The genistor, The ccg circuit board – Generac Power Systems NP-40G User Manual
Page 13
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
Section 1.2- MAJOR GENERATOR COMPONENTS
The Genistor
GENERAL:
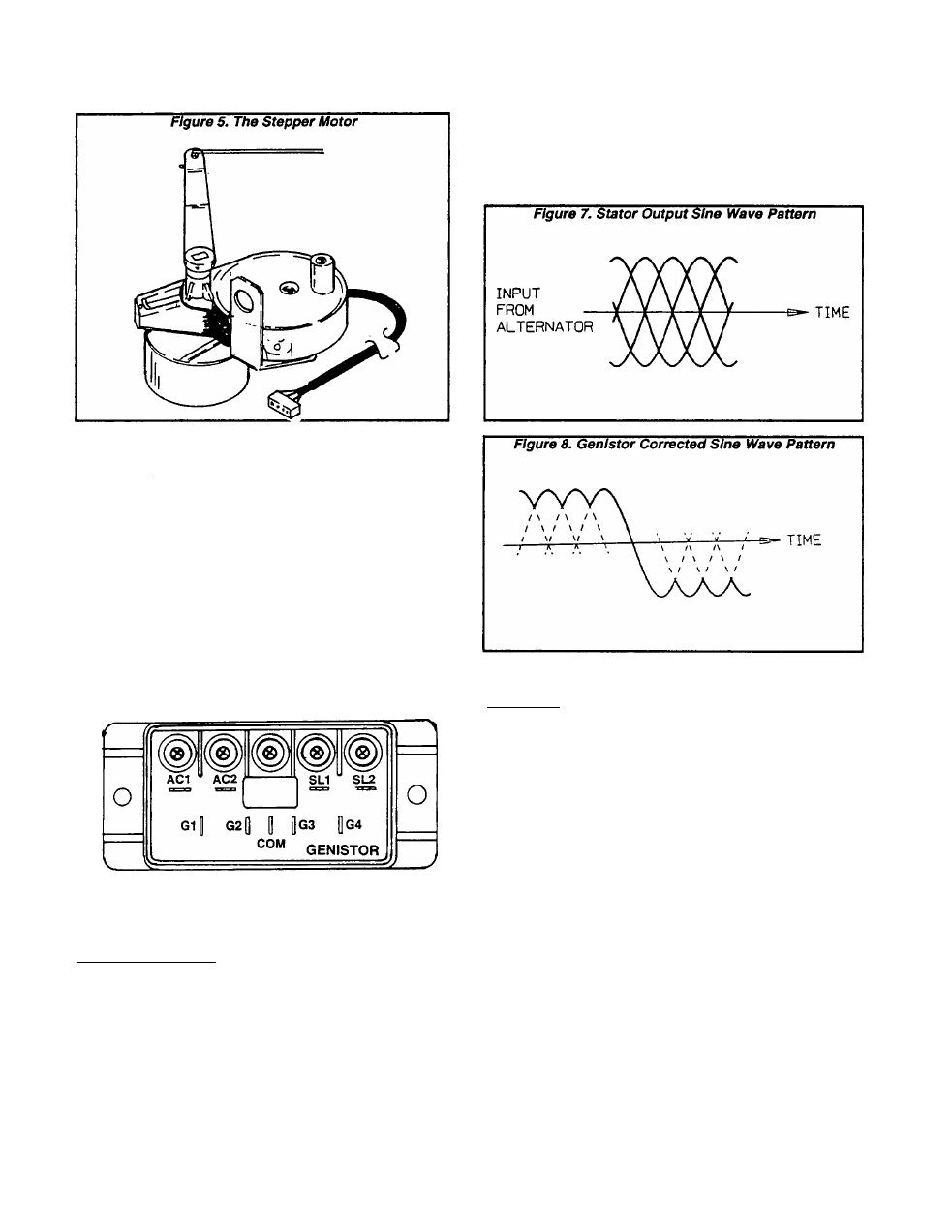
See Figure 6. The GENISTOR is often called a
“frequency converter“ (also see "Introduction to
CCG’s“ on Page 1.1-4). its function is to change the
high frequency AC output of the Stator (336-540
Hertz) to a useful frequency (about 56-60 Hertz).
The Genistor has no intelligence of Its own. It is
simply a high speed switcning device which is
controlled by the CCG circuit board.
Figure 6. The dtenhtor
GENISTOR THEORY:
The purpose of a “frequency converter“ is to
divide the Stator AC output frequency by an inte
gral factor to provide a useful output frequency.
Each of the four half-phases of the center-tapped
Stator Is Genistor-controlled.
Figure 7 shows the sine wave output from the
2-phase Stator windings. This output Is delivered
to the Genistor switching module.
Switching signals from the CCG circuit board are
also
delivered
to
the
Genistor.
These
signals
switch the Genistor on and off as required, result
ing In a sine wave output to the load as shown in
Figure 8.
The CCG Circuit Board
GENERAL:
The CCG circuit board has several functions as
follows:
1. It controls the operation of the “frequency con
verter“ (Genistor).
2.
It controls AC output voltage under all load
requirements by controlling engine speed.
3. It protects the system against various faults.
FREQUENCY CONTROL:
The CCG board will adjust the number of alterna
tor cycles In one output cycle to control AC output
frequency. The number of cycles is based on en
gine rpm and the output frequency will be main
tained in the 55-65 Hertz band.
The board uses a "zero crossing" detector to
synchronize an internal clock. The frequency of the
Stator’s
waveform
is
measured
and,
with
referencve to the required output frequency, a “fre-
guency divisor" is calculated. The circuit board
then signals the Genistor (frequency converter) to
switch on and off at the proper times so that fre
quency Is maintained in the 55-65 Hertz band.
Page 1.2-3
