Area address, System id, Routing method – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 149
133
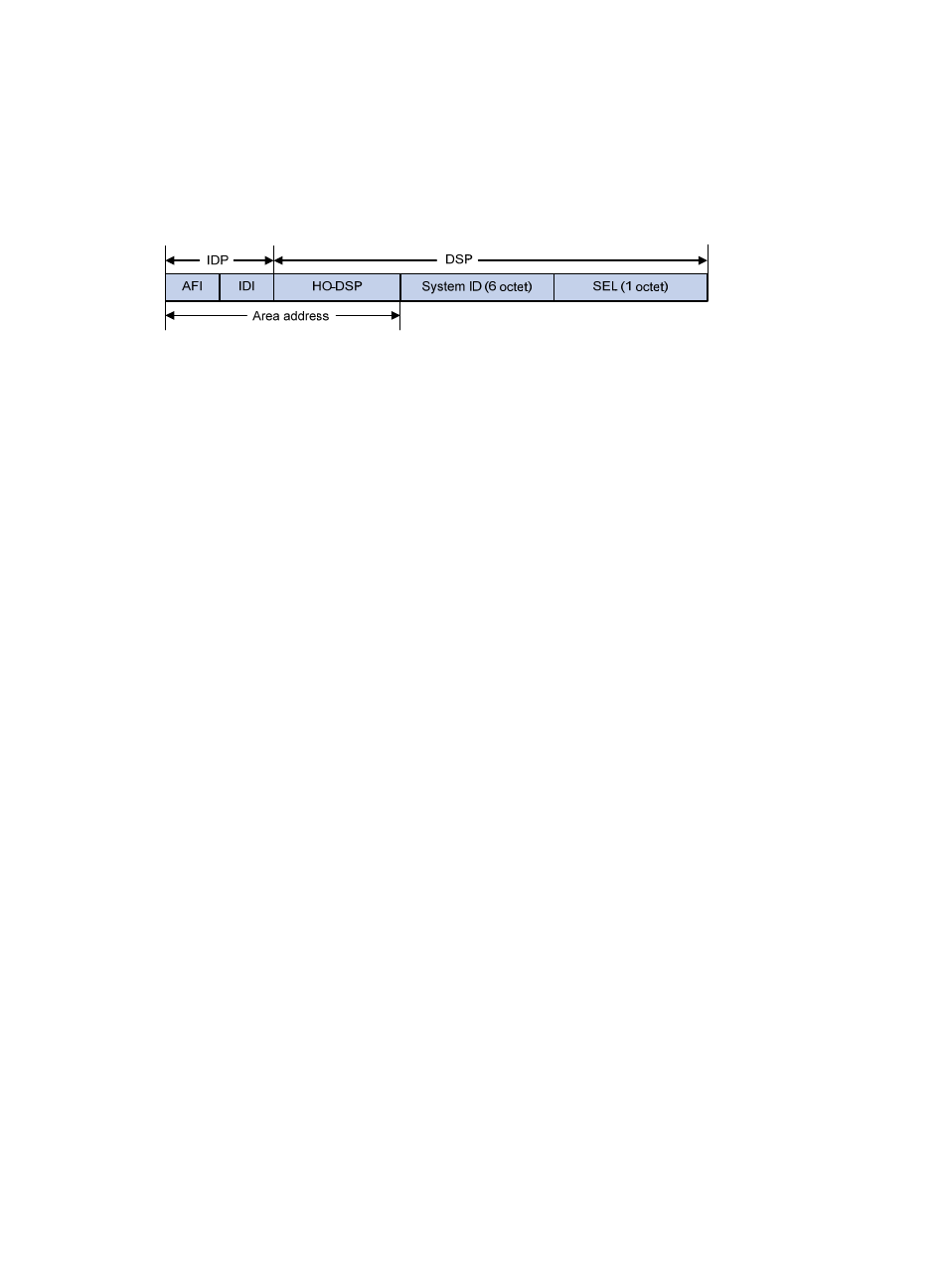
The IDP includes the authority and format identifier (AFI) and the initial domain identifier (IDI).
The DSP includes the High Order Part of DSP (HO-DSP), System ID, and SEL, where the HO-DSP identifies
the area, the System ID identifies the host, and the SEL identifies the type of service.
The IDP and DSP are variable in length. The length of an NSAP address varies from 8 bytes to 20 bytes.
Figure 52 NSAP address format
Area address
The area address comprises the IDP and the HO-DSP of the DSP, which identify the area and the routing
domain. Different routing domains cannot have the same area address.
Generally, a router only needs one area address, and all nodes in the same routing domain must share
the same area address. However, a router can have a maximum of three area addresses to support
smooth area merging, partitioning, and switching.
System ID
A system ID uniquely identifies a host or router. It has a fixed length of 48 bits (6 bytes).
The system ID of a switch can be generated from the router ID. For example, a router uses the IP address
168.10.1.1 of Loopback 0 as the router ID, and the system ID in IS-IS can be obtained in the following
way:
1.
Extend each decimal number of the IP address to 3 digits by adding 0s from the left, such as
168.010.001.001;
2.
Divide the extended IP address into three sections with 4 digits in each section to get the system ID
1680.1000.1001.
There are other methods to define a system ID. The principle is to ensure it can uniquely identify a host
or router.
SEL
The NSAP selector (SEL), or the N-SEL, is similar to the protocol identifier in IP. Different transport layer
protocols correspond to different SELs. All SELs in IP are 00.
Routing method
The area information is identified in IS-IS addresses, so a Level-1 router can easily identify packets
destined to other areas.
•
A Level-1 router makes routing decisions based on the system ID. If the destination is not in the area,
the packet is forwarded to the nearest Level-1-2 router.
•
A Level-2 router routes packets across areas according to the area address.
NET
A network entity title (NET) indicates the network layer information of an IS, and does not include
transport layer information. It is a special NSAP address with the SEL being 0; therefore, the length of the
NET is equal to the NSAP, and is in the range of 8 bytes to 20 bytes.
