5 performing data migration, Typical data migration process – HP MPX200 Multifunction Router User Manual
Page 41
5 Performing data migration
This chapter provides a number of procedures for configuring and managing data migration using
DMS.
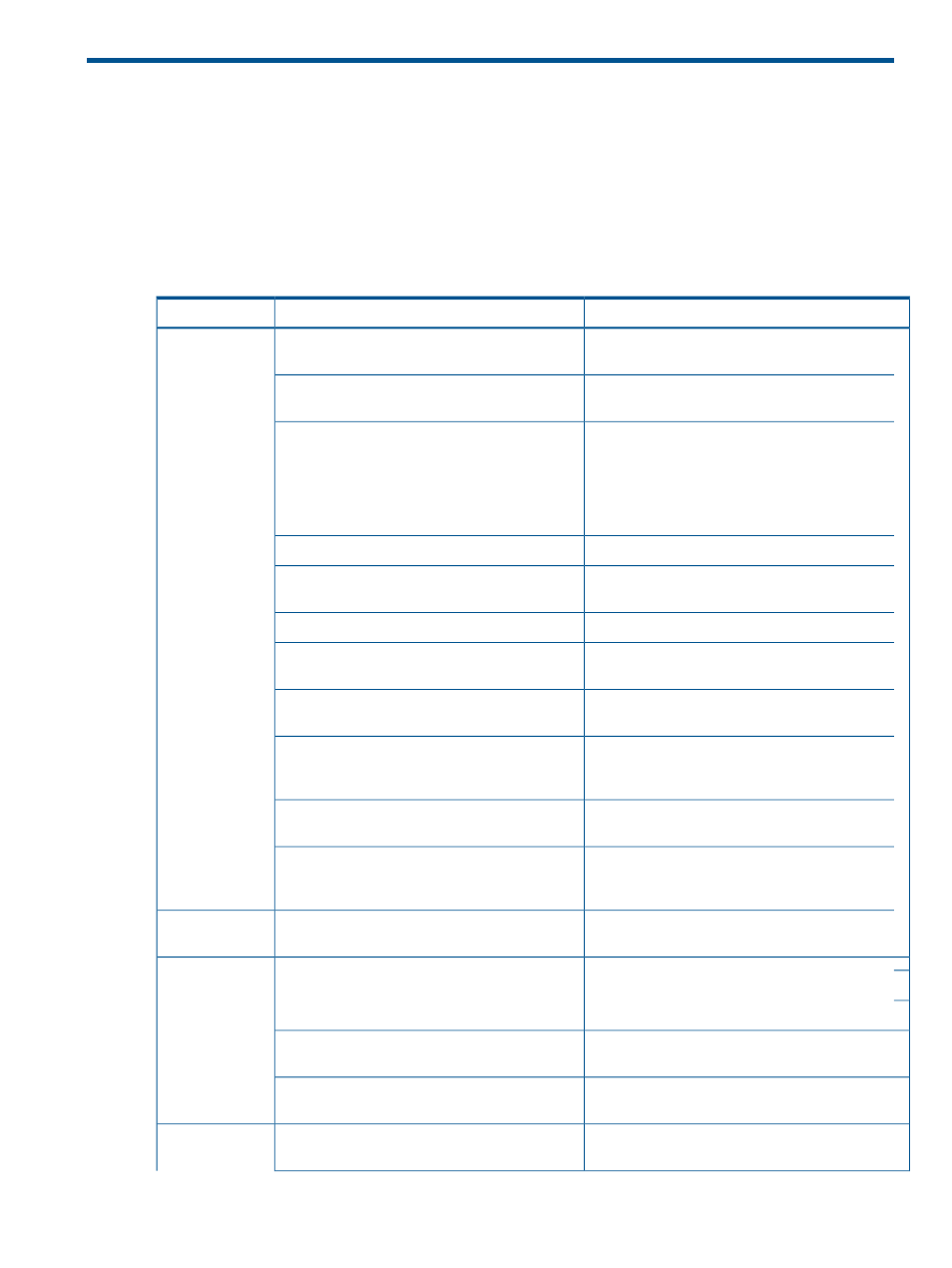
Typical data migration process
and
show the MPX200 data migration process flow by
category and activity, and references the appropriate section for each.
Table 7 Online data migration process flow
For more information, see…
Activity
Category
Data Migration Service for MPX200 Planning
Guide
1. Plan for data migration.
Pre-migration
“Viewing system and data migration job logs”
(page 63)
2. At the start of the project, clear the migration
logs.
“Installing a data migration license key” (page
37)
and
“Applying an array-based license to a
3. Verify the pre-installed data migration license
or install a license key, then apply the
array-based license key, if an array-based
migration license will be consumed for this
project. Otherwise, a per-TB license is used
automatically.
“Configuring the fabric” (page 42)
4. Configure the FC fabric.
“Presenting LUNs to the MPX200” (page 43)
5. Provide the MPX200 access to LUNs from
source and destination arrays.
“Setting array properties” (page 53)
6. Discover arrays and set array properties.
“Job failover and failback” (page 23)
7. Configure automatic failover for high
availability.
“Creating a data migration job group” (page
55)
8. Define user groups.
“Presenting LUNs to the server for online data
migration” (page 46)
9. Map source array LUNs to one or more hosts.
For online remote migration, also create a data
management LUN.
“Step 2: Create presented targets” (page 47)
10. Create presented targets to map source array
target ports with MPX200 Fibre Channel ports.
“Step 1: Inserting the MPX200 in the server data
path for online data migration” (page 46)
11. Insert the MPX200 in the server data path
and zone out direct paths from servers to the
source storage array.
“Using the data migration wizard” (page 55)
12. Configure and validate data migration jobs.
Configure
migration jobs
“Starting serial scheduled jobs” (page 60)
13. For data migration jobs that are scheduled
for a delayed start, specify the start time for the
job.
Migrate and
monitor
“Viewing job details and controlling job actions”
(page 62)
14.Monitor data migration jobs.
“Acknowledging a data migration job” (page
67)
15. Acknowledge the data migration jobs.
“Viewing system and data migration job logs”
(page 63)
16. Export data migration logs.
Post-migration
Typical data migration process
41
