Alternating current (continued), Electrical units – Generac Power Systems NP-40G User Manual
Page 6
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
Section 1.1- GENERATOR FUNDAMENTALS
Alternating Current (Continued)
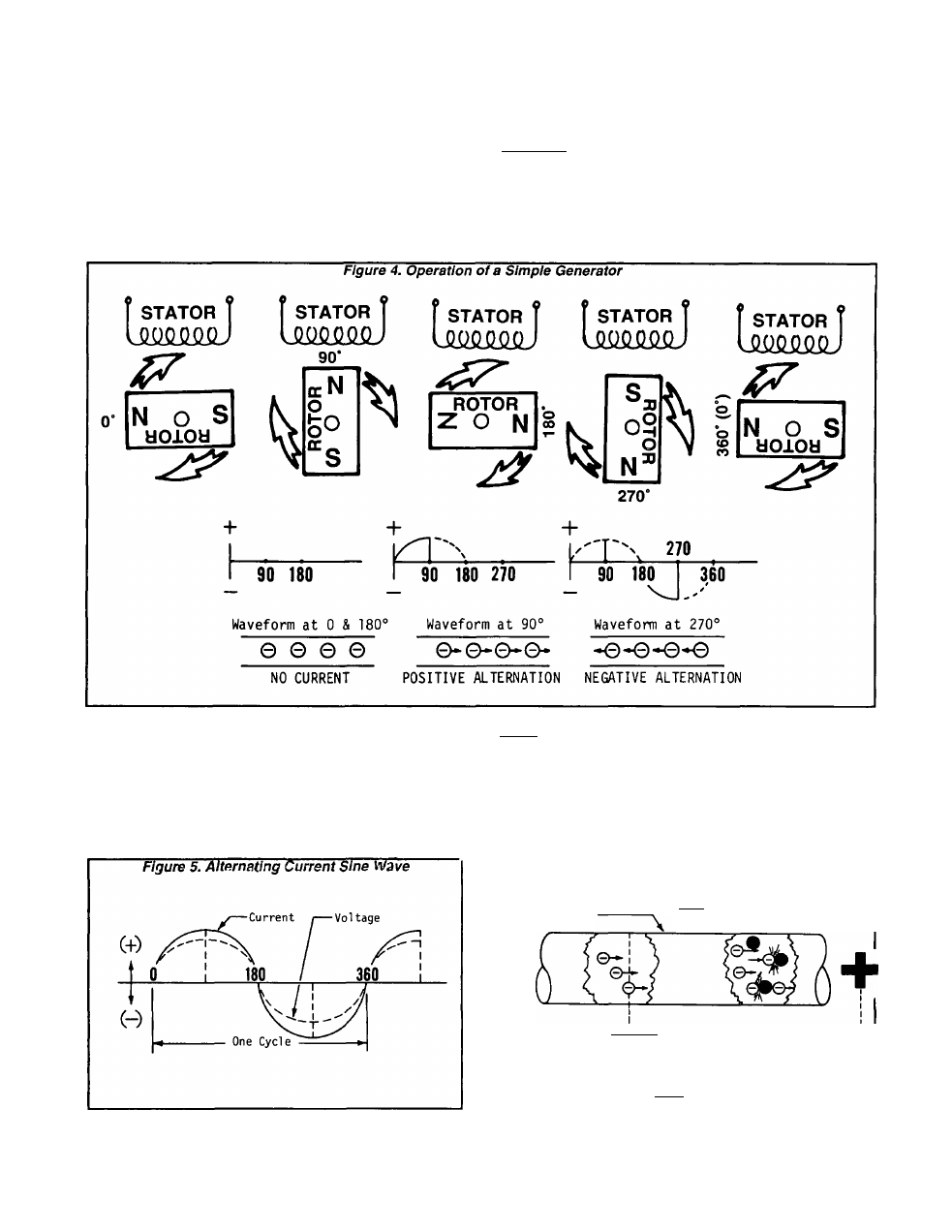
See Figure 4. The current alternates according to the
position of the Rotor’s poles in relation to the position of
the Stator. At 0* and again at 180*, no current flow Is
produced. At 90’ of Rotor rotation, current flow reaches
a maximum positive value. Rotor rotation to 270’ brings
another maximum flow of current. However, at 270’ the
current flow has reversed In polarity and now flows in the
opposite direction.
Electrical Units
AMPERE;
The rate of electron flow in a circuit is represented by
the AMPERE. The ampere is the number of electrons
flowing past a given point at a given time. One AMPERE
Is equal to Just slightly more than six thousand million
billion electrons per second.
With alternating current (AC), the electrons flow first
In one direction, then reverse and move In the opposite
direction. They will repeat this cycle at regular intervals.
A wave diagram, called a “sine wave“ shows that current
goes from zero to maximum positive value, then reverses
and goes from zero to maximum negative value. Two
reversals of current flow Is called a cycle. The number of
cycles per second Is called frequency and is usually
stated in "Hettz".
VOLT:
The VOLT is the unit used to measure electrical PRES-
SURE, or the difference In electrical potential that causes
electrons to flow. Very few electrons will flow when
voltage is weak. More electrons will flow as voltage
becomes stronger. VOLTAGE may be consdiered to be
a state of unbalance and current flow as an attempt to
regain balance. One volt is the amount of EMF that will
cause a current of 1 ampere to flow through 1 ohm of
resistance.
Figure 6. Electrical Units
Conductor of a
Circuit
OHM - Unit measuring resistance
or opposition to flow
AMPERE - Unit measuring rate of
current flow (nunfcer of elec
trons past a given point)
L.
■ VOLT - Unit measuring force or
_____ difference in potential
causing current flow
Page 1.1-2
