Fan presence and redundancy sensors, Table 28: fan speed sensor, Event trigger offset – next steps – Kontron S5500 SEL Troubleshooting User Manual
Page 41
Cooling subsystem
System Event Log Troubleshooting Guide for Intel® S5500/S3420 series Server Boards
32
Intel order number G74211-001
Revision 1.0
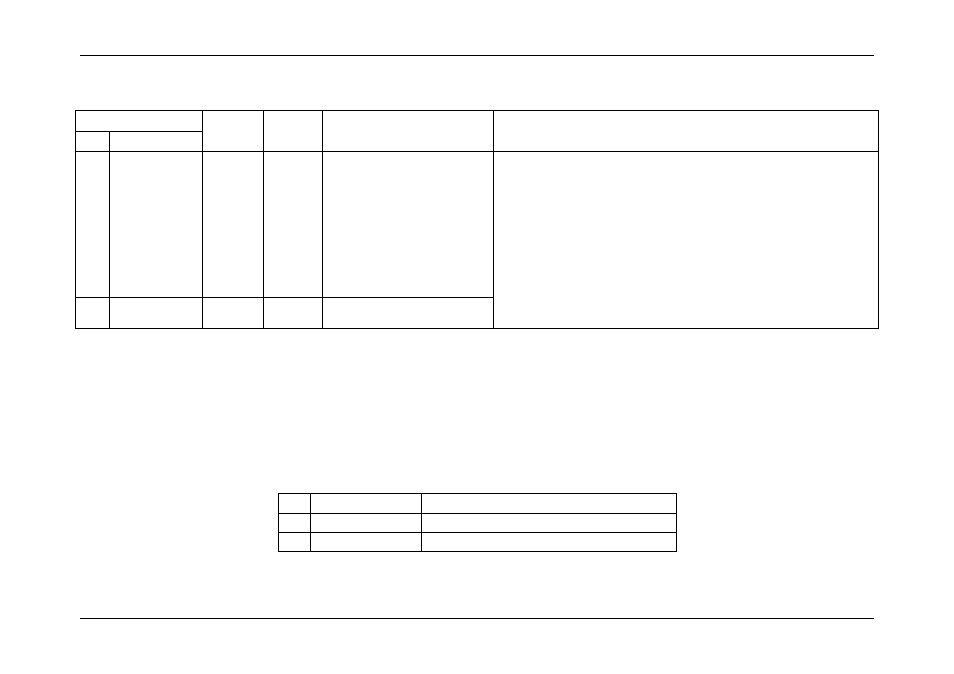
Table 28: Fan Speed Sensor
– Event Trigger Offset – Next Steps
Event Trigger Offset
Assertion
Severity
Deassert
Severity
Description
Next Steps
Hex
Description
00h
Lower non critical
going low
Degraded
OK
The fan speed has dropped below
its lower non critical threshold.
A fan speed error on a new system build is typically not caused by the fan
spinning too slowly, instead it is caused by the fan being connected to the wrong
header (the BMC expects them on certain headers for each chassis and will log
this event if there is no fan on that header).
1. Refer to the Quick Start Guide or the Service Guide to identify the correct
fan headers to use.
2. Ensure the latest FRUSDR update has been run and the correct chassis
was detected or selected.
3. If you are sure this was done, the event may be a sign of impending fan
failure (although this would only normally apply if the system has been in
use for a while). Replace the fan.
02h
Lower critical
going low
non-fatal
Degraded
The fan speed has dropped below
its lower critical threshold.
5.1.2
Fan Presence and Redundancy Sensors
Fan presence sensors are only implemented for hot-swap fans, and require an additional pin on the fan header. Fan redundancy is an
aggregate of the fan presence sensors and will warn when redundancy is lost. Typically the redundancy mode on Intel
®
servers is an n+1
redundancy (if one fan fails there are still sufficient fans to cool the system, but it is no longer redundant) although other modes are also
possible.
Table 29: Fan Presence Sensors Typical Characteristics
Byte
Field
Description
11
Sensor Type
04h = Fan
12
Sensor Number
40h
– 45h (Chassis specific)
