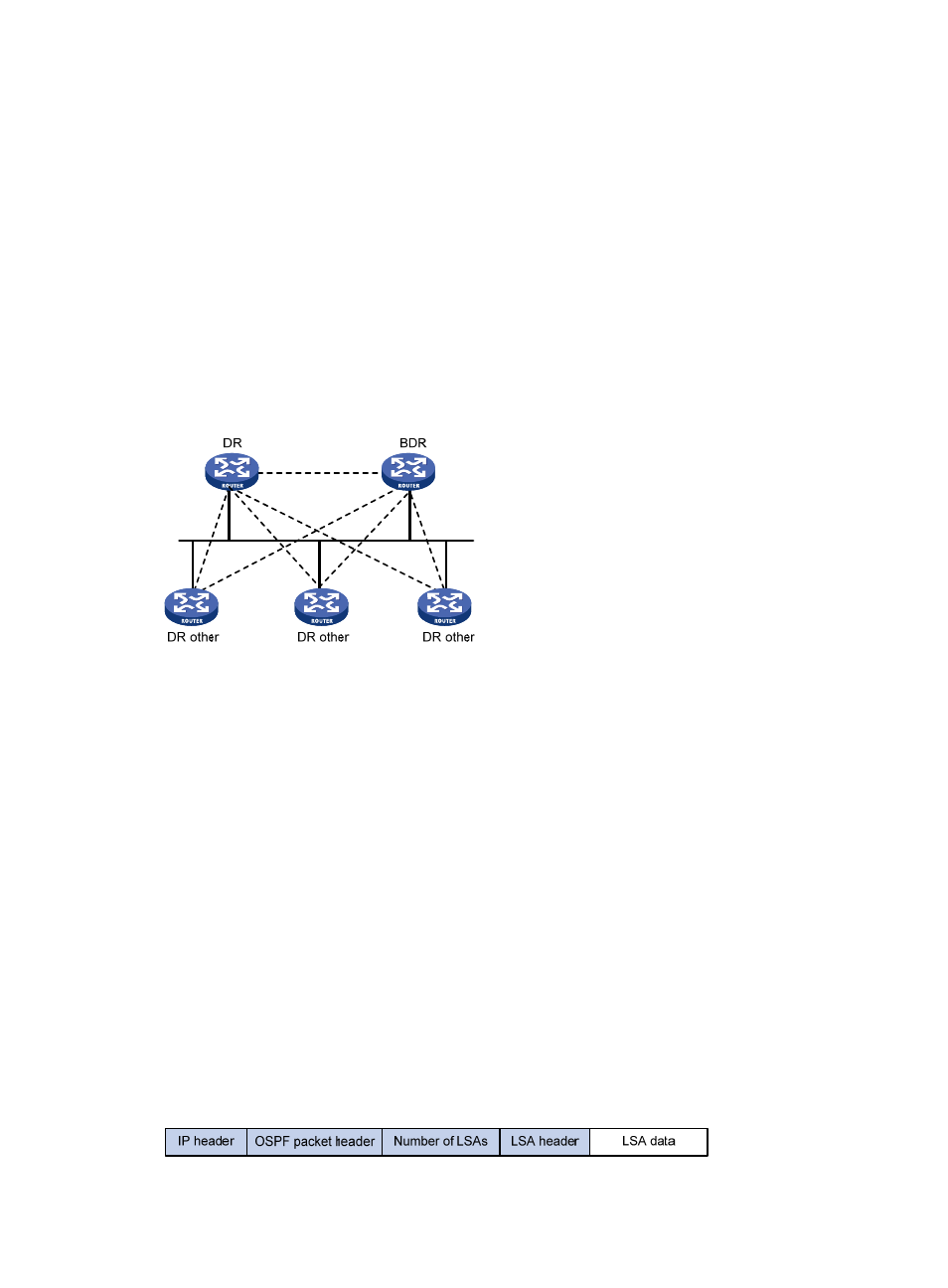
In
, solid lines are Ethernet physical links, and dashed lines represent OSPF adjacencies. With
the DR and BDR, only seven adjacencies are established.
Figure 23 DR and BDR in a network
DR and BDR election
DR election is performed on broadcast or NBMA networks but not on P2P or P2MP networks.
Routers in a broadcast or NBMA network elect the DR and BDR by router priorities and router IDs. Routers
with a router priority value higher than 0 are candidates for DR and BDR election.
The election votes are hello packets. Each router sends the DR elected by itself in a hello packet to all the
other routers. If two routers on the network declare themselves as the DR, the router with the higher router
priority wins. If router priorities are the same, the router with the higher router ID wins. In addition, a
router with the router priority 0 cannot become the DR or BDR.
If a router with a higher router priority is added to the network after DR and BDR election, the router
cannot become the DR or BDR immediately because no DR election is performed for it. Therefore, the DR
of a network might not be the router with the highest priority, and the BDR might not be the router with
the second highest priority.
OSPF packet formats
OSPF packets are directly encapsulated into IP packets. OSPF uses the IP protocol number 89. The format
of an OSPF LSU packet format is shown in
.
Figure 24 OSPF packet format
