The put command: copying your file into a new file – HP NonStop G-Series User Manual
Page 78
Copying All of Your File
Revising Text in Your File
058061 Tandem Computers Incorporated
3–35
The PUT Command:
Copying Your File Into
a New File
You can use the PUT command to copy part or all of your current file into
another, new file. The PUT command creates the new file with a name you
specify. The name of a file can be from one to eight alphanumeric
characters, the first of which must be alphabetic, and the file name can be
partially or fully qualified. (For more information on file names, refer to
Section 6.)
Copying Part of Your File
Suppose your current file, BIZMEMO, has 14 lines. Use the PUT command
to copy lines 9 through 14 of BIZMEMO into a new file you have named as
MYDATA:
*PUT MYDATA 9/14
CURRENT FILE IS $WORK.TUTOR.BIZMEMO
*
In the new file, the copied lines retain their original line numbers.
The PUT command only copies lines to another file. It does not delete the
lines from your current file. If you then want to delete the copied lines from
the current file, use the DELETE command.
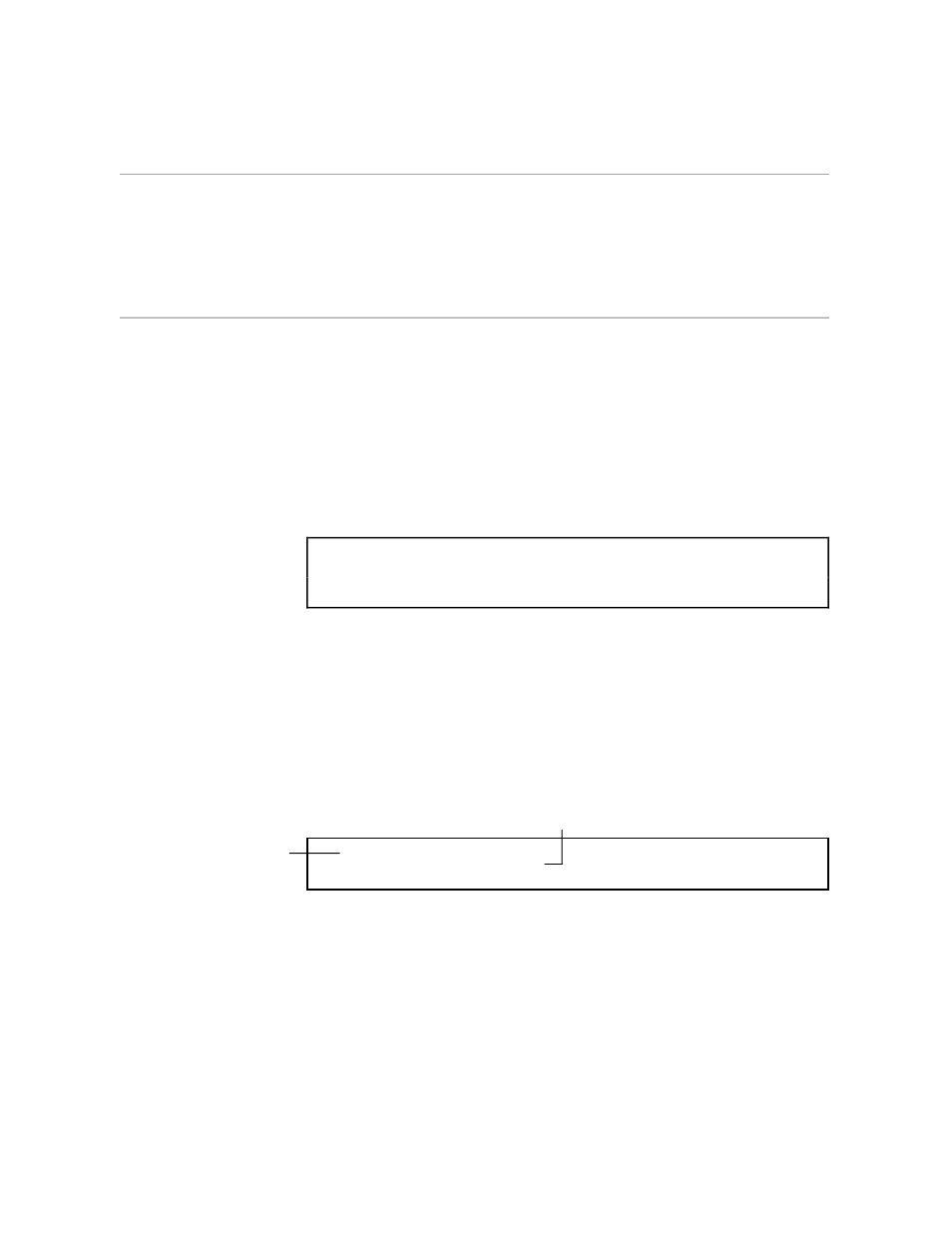
Copying All of Your File
You can use the PUT command to copy your entire file into a new EDIT file.
When you are copying your entire file, you don’t need to give a range of
lines. Simply tell EDIT where you want a copy of your current file to go:
*PUT SAVEMEMO
CURRENT FILE IS $WORK.TUTOR.BIZMEMO
*
You are still in BIZMEMO,
your current file.
All of BIZMEMO is
copied to SAVEMEMO.
