Configuration prerequisites, Configuration guidelines, Configuration procedure – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 51: Configuring bfd for rip
35
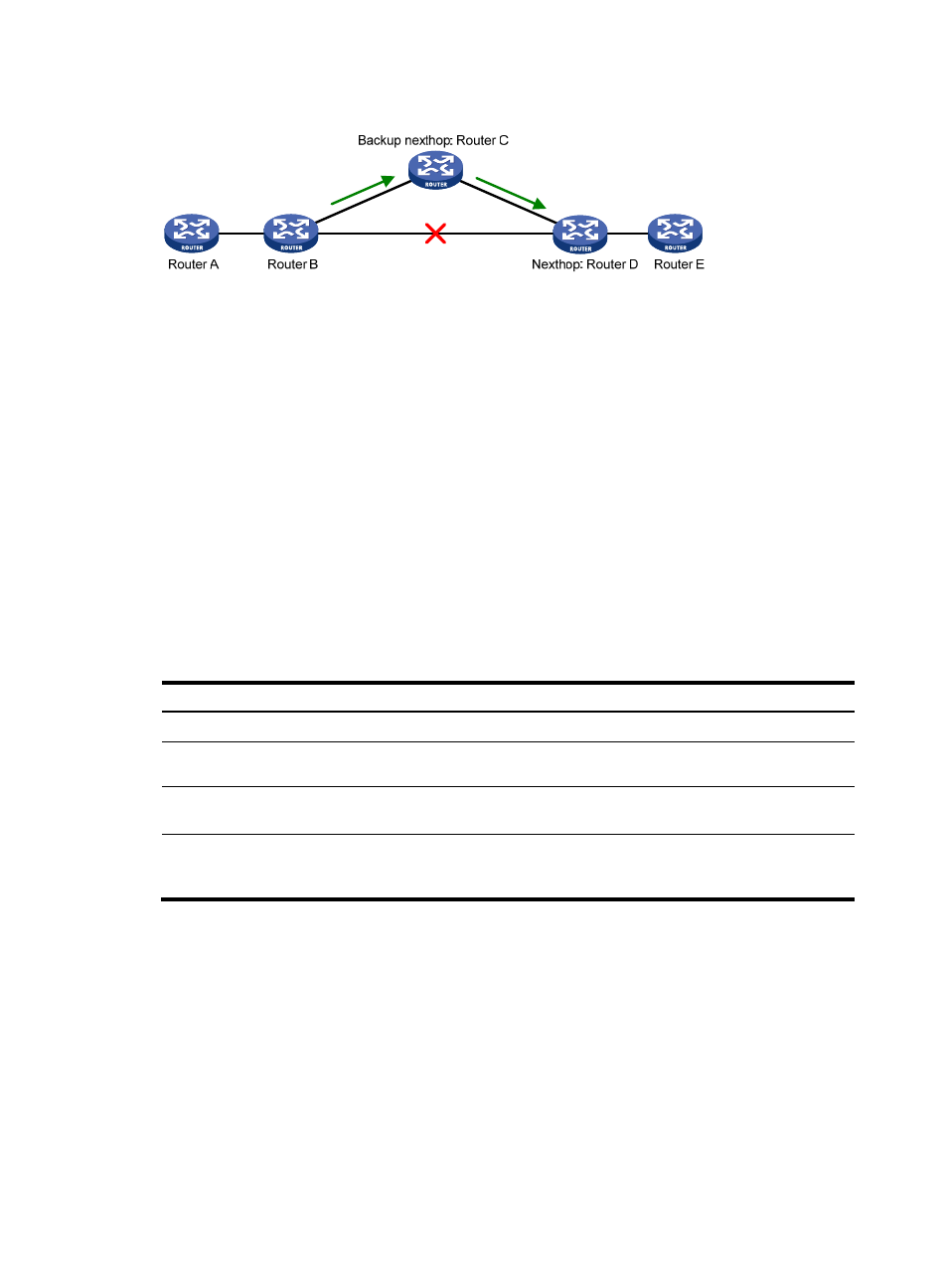
Figure 9 Network diagram
, after you enable FRR on Router B, RIP designates a backup next hop using a routing policy
when a network failure is detected. Packets are then directed to the backup next hop for forwarding,
reducing traffic recovery time. At the same time, RIP calculates the shortest path based on the new
network topology, and forwards packets over that path after network convergence.
Configuration prerequisites
You must specify a next hop by using the apply fast-reroute backup-interface command in a routing
policy and reference the routing policy with RIP FRR. For more information about routing policy
configuration, see "Configuring routing policies."
Configuration guidelines
•
RIP FRR is only effective for non-recursive RIP routes (that are learned from directly connected
neighbors).
•
Do not use RIP FRR and BFD (for RIP) at the same time. Otherwise, RIP FRR might fail to take effect.
Configuration procedure
To configure RIP FRR:
Step Command
Remarks
1.
Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2.
Configure the source address
of echo packets.
bfd echo-source-ip ip-address
Not configured by default.
3.
Enter RIP view.
rip [ process-id ] [ vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name ]
N/A
4.
Enable RIP FRR and reference
a routing policy to designate
a backup next hop.
fast-reroute route-policy
route-policy-name
Disabled by default.
Configuring BFD for RIP
BFD for RIP provides the following link detection modes:
•
Single-hop echo detection mode for a directly connected neighbor. In this mode, a BFD session is
established only when the neighbor has route information to send.
•
Bidirectional control detection mode for an indirectly connected neighbor. In this mode, a BFD
session is established only when both ends have routes to send and BFD is enabled on the receiving
interface.
For more information about BFD, see High Availability Configuration Guide.
