Brocade Communications Systems Layer 3 Routing Configuration ICX 6650 User Manual
Page 200
182
Brocade ICX 6650 Layer 3 Routing Configuration Guide
53-1002603-01
Configuring OSPF
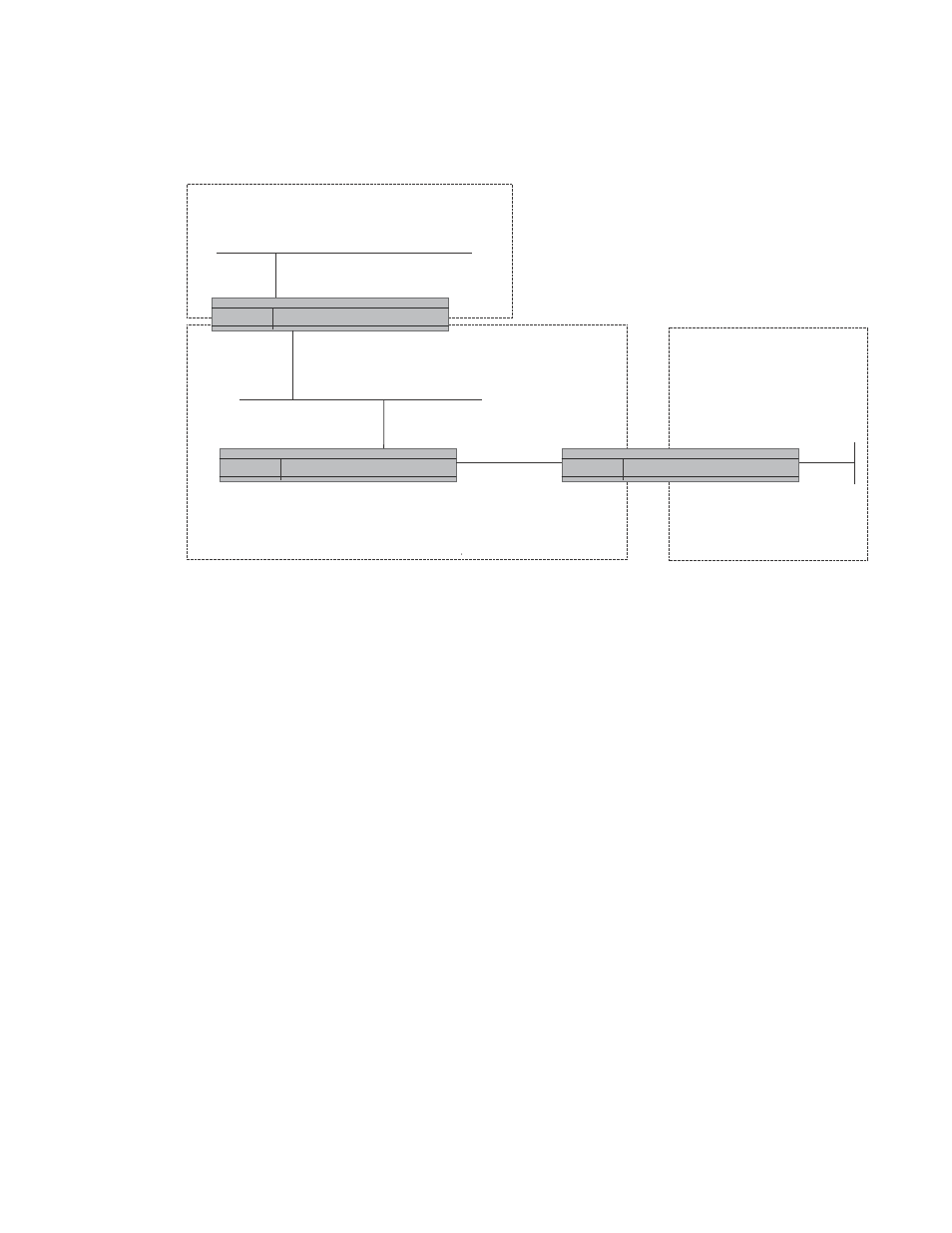
FIGURE 21
OSPF network containing an NSSA
This example shows two routing domains, a RIP domain and an OSPF domain. The ASBR inside the
NSSA imports external routes from RIP into the NSSA as Type-7 LSAs, which the ASBR floods
throughout the NSSA.
The ABR translates the Type-7 LSAs into Type-5 LSAs. If an area range is configured for the NSSA,
the ABR also summarizes the LSAs into an aggregate LSA before flooding the Type-5 LSAs into the
backbone.
Since the NSSA is partially “stubby” the ABR does not flood external LSAs from the backbone into
the NSSA. To provide access to the rest of the Autonomous System (AS), the ABR generates a
default Type-7 LSA into the NSSA.
Configuring an NSSA
To configure OSPF area 10.1.1.1 as an NSSA, enter the following commands.
Brocade(config)#router ospf
Brocade(config-ospf-router)#area 10.1.1.1 nssa 1
Brocade(config-ospf-router)#write memory
Syntax: area num | ip-addr nssa cost | default-information-originate
The num | ip-addr parameter specifies the area number, which can be a number or in IP address
format. If you specify a number, the number can be from 0 through 18.
The nssa cost | default-information-originate parameter specifies that this is a Not-So-Stubby Area
(NSSA). The cost specifies an additional cost for using a route to or from this NSSA and can be
from 1 through 16777215. There is no default. Normal areas do not use the cost parameter.
Alternatively, the default-information-originate parameter causes the Layer 3 Switch to inject the
default route into the NSSA.
RIP Domain
Layer 3 Switch
Layer 3 Switch
Layer 3 Switch
NSSA Area 10.1.1.1
Internal ASBR
OSPF ABR
OSPF Area 0
Backbone
